|
Glycosome
The glycosome is a membrane-enclosed organelle that contains the glycolytic enzymes. The term was first used by Scott and Still in 1968 after they realized that the glycogen in the cell was not static but rather a dynamic molecule. It is found in a few species of protozoa including the Kinetoplastida which include the suborders Trypanosomatida and Bodonina, most notably in the human pathogenic trypanosomes, which can cause sleeping sickness, Chagas's disease, and leishmaniasis. The organelle is bounded by a single membrane and contains a dense proteinaceous matrix. It is believed to have evolved from the peroxisome. This has been verified by work done on Leishmania genetics. The glycosome is currently being researched as a possible target for drug therapies. Glycosomes are unique to kinetoplastids and their sister diplonemids. The term glycosome is also used for glycogen-containing structures found in hepatocytes responsible for storing sugar, but these are not membrane bound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peroxisome
A peroxisome () is a membrane-bound organelle, a type of microbody, found in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. Peroxisomes are oxidative organelles. Frequently, molecular oxygen serves as a co-substrate, from which hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is then formed. Peroxisomes owe their name to hydrogen peroxide generating and scavenging activities. They perform key roles in lipid metabolism and the conversion of reactive oxygen species. Peroxisomes are involved in the catabolism of very long chain fatty acids, branched chain fatty acids, bile acid intermediates (in the liver), D-amino acids, and polyamines, the reduction of reactive oxygen species – specifically hydrogen peroxide – and the biosynthesis of plasmalogens, i.e., ether phospholipids critical for the normal function of mammalian brains and lungs. They also contain approximately 10% of the total activity of two enzymes ( Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and 6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase) in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence ''organelle,'' the suffix ''-elle'' being a diminutive. Organelles are either separately enclosed within their own lipid bilayers (also called membrane-bound organelles) or are spatially distinct functional units without a surrounding lipid bilayer (non-membrane bound organelles). Although most organelles are functional units within cells, some function units that extend outside of cells are often termed organelles, such as cilia, the flagellum and archaellum, and the trichocyst. Organelles are identified by microscopy, and can also be purified by cell fractionation. There are many types of organelles, particularly in eukaryotic cells. They include structures that make up the endomembrane system (such as the nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diplonemids
Diplonemidae is a family of biflagellated unicellular protists that may be among the more diverse and common groups of planktonic organisms in the ocean. Although this family is currently made up of three named genera; '' Diplonema'', ''Rhynchopus'', and '' Hemistasia'', there likely exist thousands of still unnamed genera. Organisms are generally colourless and oblong in shape, with two flagella emerging from a subapical pocket. They possess a large mitochondrial genome composed of fragmented linear DNA. These non-coding sequences must be massively trans-spliced, making it one of the most complicated post-transcriptional editing process known to eukaryotes. Etymology The word “Diplonemidae” come from the Greek words ‘diplo’, meaning two, and ‘nemat’, meaning thread. Together, Diplonemidae roughly translates to ‘two threads’, likely referring to the characteristic two flagella of the organism. History of Knowledge Primary studies done in the 1900s by Griessmann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trypanosomatida
Trypanosomatida is a group of kinetoplastid excavates distinguished by having only a single flagellum. The name is derived from the Greek language, Greek ''trypano'' (borer) and ''soma'' (body) because of the corkscrew-like motion of some trypanosomatid species. All members are exclusively parasite, parasitic, found primarily in insects. A few genera have life-cycles involving a secondary host, which may be a vertebrate, invertebrate or plant. These include several species that cause major diseases in humans. Some trypanosomatida are intracellular parasites, with the important exception of Trypanosoma brucei. Medical importance The three major human diseases caused by trypanosomatids are; African trypanosomiasis (African trypanosomiasis, sleeping sickness, caused by ''Trypanosoma brucei'' and transmitted by Tsetse fly, tsetse flies), South American trypanosomiasis (Chagas disease, caused by ''Trypanosoma cruzi, T. cruzi'' and transmitted by Triatominae, triatomine bugs), and le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trypanosomes
Trypanosomatida is a group of kinetoplastid excavates distinguished by having only a single flagellum. The name is derived from the Greek ''trypano'' (borer) and ''soma'' (body) because of the corkscrew-like motion of some trypanosomatid species. All members are exclusively parasitic, found primarily in insects. A few genera have life-cycles involving a secondary host, which may be a vertebrate, invertebrate or plant. These include several species that cause major diseases in humans. Some trypanosomatida are intracellular parasites, with the important exception of Trypanosoma brucei. Medical importance The three major human diseases caused by trypanosomatids are; African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness, caused by ''Trypanosoma brucei'' and transmitted by tsetse flies), South American trypanosomiasis (Chagas disease, caused by '' T. cruzi'' and transmitted by triatomine bugs), and leishmaniasis (a set of trypanosomal diseases caused by various species of ''Leishmania'' tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Membrane
