|
Gateshead Works
Gateshead TMD was a railway traction maintenance depot situated in Gateshead, England. The depot code was 52A during the steam era and GD later on. It was known, along with the adjacent locomotive works, as Greenesfield or Greensfield, after a Mr. Greene, from whom the North Eastern Railway (NER) bought the land . In 1958, all BR locomotive depots on Tyneside, Wearside and in Northumberland became sub-sheds of Gateshead. The depot closed in 1991. Housing now occupies the site, now known as Ochre Yards. The street names reflect the site's history, with Worsdell Drive and Fletcher Road named after former locomotive superintendents of the NER. Engine shed and infrastructure The main shed housed four turntables for most of its working life. Prior to 1908, all four turntables had been 48' 5", which proved to be a problem as locomotives were steadily increasing in size. However, in that same year, the Redheugh Incline was closed, thereby allowing the track running alongsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gateshead
Gateshead () is a large town in northern England. It is on the River Tyne's southern bank, opposite Newcastle upon Tyne, Newcastle to which it is joined by seven bridges. The town contains the Gateshead Millennium Bridge, Millennium Bridge, Sage Gateshead, The Sage, and the Baltic Centre for Contemporary Art, and has on its outskirts the twenty metre tall Angel of the North sculpture. Historic counties of England, Historically part of County Durham, under the Local Government Act 1888 the town was made a county borough, meaning it was administered independently of the county council. Since 1974, the town has been administered as part of the Metropolitan Borough of Gateshead within Tyne and Wear. In the 2011 Census, town had a population 120,046 while the wider borough had 200,214. Toponymy Gateshead is first mentioned in Latin translation in Bede, Bede's ''Ecclesiastical History of the English People'' as ''ad caput caprae'' ("at the goat's head"). This interpretation is consis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Northern Railway (Great Britain)
The Great Northern Railway (GNR) was a British railway company incorporated in 1846 with the object of building a line from London to York. It quickly saw that seizing control of territory was key to development, and it acquired, or took leases of, many local railways, whether actually built or not. In so doing, it overextended itself financially. Nevertheless, it succeeded in reaching into the coalfields of Nottinghamshire, Derbyshire and Yorkshire, as well as establishing dominance in Lincolnshire and north London. Bringing coal south to London was dominant, but general agricultural business, and short- and long-distance passenger traffic, were important activities too. Its fast passenger express trains captured the public imagination, and its Chief Mechanical Engineer Nigel Gresley became a celebrity. Anglo-Scottish travel on the East Coast Main Line became commercially important; the GNR controlled the line from London to Doncaster and allied itself with the North Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consett Iron Company
