|
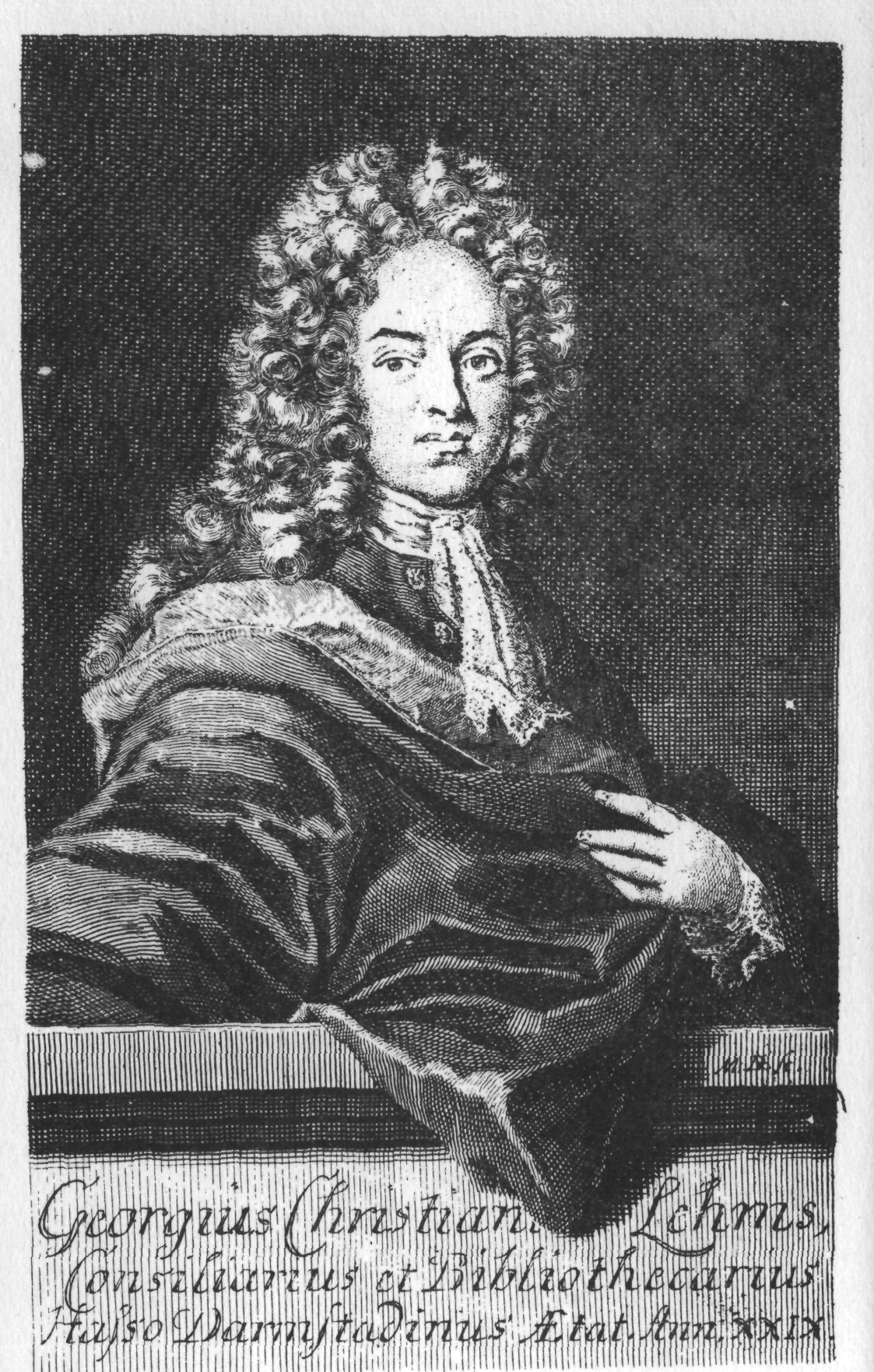
Georg Christian Lehms
Georg Christian Lehms (; 1684 – 15 May 1717) was a German poet and novelist who sometimes used the pen-name ''Pallidor''. He published poetry, novels, libretti for operas, and the texts of cantatas. Life Born in Liegnitz (now in Poland) in 1684, Lehms attended the '' Gymnasium'' (high school) in Görlitz and later studied at the University of Leipzig. After spending some time at the court of Johann Georg, Duke of Saxe-Weissenfels, at the end of 1710 Lehms gained a position as court librarian and poet in Darmstadt, capital of the Landgraviate of Hesse-Darmstadt, where by 1713 he had been appointed to the Prince's council.Georg Christian Lehms (Librettist) at bach-cantatas.com, Retrieved 1 January 2012 Lehms died of |
Galante Poetinnen 0001
Galante is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Galante (pedigree), a family of Jewish scholars which flourished in the Middle Ages ** Abraham ben Mordecai Galante (died 1560), kabalist and author ** Mordecai Galante (died 1781), rabbi of Damascus ** Moses Galante (died 1806), rabbi of Damascus ** Moses Galante (the Elder) (or Moshe ben Mordechai Galante; died 1608), rabbi, disciple of Joseph Caro ** Moses Galante (the Younger) (or Moshe ben Yonatan Galante; 1621-1689), rabbi ** Mordecai Galante (died 1781), Chief rabbi of Damascus and author of Gedullat Mordekai ** Moses Galante (died 1806), chief rabbi of Damascus * Andrea Galante (born 1982), Argentine actress * Anyela Galante Salerno (born 1991), Venezuelan model and beauty pageant titleholder * Carmine Galante (1910-1979), a member of the Bonanno crime family * Cecilia (Plummer) Galante, American author * Fabio Galante (born 1973), Italian footballer * Forrest Galante (born 1988), American outdoor advent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Literature
German literature () comprises those literary texts written in the German language. This includes literature written in Germany, Austria, the German parts of Switzerland and Belgium, Liechtenstein, Luxembourg, South Tyrol in Italy and to a lesser extent works of the German diaspora. German literature of the modern period is mostly in Standard German, but there are some currents of literature influenced to a greater or lesser degree by dialects (e.g. Alemannic). Medieval German literature is literature written in Germany, stretching from the Carolingian dynasty; various dates have been given for the end of the German literary Middle Ages, the Reformation (1517) being the last possible cut-off point. The Old High German period is reckoned to run until about the mid-11th century; the most famous works are the '' Hildebrandslied'' and a heroic epic known as the '' Heliand''. Middle High German starts in the 12th century; the key works include '' The Ring'' (ca. 1410) and the poems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BWV Anh
