|
Gilbert Shakespeare
Gilbert Shakespeare (baptised 13 October 1566, buried probably 3 February 1612) was a 16th-/17th-century English haberdasher, and a younger brother of playwright and poet William Shakespeare. His name is found in local records of Stratford-upon-Avon and London. Life Gilbert's father, John Shakespeare, was a glover living in Henley Street, Stratford, and an alderman of the town from 1564. Gilbert may have been named after Gilbert Bradley, also a glover, who lived on the same street and who in 1565 was one of the capital burgesses of Stratford. He was baptized in the Holy Trinity on 13 October 1566.William Shakespeare Brothers & Sisters ''William-shakespeare.info'' Gilbert contracted and survived the plague. A single surviving signature shows h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gilbert Shakespeare Signature 1609
Gilbert may refer to: People and fictional characters *Gilbert (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters *Gilbert (surname), including a list of people Places Australia * Gilbert River (Queensland) * Gilbert River (South Australia) Kiribati * Gilbert Islands, a chain of atolls and islands in the Pacific Ocean United States * Gilbert, Arizona, a town * Gilbert, Arkansas, a town * Gilbert, Florida, the airport of Winterhaven * Gilbert, Iowa, a city * Gilbert, Louisiana, a village * Gilbert, Michigan, and unincorporated community * Gilbert, Minnesota, a city * Gilbert, Nevada, ghost town * Gilbert, Ohio, an unincorporated community * Gilbert, Pennsylvania, an unincorporated community * Gilbert, South Carolina, a town * Gilbert, West Virginia, a town * Gilbert, Wisconsin, an unincorporated community * Mount Gilbert (other), various mountains * Gilbert River (Oregon) Outer space * Gilbert (lunar crater) * Gilbert (Martian crater) Arts and enterta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italic Script
Italic script, also known as chancery cursive and Italic hand, is a semi-cursive, slightly sloped style of handwriting and calligraphy that was developed during the Renaissance in Italy. It is one of the most popular styles used in contemporary Western calligraphy. History Italic script is based largely on Humanist minuscule, which itself draws on Carolingian minuscule. The capital letters are the same as the Humanist capitals, modeled on Roman square capitals. The Italian scholar Niccolò de' Niccoli was dissatisfied with the lowercase forms of Humanist minuscule, finding it too slow to write. In response, he created the Italic script, which incorporates features and techniques characteristic of a quickly written hand: oblique forms, fewer strokes per character, and the joining of letters. Perhaps the most significant change to any single character was to the form of the ''a'', which he simplified from the two-story form to the one-story form ⟨ɑ⟩ now common to most handwri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Wisconsin Press
The University of Wisconsin Press (sometimes abbreviated as UW Press) is a non-profit university press publishing peer-reviewed books and journals. It publishes work by scholars from the global academic community; works of fiction, memoir and poetry under its imprint, Terrace Books; and serves the citizens of Wisconsin by publishing important books about Wisconsin, the Upper Midwest, and the Great Lakes region. UW Press annually awards the Brittingham Prize in Poetry, the Felix Pollak Prize in Poetry, and The Four Lakes Prize in Poetry. The press was founded in 1936 in Madison and is one of more than 120 member presses in the