The Consett Iron Company Ltd was an industrial business based in the Consett area of County Durham in the United Kingdom. The company owned coal mines and limestone quarries, and manufactured iron and steel. It was registered on 4 April 1864 as successor to the Derwent & Consett Iron Company Ltd. This in turn was the successor to the Derwent Iron Company, founded in 1840. The company's seven collieries and various coke ovens came into the ownership of the National Coal Board, when British coal companies were nationalised in 1947. The Consett Iron Company itself was nationalised in 1951, becoming part of the Iron and Steel Corporation of Great Britain. It was denationalised shortly afterwards, then renationalised in 1967. The Consett Iron Company was absorbed into British Steel Corporation in 1967, and the location became known as the Consett Steel Works. British Steel Consett Works was closed in 1980. Early history In 1840 a group of local businessmen led by Jonathan Richard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westinghouse Brake And Signal Company Ltd
The Westinghouse Brake & Signal Company Ltd was a British manufacturer of railroad signs. Founded by George Westinghouse, it was registered as "Westinghouse Brake Company" in 1881. The company reorganised in 1920, associating with Evans O'Donnell, and Saxby and Farmer which merged to form the "Westinghouse Brake & Saxby Signal Company". The 'Saxby' would be dropped from their title in 1935.Westinghouse Brake and Signal Co on Grace's Guide to British Industrial History For most of the 20th century, Westinghouse manufactured air brakes, , mining & colliery equipment, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
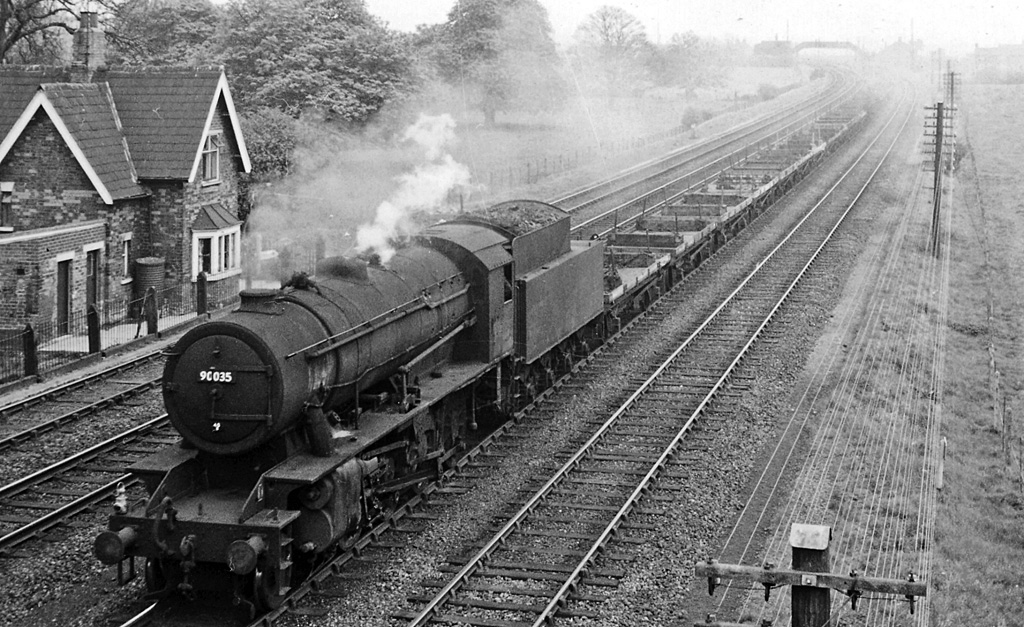
British Railways Steam Locomotives
The steam locomotives of British Railways were used by British Railways over the period 1948–1968. The vast majority of these were inherited from its four constituent companies, the " Big Four". In addition, BR built 2,537 steam locomotives in the period 1948–1960, 1,538 to pre-nationalisation designs and 999 to its own standard designs. These locomotives had short working lives, some as little as five years, because of the decision to end the use of steam traction by 1968, against a design life of over 30 years and a theoretical final withdrawal date of between 1990 and 2000. Background British Railways was created on 1 January 1948 principally by the merger of the " Big Four" grouped railway companies: the Great Western Railway (GWR), the London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS), the London and North Eastern Railway (LNER) and the Southern Railway (SR). It inherited a wide legacy of locomotives and rolling stock, much of which needed replacing due to the ravages of Wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LNER Class W1
The LNER W1 No. 10000 (also known as the ''Hush-Hush'' due to its secrecy) was an experimental steam locomotive fitted with a high pressure water-tube boiler. Nigel Gresley was impressed by the results of using high-pressure steam in marine applications and so in 1924 he approached Harold Yarrow of shipyard and boilermakers Yarrow & Company of Glasgow to design a suitable boiler for a railway locomotive, based on Yarrow's design. Boiler The boiler was not the usual Yarrow design. In operation, particularly its circulation paths, the boiler had more in common with other three-drum designs such as the Woolnough. It has also been described as an evolution of the Brotan-Deffner water-tube firebox, with the firebox extended to become the entire boiler. The boiler resembled two elongated marine Yarrow boilers, joined end to end. Both had the usual Yarrow triangular arrangement of a central large steam drum above two separated water drums, linked by multiple rows of slightly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water-tube Boiler
