|
Gaonim
''Geonim'' ( he, גאונים; ; also transliterated Gaonim, singular Gaon) were the presidents of the two great Babylonian Talmudic Academies of Sura and Pumbedita, in the Abbasid Caliphate, and were the generally accepted spiritual leaders of the Jewish community worldwide in the early medieval era, in contrast to the ''Resh Galuta'' (exilarch) who wielded secular authority over the Jews in Islamic lands. ''Geonim'' is the plural of (''Gaon) , which means "pride" or "splendor" in Biblical Hebrew and since the 19th century "genius" as in modern Hebrew. As a title of a Babylonian college president it meant something like "His Excellency". The ''Geonim'' played a prominent and decisive role in the transmission and teaching of Torah and Jewish law. They taught Talmud and decided on issues on which no ruling had been rendered during the period of the Talmud. The Geonim were also spiritual leaders of the Jewish community of their time. Era The period of the Geonim began in 589 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sura Academy
Sura Academy (Hebrew: ישיבת סורא) was a Jewish yeshiva located in Sura, Babylonia. With Pumbedita Academy, it was one of the two major Jewish academies from the year 225 CE at the beginning of the era of the Amora sages until 1033 CE at the end of the era of the Gaonim. Sura Yeshiva Academy was founded by the Amora Abba Arika ("Rav"), a disciple of Judah ha-Nasi. Among the well-known sages that headed the yeshiva were Rav Huna, Rav Chisda, Rav Ashi, Yehudai Gaon, Natronai Gaon, Saadia Gaon, and others. History Rav (Abba Arikha) arrived at Sura city to find no lively Jewish religious public life, and since he was worried about the continuity of the Jewish community in Babylonia, he left his colleague Samuel of Nehardea in Nehardea and began working to establish the yeshiva that would become Sura Academy. Upon Rav's arrival, teachers from surrounding cities and towns descended upon Sura. The Academy of Sura was formally founded in the year 225 CE, several years after Rav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sura Academy
Sura Academy (Hebrew: ישיבת סורא) was a Jewish yeshiva located in Sura, Babylonia. With Pumbedita Academy, it was one of the two major Jewish academies from the year 225 CE at the beginning of the era of the Amora sages until 1033 CE at the end of the era of the Gaonim. Sura Yeshiva Academy was founded by the Amora Abba Arika ("Rav"), a disciple of Judah ha-Nasi. Among the well-known sages that headed the yeshiva were Rav Huna, Rav Chisda, Rav Ashi, Yehudai Gaon, Natronai Gaon, Saadia Gaon, and others. History Rav (Abba Arikha) arrived at Sura city to find no lively Jewish religious public life, and since he was worried about the continuity of the Jewish community in Babylonia, he left his colleague Samuel of Nehardea in Nehardea and began working to establish the yeshiva that would become Sura Academy. Upon Rav's arrival, teachers from surrounding cities and towns descended upon Sura. The Academy of Sura was formally founded in the year 225 CE, several years after Rav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geonim