The (BWV; ; ) is a catalogue of compositions by Johann Sebastian Bach. It was first published in 1950, edited by Wolfgang Schmieder. The catalogue's second edition appeared in 1990. An abbreviated version of that second edition, known as BWV2a, was published in 1998. The catalogue groups compositions by genre. Even within a genre, compositions are not necessarily collated chronologically. For example, BWV 992 was composed many years before BWV 1. BWV numbers were assigned to 1,126 compositions in the 20th century, and more have been added to the catalogue in the 21st century. The Anhang (Anh.; Annex) of the BWV lists over 200 lost, doubtful and spurious compositions. History The first edition of the ''Bach-Werke-Verzeichnis'' was published in 1950. It allocated a unique number to every known composition by Bach. Wolfgang Schmieder, the editor of that catalogue, grouped the compositions by genre, largely following the 19th-century Bach Gesellschaft (BG) edition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard D
Richard is a male given name. It originates, via Old French, from Old Frankish and is a compound of the words descending from Proto-Germanic ''*rīk-'' 'ruler, leader, king' and ''*hardu-'' 'strong, brave, hardy', and it therefore means 'strong in rule'. Nicknames include "Richie", "Dick", "Dickon", " Dickie", " Rich", "Rick", " Rico", " Ricky", and more. Richard is a common English, German and French male name. It's also used in many more languages, particularly Germanic, such as Norwegian, Danish, Swedish, Icelandic, and Dutch, as well as other languages including Irish, Scottish, Welsh and Finnish. Richard is cognate with variants of the name in other European languages, such as the Swedish "Rickard", the Catalan "Ricard" and the Italian "Riccardo", among others (see comprehensive variant list below). People named Richard Multiple people with the same name * Richard Andersen (other) * Richard Anderson (other) * Richard Cartwright (other) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Dürr
Alfred Dürr (3 March 1918 – 7 April 2011) was a German musicologist. He was a principal editor of the Neue Bach-Ausgabe, the second edition of the complete works of Johann Sebastian Bach. Professional career Dürr studied musicology and Classical philology at the Georg-August-Universität Göttingen from 1945 to 1950. He wrote his thesis about Bach's early cantatas. From 1951 until his retirement in 1983 he was an employee of the Johann Sebastian Bach Institute in Göttingen, West Germany, from 1962 to 1981 its deputy director. His work involved collaboration with colleagues in East Germany. He was a principal editor of the Neue Bach-Ausgabe, a project which was divided between the Johann Sebastian Bach Institute and the Bach-Archiv Leipzig in East Germany. From 1953 to 1974 Dürr was editor of the '' Bach-Jahrbuch'' (Bach almanach), together with Werner Neumann, the founder and director of the Bach-Archiv Leipzig. Dürr received honorary doctorates of music from the Hum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Sebastian Bach