A high pressure watertube boiler (also spelled water-tube and water tube) is a type of boiler in which water circulates in tubes heated externally by the fire. Fuel is burned inside the furnace, creating hot gas which boils water in the steam-generating tubes. In smaller boilers, additional generating tubes are separate in the furnace, while larger utility boilers rely on the water-filled tubes that make up the walls of the furnace to generate steam. The heated water/steam mixture then rises into the steam drum. Here, saturated steam is drawn off the top of the drum. In some services, the steam passes through tubes in the hot gas path, (a superheater) to become superheated. Superheated steam is defined as steam that is heated above the boiling point at a given pressure. Superheated steam is a dry gas and therefore is typically used to drive turbines, since water droplets can severely damage turbine blades. Saturated water at the bottom of the steam drum returns to the lower drum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
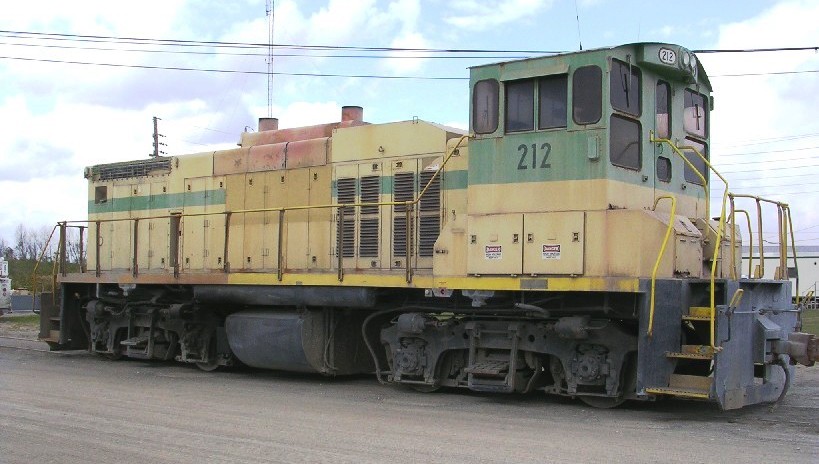
Switcher
A switcher, shunter, yard pilot, switch engine, yard goat, or shifter is a small railroad locomotive used for manoeuvring railroad cars inside a rail yard in a process known as ''switching'' (US) or ''shunting'' (UK). Switchers are not intended for moving trains over long distances but rather for assembling trains in order for another locomotive to take over. They do this in classification yards (Great Britain: ''marshalling yards''). Switchers may also make short transfer runs and even be the only motive power on branch lines and switching and terminal railroads. The term can also be used to describe the workers operating these engines or engaged in directing shunting operations. Switching locomotives may be purpose-built engines, but may also be downgraded main-line engines, or simply main-line engines assigned to switching. Switchers can also be used on short excursion train rides. The typical switcher is optimised for its job, being relatively low-powered but with a high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
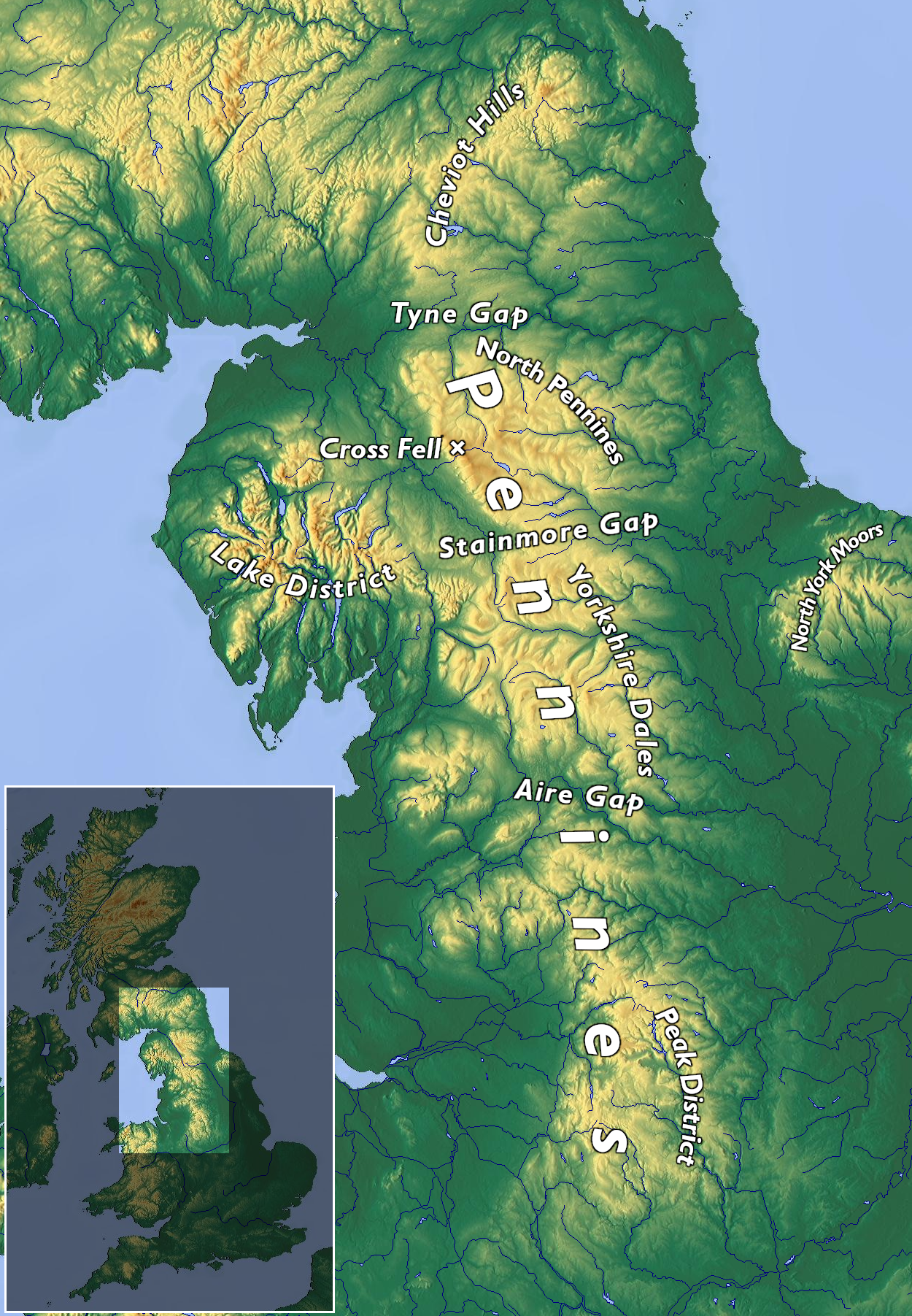
Pennines
The Pennines (), also known as the Pennine Chain or Pennine Hills, are a range of uplands running between three regions of Northern England: North West England on the west, North East England and Yorkshire and the Humber on the east. Commonly described as the "backbone of England", the range stretches northwards from the Peak District at the southern end, through the South Pennines, Yorkshire Dales and North Pennines to the Tyne Gap, which separates the range from the Border Moors and Cheviot Hills across the Anglo-Scottish border, although some definitions include them. South of the Aire Gap is a western spur into east Lancashire, comprising the Rossendale Fells, West Pennine Moors and the Bowland Fells in North Lancashire. The Howgill Fells and Orton Fells in Cumbria are sometimes considered to be Pennine spurs to the west of the range. The Pennines are an important water catchment area with numerous reservoirs in the head streams of the river valleys. The North Pennin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail Class ES1