A biological membrane, biomembrane or cell membrane is a selectively permeable membrane that separates the interior of a cell from the external environment or creates intracellular compartments by serving as a boundary between one part of the cell and another. Biological membranes, in the form of eukaryotic cell membranes, consist of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded, integral and peripheral proteins used in communication and transportation of chemicals and ions. The bulk of lipids in a cell membrane provides a fluid matrix for proteins to rotate and laterally diffuse for physiological functioning. Proteins are adapted to high membrane fluidity environment of the lipid bilayer with the presence of an annular lipid shell, consisting of lipid molecules bound tightly to the surface of integral membrane proteins. The cell membranes are different from the isolating tissues formed by layers of cells, such as mucous membranes, basement membranes, and serous membranes. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myosin
Myosins () are a superfamily of motor proteins best known for their roles in muscle contraction and in a wide range of other motility processes in eukaryotes. They are ATP-dependent and responsible for actin-based motility. The first myosin (M2) to be discovered was in 1864 by Wilhelm Kühne. Kühne had extracted a viscous protein from skeletal muscle that he held responsible for keeping the tension state in muscle. He called this protein ''myosin''. The term has been extended to include a group of similar ATPases found in the cells of both striated muscle tissue and smooth muscle tissue. Following the discovery in 1973 of enzymes with myosin-like function in ''Acanthamoeba castellanii'', a global range of divergent myosin genes have been discovered throughout the realm of eukaryotes. Although myosin was originally thought to be restricted to muscle cells (hence '' myo-''(s) + '' -in''), there is no single "myosin"; rather it is a very large superfamily of genes whose prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing energy, signaling, and acting as structural components of cell membranes. Lipids have applications in the cosmetic and food industries, and in nanotechnology. Lipids may be broadly defined as hydrophobic or amphiphilic small molecules; the amphiphilic nature of some lipids allows them to form structures such as vesicles, multilamellar/ unilamellar liposomes, or membranes in an aqueous environment. Biological lipids originate entirely or in part from two distinct types of biochemical subunits or "building-blocks": ketoacyl and isoprene groups. Using this approach, lipids may be divided into eight categories: fatty acyls, glycerolipids, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids, saccharolipids, and polyketides (derived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytosol
The cytosol, also known as cytoplasmic matrix or groundplasm, is one of the liquids found inside cells ( intracellular fluid (ICF)). It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments. In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is surrounded by the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. The cytosol is thus a liquid matrix around the organelles. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others take place within organelles. The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and propert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purine Salvage Pathway
A salvage pathway is a pathway in which a biological product is produced from intermediates in the degradative pathway of its own or a similar substance. The term often refers to nucleotide salvage in particular, in which nucleotides (purine and pyrimidine) are synthesized from intermediates in their degradative pathway. Nucleotide salvage pathways are used to recover bases and nucleosides that are formed during degradation of RNA and DNA. This is important in some organs because some tissues cannot undergo de novo synthesis. The salvaged products can then be converted back into nucleotides. Salvage pathways are targets for drug development, one family being called antifolates. A number of other biologically-important substances, like methionine and nicotinate, have their own salvage pathways to recycle parts of the molecule. Substrates The nucleotide salvage pathway requires distinct substrates: Pyrimidines Uridine phosphorylase or pyrimidine-nucleoside phosphorylase subs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
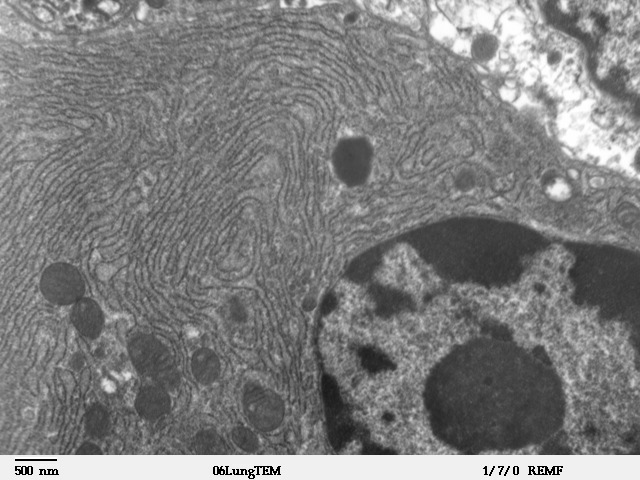
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is, in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). The endoplasmic reticulum is found in most eukaryotic cells and forms an interconnected network of flattened, membrane-enclosed sacs known as cisternae (in the RER), and tubular structures in the SER. The membranes of the ER are continuous with the outer nuclear membrane. The endoplasmic reticulum is not found in red blood cells, or spermatozoa. The two types of ER share many of the same proteins and engage in certain common activities such as the synthesis of certain lipids and cholesterol. Different types of cells contain different ratios of the two types of ER depending on the activities of the cell. RER is found mainly toward the nucleus of cell and SER towards the cell membrane or plasma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the conversion of food to building blocks for proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and some carbohydrates; and the elimination of metabolic wastes. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to the sum of all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transportation of substances into and between different cells, in which case the above described set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary (or intermediate) metabolism. Metabolic reactions may be categorized as '' catabolic'' – the ''breaking down'' of compounds (for example, of glucose to pyruv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_Trypanosoma_equiperdum.jpg)