Johann Sebastian Bach (28 July 1750) was a German composer and musician of the late Baroque period. He is known for his orchestral music such as the '' Brandenburg Concertos''; instrumental compositions such as the Cello Suites; keyboard works such as the '' Goldberg Variations'' and '' The Well-Tempered Clavier''; organ works such as the '' Schubler Chorales'' and the Toccata and Fugue in D minor; and vocal music such as the '' St Matthew Passion'' and the Mass in B minor. Since the 19th-century Bach revival he has been generally regarded as one of the greatest composers in the history of Western music. The Bach family already counted several composers when Johann Sebastian was born as the last child of a city musician in Eisenach. After being orphaned at the age of 10, he lived for five years with his eldest brother Johann Christoph, after which he continued his musical education in Lüneburg. From 1703 he was back in Thuringia, working as a musician for Protest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gottfried Grünewald
Gottfried Grünewald (also Grunewald; baptised 15 October 1673 – 19 December 1739) was a German operatic bass, harpsichordist, pantaleon virtuoso and composer. Life Grünewald was baptised in Seifhennersdorf near Zittau, on 15 October 1673. He studied music under his father, a school teacher, and attended the Zittau Gymnasium as a student. In 1696 he began studying at Leipzig University. During his studies, he performed as a bass singer at the Thomaskirche and in various operas. From 1703 he was a bass singer and composer at the Oper am Gänsemarkt in Hamburg. Two of his operas were performed there with him in the title roles: ''Der ungetreue Schäfer Cardillo in'' 1704 and ''Germanicus'' in 1705 which had received its world premiere in Leipzig the previous year. From 1709, he worked as vice ''kapellmeister'' at the court of Johann Georg, Duke of Saxe-Weissenfels, where he married Johanna Rosina Krieger, the daughter of Johann Philipp Krieger. Together, they had ten childr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kapellmeister
(, also , ) from German ''Kapelle'' (chapel) and ''Meister'' (master)'','' literally "master of the chapel choir" designates the leader of an ensemble of musicians. Originally used to refer to somebody in charge of music in a chapel, the term has evolved considerably in its meaning and is today used for denoting the leader of a musical ensemble, often smaller ones used for TV, radio, and theatres. Historical usage In German-speaking countries during the approximate period 1500–1800, the word often designated the director of music for a monarch or nobleman. For English speakers, it is this sense of the term that is most often encountered, since it appears frequently in biographical writing about composers who worked in German-speaking countries. During that period, in Italy, the position (Italian: ''maestro di capella'') largely referred to directors of music assigned to cathedrals and sacred institutions rather than those under royal or aristocratic patronage. A Kapellmeister ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
