|
Gender Differences In Suicide
Gender differences in suicide rates have been shown to be significant. There are different rates of suicides and suicidal behavior between males and females (among both adults and adolescents). While females more often have suicidal thoughts, males die by suicide more frequently. This discrepancy is also known as the gender paradox in suicide. Globally, death by suicide occurred about 1.8 times more often among males than among females in 2008, and 1.7 times in 2015. In the Western world, males die by suicide three to four times more often than do females. This greater male frequency is increased in those over the age of 65. Suicide attempts are between two and four times more frequent among females. Researchers have partly attributed the difference between suicide and attempted suicide among the sexes to males using more lethal means to end their lives. Other reasons, including disparities in the strength or genuineness of suicidal thoughts, have also been given. Overview ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silvia Sara Canetto
Silvia Sara Canetto is a psychologist known for her research in diversity issues (including gender, sexual orientation, and social economic status) related to suicidal behaviors, aging, and end of life. She is a professor of applied social health psychology, and counseling psychology at Colorado State University (CSU). Canetto is a Fellow of the Association for Psychological Science, the Gerontological Society of America, and the American Psychological Association (APA) (Society for the Psychology of Women, Division of International Psychology, Society of Counseling Psychology, Division of Trauma Psychology, Division of Adult Development and Aging, and Society for the Psychological Study of Men and Masculinities). Canetto co-edited ''Focus on women. Women and suicidal behavior'' with David Lester,' and ''Review of Suicidology'' with Ronald W. Maris and Morton M. Silverman. Awards * 1997 Shneidman Award from the American Association of Suicidology for outstanding contributio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scandinavian Journal Of Psychology
The ''Scandinavian Journal of Psychology'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal on psychology. It is published in association with the Nordic Psychological Association Nordic most commonly refers to: * Nordic countries, written in plural as Nordics, the northwestern European countries, including Scandinavia, Fennoscandia and the North Atlantic * Scandinavia, a cultural, historical and ethno-linguistic region ... and on behalf of the Scandinavian Psychological Associations. It was first published in 1960. The journal is divided into four sections: ''Cognition and Neurosciences'', ''Development and Ageing'', ''Personality and Social Psychology'' and ''Health and Disability''. References Publications established in 1960 Psychology journals Bimonthly journals Wiley-Blackwell academic journals Academic journals associated with learned and professional societies {{psych-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infertility
Infertility is the inability of a person, animal or plant to reproduce by natural means. It is usually not the natural state of a healthy adult, except notably among certain eusocial species (mostly haplodiploid insects). It is the normal state of a human child or other young offspring, because they have not undergone puberty, which is the body's start of reproductive capacity. In humans, infertility is the inability to become pregnant after one year of unprotected and regular sexual intercourse involving a male and female partner.Chowdhury SH, Cozma AI, Chowdhury JH. Infertility. Essentials for the Canadian Medical Licensing Exam: Review and Prep for MCCQE Part I. 2nd edition. Wolters Kluwer. Hong Kong. 2017. There are many causes of infertility, including some that medical intervention can treat. Estimates from 1997 suggest that worldwide about five percent of all heterosexual couples have an unresolved problem with infertility. Many more couples, however, experience involu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Developing Country
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreement on which countries fit this category. The term low and middle-income country (LMIC) is often used interchangeably but refers only to the economy of the countries. The World Bank classifies the world's economies into four groups, based on gross national income per capita: high, upper-middle, lower-middle, and low income countries. Least developed countries, landlocked developing countries and small island developing states are all sub-groupings of developing countries. Countries on the other end of the spectrum are usually referred to as high-income countries or developed countries. There are controversies over this term's use, which some feel it perpetuates an outdated concept of "us" and "them". In 2015, the World Bank declared that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unemployment
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for Work (human activity), work during the reference period. Unemployment is measured by the unemployment rate, which is the number of people who are unemployed as a percentage of the labour force (the total number of people employed added to those unemployed). Unemployment can have many sources, such as the following: * new technology, technologies and inventions * the status of the economy, which can be influenced by a recession * competition caused by globalization and international trade * Policy, policies of the government * regulation and market (economics), market Unemployment and the status of the economy can be influenced by a country through, for example, fiscal policy. Furthermore, the monetary authority of a country, such as the central bank, can influ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Divorce