The NER Class ES1 (''Electric Shunting 1'') was a class of two steeplecab electric locomotives commissioned by the North Eastern Railway in 1902. Both locomotives passed to the London and North Eastern Railway in 1923 and then to British Railways in 1948, but both were withdrawn before TOPS numbers could be applied. History The North Eastern Railway was an enthusiastic and relatively early adopter of electric traction for railways. As part of a 1902 scheme to electrify the suburban railway networks in the Tyneside area, the NER's Chief Mechanical Engineer, Wilson Worsdell, also wished to electrify a , horseshoe-shaped freight line that went from Trafalgar Yard in Manors to Newcastle Quayside Yard. Passing through three tunnels, this line had gradients as steep as 1:27 ( 3.70 %) and a number of sharp curves: it presented a formidable challenge for steam traction. Working conditions inside the tunnels were atrocious because the locomotives had to work exceptionally har ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coaling Tower
A coaling tower, coal stage, coaling plant or coaling station is a facility used to load coal as fuel into railway steam locomotives. Coaling towers were often sited at motive power depots or locomotive maintenance shops. In the early years of railways, coal was shovelled by hand into locomotive tenders, the first attempt in Britain to replace manual labour by gravity in the refuelling process being found at Shildon, County Durham, where coal drops were built by the Stockton and Darlington Railway in 1847. In time, railway companies constructed more elaborate coaling towers, made from wood, steel, or reinforced concrete (ferroconcrete). In almost all cases coaling stations used a gravity fed method, with one or more large storage bunkers for the coal elevated on columns above the railway tracks, from which the coal could be released to slide down a chute into the waiting locomotive's coal storage area. The method of lifting the bulk coal into the storage bin varied. The coal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1955 Modernisation Plan
Events January * January 3 – José Ramón Guizado becomes president of Panama. * January 17 – , the first nuclear-powered submarine, puts to sea for the first time, from Groton, Connecticut. * January 18– 20 – Battle of Yijiangshan Islands: The Chinese Communist People's Liberation Army seizes the islands from the Republic of China (Taiwan). * January 22 – In the United States, The Pentagon announces a plan to develop intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs), armed with nuclear weapons. * January 23 – The Sutton Coldfield rail crash kills 17, near Birmingham, England. * January 25 – The Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union announces the end of the war between the USSR and Germany, which began during World War II in 1941. * January 28 – The United States Congress authorizes President Dwight D. Eisenhower to use force to protect Formosa from the People's Republic of China. February * February 10 – The United States Seventh Fleet hel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

_(14575234558).jpg)