''Geonim'' ( he, גאונים; ; also transliterated Gaonim, singular Gaon) were the presidents of the two great Babylonian Talmudic Academies of Sura and Pumbedita, in the Abbasid Caliphate, and were the generally accepted spiritual leaders of the Jewish community worldwide in the early medieval era, in contrast to the ''Resh Galuta'' (exilarch) who wielded secular authority over the Jews in Islamic lands. ''Geonim'' is the plural of (''Gaon) , which means "pride" or "splendor" in Biblical Hebrew and since the 19th century "genius" as in modern Hebrew. As a title of a Babylonian college president it meant something like "His Excellency". The ''Geonim'' played a prominent and decisive role in the transmission and teaching of Torah and Jewish law. They taught Talmud and decided on issues on which no ruling had been rendered during the period of the Talmud. The Geonim were also spiritual leaders of the Jewish community of their time. Era The period of the Geonim began in 589 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanization Of Hebrew
The Hebrew language uses the Hebrew alphabet with optional vowel diacritics. The romanization of Hebrew is the use of the Latin alphabet to transliterate Hebrew words. For example, the Hebrew name spelled ("Israel") in the Hebrew alphabet can be romanized as ' or ' in the Latin alphabet. Romanization includes any use of the Latin alphabet to transliterate Hebrew words. Usually, it is to identify a Hebrew word in a non-Hebrew language that uses the Latin alphabet, such as German, Spanish, Turkish, and so on. Transliteration uses an alphabet to represent the letters and sounds of a word spelled in another alphabet, whereas transcription uses an alphabet to represent the sounds only. Romanization can refer to either. To go the other way, that is from English to Hebrew, see Hebraization of English. Both Hebraization of English and Romanization of Hebrew are forms of transliteration. Where these are formalized these are known as "transliteration systems", and, where only some wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buyid Dynasty
The Buyid dynasty ( fa, آل بویه, Āl-e Būya), also spelled Buwayhid ( ar, البويهية, Al-Buwayhiyyah), was a Shia Iranian dynasty of Daylamite origin, which mainly ruled over Iraq and central and southern Iran from 934 to 1062. Coupled with the rise of other Iranian dynasties in the region, the approximate century of Buyid rule represents the period in Iranian history sometimes called the 'Iranian Intermezzo' since, after the Muslim conquest of Persia, it was an interlude between the rule of the Abbasid Caliphate and the Seljuk Empire. The Buyid dynasty was founded by 'Ali ibn Buya, who in 934 conquered Fars and made Shiraz his capital. His younger brother Hasan ibn Buya conquered parts of Jibal in the late 930s, and by 943 managed to capture Ray, which he made his capital. In 945, the youngest brother, Ahmad ibn Buya, conquered Iraq and made Baghdad his capital. He received the ''laqab'' or honorific title of ''Mu'izz al-Dawla'' ("Fortifier of the State"). The e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siddur