Association of American University Presses. The Journals Division was established in 1965. The press employs approximately 25 full and part-time staff, produces 40 to 60 new books a year, and publishes 11 journals. It also distributes books and some annual journals for selected smaller publishers. The press is a unit of the Graduate School of the University ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586, it is the second oldest university press after Cambridge University Press. It is a department of the University of Oxford and is governed by a group of 15 academics known as the Delegates of the Press, who are appointed by the vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho. For the last 500 years, OUP has primarily focused on the publication of pedagogical texts and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles II Of England
Charles II (29 May 1630 – 6 February 1685) was King of Scotland from 1649 until 1651, and King of England, Scotland and Ireland from the 1660 Restoration of the monarchy until his death in 1685. Charles II was the eldest surviving child of Charles I of England, Scotland and Ireland and Henrietta Maria of France. After Charles I's execution at Whitehall on 30 January 1649, at the climax of the English Civil War, the Parliament of Scotland proclaimed Charles II king on 5 February 1649. But England entered the period known as the English Interregnum or the English Commonwealth, and the country was a de facto republic led by Oliver Cromwell. Cromwell defeated Charles II at the Battle of Worcester on 3 September 1651, and Charles fled to mainland Europe. Cromwell became virtual dictator of England, Scotland and Ireland. Charles spent the next nine years in exile in France, the Dutch Republic and the Spanish Netherlands. The political crisis that followed Cromwell's death in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stuart Restoration
The Restoration of the Stuart monarchy in the kingdoms of England, Scotland and Ireland took place in 1660 when King Charles II returned from exile in continental Europe. The preceding period of the Protectorate and the civil wars came to be known as the Interregnum (1649–1660). The term ''Restoration'' is also used to describe the period of several years after, in which a new political settlement was established. It is very often used to cover the whole reign of King Charles II (1660–1685) and often the brief reign of his younger brother King James II (1685–1688). In certain contexts it may be used to cover the whole period of the later Stuart monarchs as far as the death of Queen Anne and the accession of the Hanoverian King George I in 1714. For example, Restoration comedy typically encompasses works written as late as 1710. The Protectorate After Richard Cromwell, Lord Protector from 1658 to 1659, ceded power to the Rump Parliament, Charles Fleetwood and J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
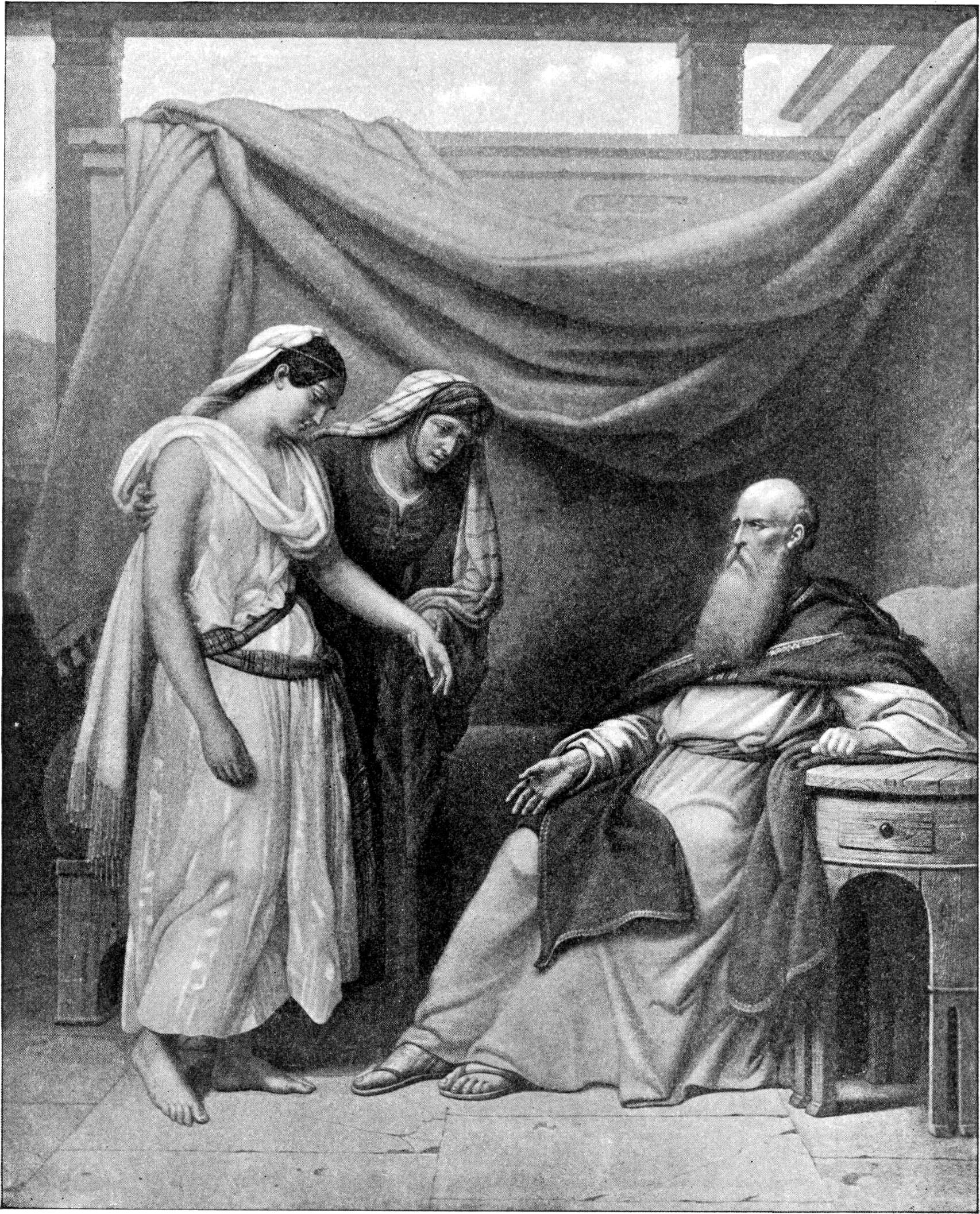
Patriarchs (Bible)
The patriarchs ( he, אבות ''Avot'', singular he, אב ''Ab (Semitic), Av'') of the Bible, when narrowly defined, are Abraham, his son Isaac, and Isaac's son Jacob, also named Israel, the ancestor of the Israelites. These three figures are referred to collectively as the patriarchs, and the period in which they lived is known as the patriarchal age. Judaism, Christianity, and Islam hold that the patriarchs, along with their primary wives, known as the #Matriarchs, matriarchs (Sarah, Rebekah and Leah) are entombed at the Cave of the Patriarchs, a site held holy by the three religions. Rachel, Jacob's other wife, is said to be buried separately at what is known as Rachel's Tomb, near Bethlehem, at the site where she is believed to have died in childbirth. More widely, the term patriarchs can be used to refer to the twenty male ancestor-figures between Adam and Abraham. The first ten of these are called the antediluvian patriarchs, because they came before Genesis flood na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Oldys