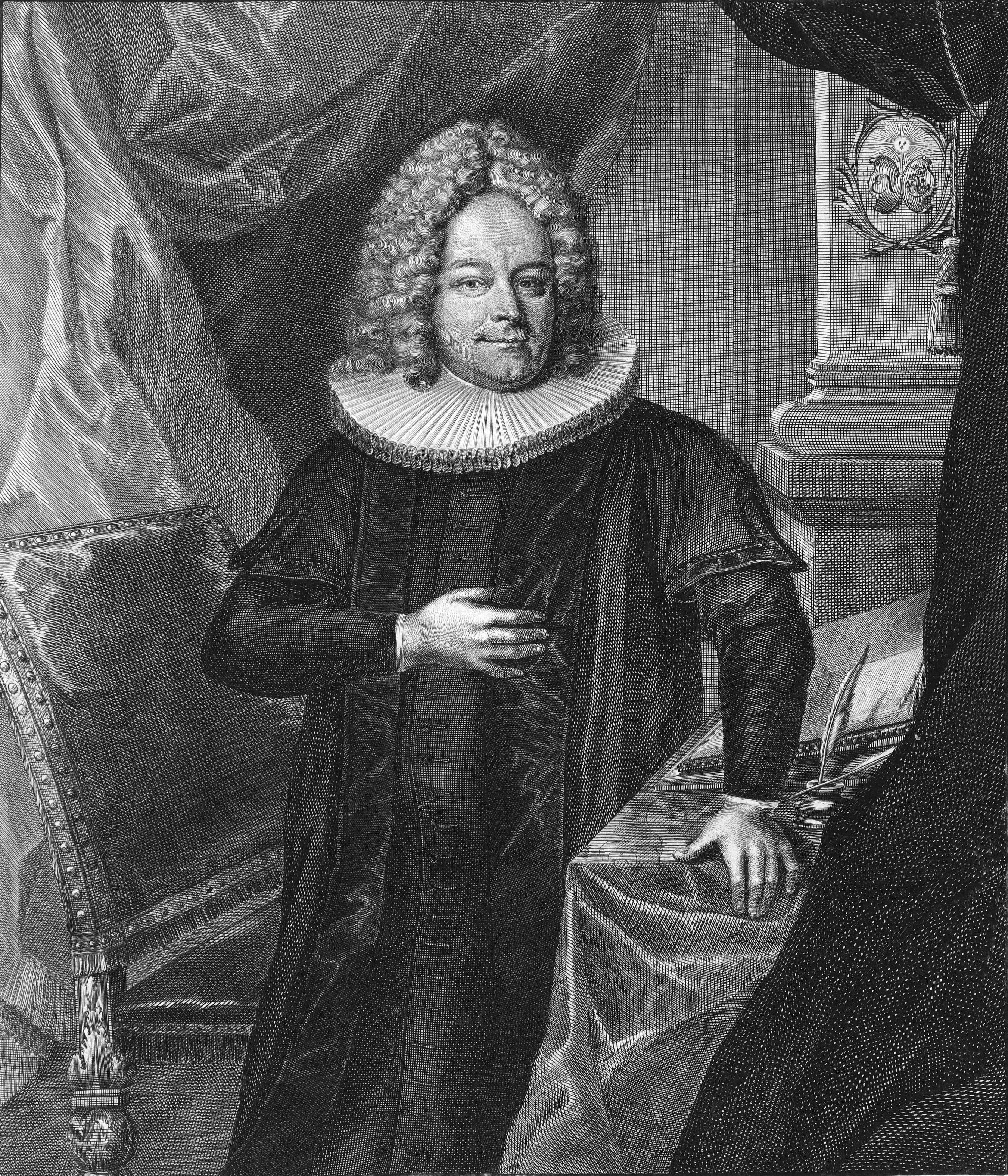
Christoph Graupner
Christoph Graupner (13 January 1683 – 10 May 1760) was a German composer and harpsichordist of late Baroque music who was a contemporary of Johann Sebastian Bach, Georg Philipp Telemann and George Frideric Handel. Life Born in Hartmannsdorf near Kirchberg in Saxony, Graupner received his first musical instruction from his uncle, an organist named Nicolaus Kuester. Graupner went to the University of Leipzig where he studied law (as did many composers of the time) and then completed his musical studies with Johann Kuhnau, the cantor of the Thomasschule (St. Thomas School). In 1705, Graupner left Leipzig to play the harpsichord in the orchestra of the Hamburg Opera under the direction of Reinhard Keiser, alongside George Frideric Handel, then a young violinist. In addition to playing the harpsichord, Graupner composed six operas in Hamburg, some of them in collaboration with Keiser, a popular composer of operas in Germany. In 1709, Graupner accepted a post at the court ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erdmann Neumeister
Erdmann Neumeister (12 May 1671 – 18 August 1756) was a German Lutheran pastor and hymnologist. He was born in Uichteritz near Weißenfels in the province Saxonia of Germany. As a fifteen-year-old boy he started his studies in Schulpforta, an old humanistic gymnasium. He became a student of poetology and theology in the University of Leipzig between 1691 and 1697. He began his career as a minister of religion in the spa town of Bibra. He became diaconus (deacon) for the duke of Saxonia-Weissenfels. From 1705 to 1715, he was superintendent in Sorau (today Zary in Poland). He left for Hamburg because of theological disputes. (As an adult, he would become a vehement opponent of Pietism). He died in Hamburg as an honoured main pastor. His grave in the St. Jacobi Church was destroyed during World War II. Works Hymns He is remembered for several hymns, including "Jesus, Great and Wondrous Star" and "Sinners Jesus Will Receive". Cantatas Neumeister was an influential writ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched the Reformation, Protestant Reformation. The reaction of the government and church authorities to the international spread of his writings, beginning with the ''Ninety-five Theses'', divided Western Christianity. During the Reformation, Lutheranism became the state religion of numerous states of northern Europe, especially in northern Germany, Scandinavia and the then-Livonian Order. Lutheran clergy became civil servants and the Lutheran churches became part of the state. The split between the Lutherans and the Roman Catholics was made public and clear with the 1521 Edict of Worms: the edicts of the Diet (assembly), Diet condemned Luther and officially banned citizens of the Holy Roman Empire from defending or propagatin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



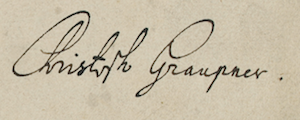

.jpg)