Divorce (also known as dissolution of marriage) is the process of terminating a marriage or marital union. Divorce usually entails the canceling or reorganizing of the legal duties and responsibilities of marriage, thus dissolving the bonds of matrimony between a married couple under the rule of law of the particular country or state. Divorce laws vary considerably around the world, but in most countries, divorce requires the sanction of a court or other authority in a legal process, which may involve issues of distribution of property, child custody, alimony (spousal support), child visitation / access, parenting time, child support, and division of debt. In most countries, monogamy is required by law, so divorce allows each former partner to marry another person. Divorce is different from annulment, which declares the marriage null and void, with legal separation or ''de jure'' separation (a legal process by which a married couple may formalize a ''de facto'' se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major Depressive Disorder
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive low mood, low self-esteem, and loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities. Introduced by a group of US clinicians in the mid-1970s, the term was adopted by the American Psychiatric Association for this symptom cluster under mood disorders in the 1980 version of the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM-III), and has become widely used since. The diagnosis of major depressive disorder is based on the person's reported experiences, behavior reported by relatives or friends, and a mental status examination. There is no laboratory test for the disorder, but testing may be done to rule out physical conditions that can cause similar symptoms. The most common time of onset is in a person's 20s, with females affected about twice as often as males. The course of the disorder varies widely, from one epis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Individualism
Individualism is the moral stance, political philosophy, ideology and social outlook that emphasizes the intrinsic worth of the individual. Individualists promote the exercise of one's goals and desires and to value independence and self-reliance and advocate that interests of the individual should achieve precedence over the state or a social group while opposing external interference upon one's own interests by society or institutions such as the government. Individualism is often defined in contrast to totalitarianism, collectivism and more corporate social forms. Individualism makes the individual its focus and so starts "with the fundamental premise that the human individual is of primary importance in the struggle for liberation". Anarchism, existentialism, liberalism and libertarianism are examples of movements that take the human individual as a central unit of analysis.L. Susan Brown. '' The Politics of Individualism: Liberalism, Liberal Feminism, and Anarchism''. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socioeconomic Status
Socioeconomic status (SES) is an economic and sociological combined total measure of a person's work experience and of an individual's or family's economic access to resources and social position in relation to others. When analyzing a family's SES, the household income, earners' education, and occupation are examined, as well as combined income, whereas for an individual's SES only their own attributes are assessed. Recently, research has revealed a lesser recognized attribute of SES as perceived financial stress, as it defines the "balance between income and necessary expenses". Perceived financial stress can be tested by deciphering whether a person at the end of each month has more than enough, just enough, or not enough money or resources. However, SES is more commonly used to depict an economic difference in society as a whole. Socioeconomic status is typically broken into three levels (high, middle, and low) to describe the three places a family or an individual may fal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femininity
Femininity (also called womanliness) is a set of attributes, behaviors, and roles generally associated with women and girls. Femininity can be understood as socially constructed, and there is also some evidence that some behaviors considered feminine are influenced by both cultural factors and biological factors. To what extent femininity is biologically or socially influenced is subject to debate. It is conceptually distinct from both the female biological sex and from womanhood, as all humans can exhibit feminine and masculine traits, regardless of sex and gender. Traits traditionally cited as feminine include gracefulness, gentleness, empathy, humility, and sensitivity, though traits associated with femininity vary across societies and individuals, and are influenced by a variety of social and cultural factors. Overview and history Despite the terms ''femininity'' and ''masculinity'' being in common usage, there is little scientific agreement about what femininity and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
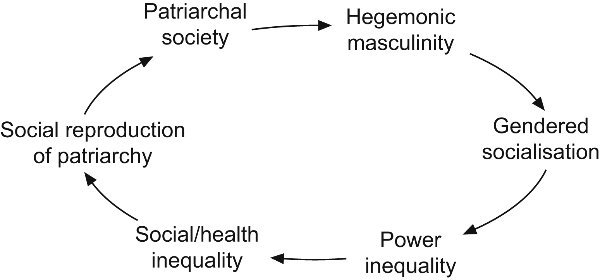
Hegemonic Masculinity
In gender studies, hegemonic masculinity is part of R. W. Connell's gender order theory, which recognizes multiple masculinities that vary across time, society, culture, and the individual. Hegemonic masculinity is defined as a practice that legitimizes men's dominant position in society and justifies the subordination of the common male population and women, and other marginalized ways of being a man. Conceptually, hegemonic masculinity proposes to explain how and why men maintain dominant social roles over women, and other gender identities, which are perceived as "feminine" in a given society. As a sociological concept, the nature of hegemonic masculinity derives from the theory of cultural hegemony, by Marxist theorist Antonio Gramsci, which analyses the power relations among the social classes of a society. Hence, in the term ''hegemonic masculinity'', the adjective ''hegemonic'' refers to the cultural dynamics by means of which a social group claims, and sustains, a lead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)