William Oldys (14 July 1696 – 15 April 1761) was an English antiquarian and bibliographer. Life He was probably born in London, the illegitimate son of Dr William Oldys (1636–1708), chancellor of Lincoln diocese. His father had held the office of advocate of the admiralty, but lost it in 1693 because he would not prosecute as traitors and pirates the sailors who had served against England under James II. William Oldys, the younger, lost part of his small patrimony in the South Sea Bubble, and in 1724 went to Yorkshire, spending the greater part of the next six years as the guest of the Earl of Malton. On his return to London he found that his landlord had disposed of the books and papers left in his charge. Among these was an annotated copy of Gerard Langbaine's ''Dramatick Poets''. The book came into the hands of Thomas Coxeter, and subsequently into those of Theophilus Cibber, furnishing the basis of the ''Lives of the Poets'' (1753) published with Cibber's name on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sidney Lee
Sir Sidney Lee (5 December 1859 – 3 March 1926) was an English biographer, writer, and critic. Biography Lee was born Solomon Lazarus Lee in 1859 at 12 Keppel Street, Bloomsbury, London. He was educated at the City of London School , established = , closed = , type = Public school Boys' independent day school , president = , head_label = Headmaster , head = Alan Bird , chair_label = Chair of Governors , chair = Ian Seaton , founder = John Carpenter , speciali ... and at Balliol College, Oxford, where he graduated in modern history in 1882. In 1883, Lee became assistant-editor of the ''Dictionary of National Biography''. In 1890 he became joint editor and, on the retirement of Sir Leslie Stephen in 1891, succeeded him as editor. Lee wrote over 800 articles in the ''Dictionary'', mainly on Elizabethan era, Elizabethan authors or politician, statesmen. His sister Elizabeth Lee (writer), Elizabeth Lee also contributed. While still at Balliol, Lee had written t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shakespeare's Will
William Shakespeare's last will and testament was signed on 25 March 1616, just under a month before his death. The document has been studied for details of his personal life, for his opinions, and for his attitudes towards his two daughters, Susanna and Judith, and their respective husbands, John Hall and Thomas Quiney. The best-known passage of the will is the bequest to the wife of his "second best bed". The significance of this phrase is not certain. The content of the will has also been studied for clues about Shakespeare's religious beliefs, his health, and his relationship to his colleagues in the London theatre-world. Context Shakespeare's will was made shortly after his daughter Judith was married to Thomas Quiney. He first summoned his lawyer, Francis Collins, in January 1616, shortly before the couple's wedding on 10 February. A draft of the will was made, but not signed. It was soon revealed that Quiney had made a girl called Margaret Wheeler pregnant. In mid-Marc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)