A siddur ( he, סִדּוּר ; plural siddurim ) is a Jewish prayer book containing a set order of daily prayers. The word comes from the Hebrew root , meaning 'order.' Other terms for prayer books are ''tefillot'' () among Sephardi Jews, ''tefillah'' among German Jews, and ''tiklāl'' () among Yemenite Jews. History The earliest parts of Jewish prayer books are the ''Shema Yisrael'' ("Hear O Israel") ( Deuteronomy 6:4 ''et seq'') and the Priestly Blessing (Numbers 6:24-26), which are in the Torah. A set of eighteen (currently nineteen) blessings called the ''Shemoneh Esreh'' or the '' Amidah'' (Hebrew, "standing rayer), is traditionally ascribed to the Great Assembly in the time of Ezra, at the end of the biblical period. The name ''Shemoneh Esreh'', literally "eighteen", is a historical anachronism, since it now contains nineteen blessings. It was only near the end of the Second Temple period that the eighteen prayers of the weekday Amidah became standardized. Even at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semicha
Semikhah ( he, סמיכה) is the traditional Jewish name for rabbinic ordination. The original ''semikhah'' was the formal "transmission of authority" from Moses through the generations. This form of ''semikhah'' ceased between 360 and 425 CE. Since then ''semikhah'' has continued in a less formal way. Throughout history there have been several attempts to reestablish the classical ''semikhah''. In recent times, some institutions grant ordination for the role of ''hazzan'' (cantor), extending the "investiture" granted there from the 1950s. Less commonly, since the 1990s, ordination is granted for the role of lay leader - sometimes titled '' darshan''. Ordination may then also be specifically termed , "rabbinical ordination", , "cantorial ordination", or , "maggidic ordination". The title of "rabbi" has "proliferated greatly over the last century". Nowadays ''Semikha'' is also granted for a limited form of ordination, focused on the application of Halakha in specific settin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Responsa
''Responsa'' (plural of Latin , 'answer') comprise a body of written decisions and rulings given by legal scholars in response to questions addressed to them. In the modern era, the term is used to describe decisions and rulings made by scholars in historic religious law. In the Roman Empire Roman law recognised , i.e., the responses and thoughts of jurists, as one of the sources of (written law), along with laws originating from magistrates, from the Senate, or from the emperor. A particularly well-known and highly influential example of such ''responsa'' was the ''Digesta'' (or ''Digests''), in 90 books, the principal work of the prominent second century jurist Salvius Julianus. This was a systematic treatise on civil and praetorian law, consisting of responsa on real and hypothetical cases, cited by many later Roman legal writers. In the Catholic Church In the Catholic Church, ''responsa'' are answers of the competent executive authority to specific questions (in Latin, ''dub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
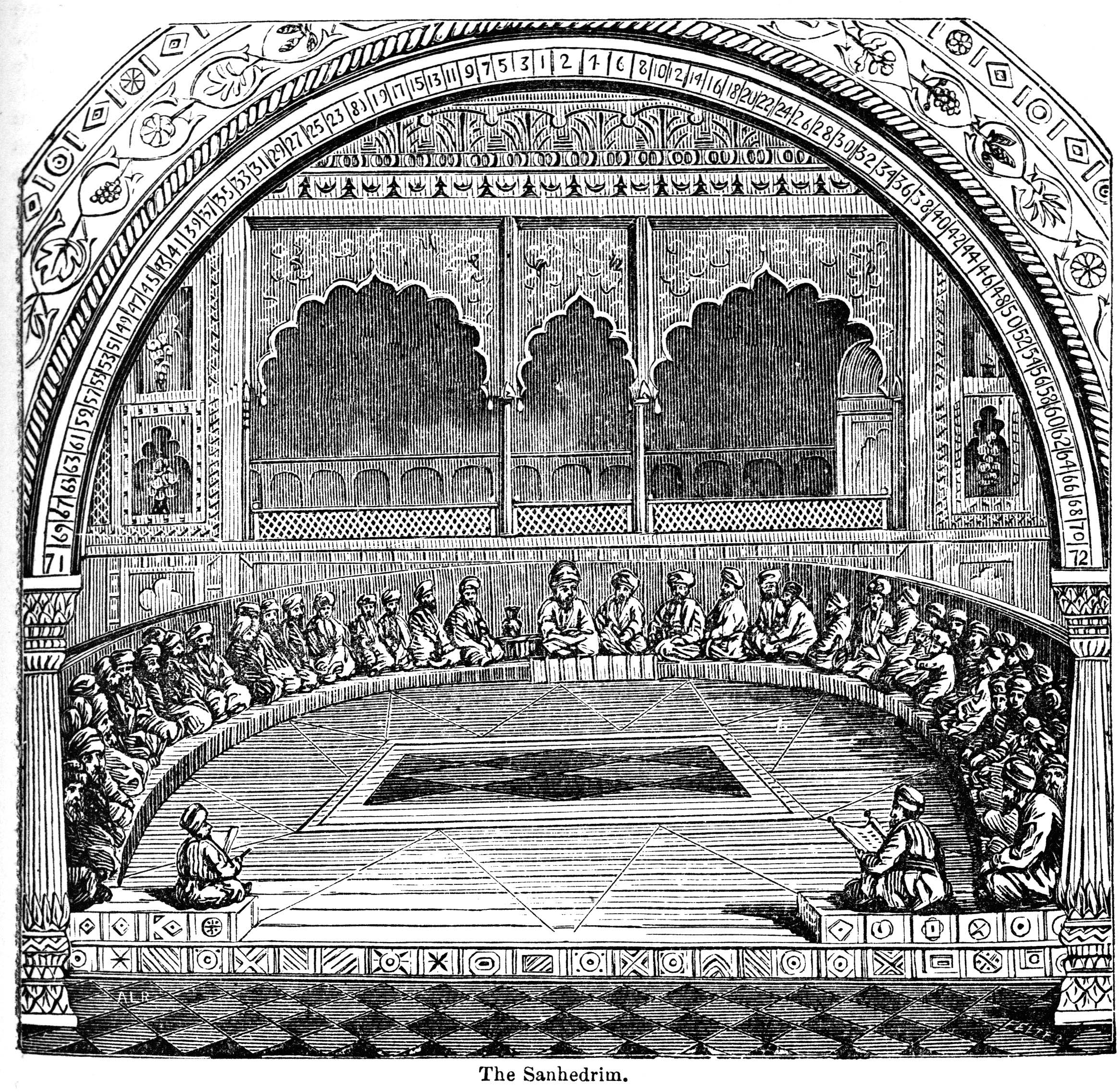
Sanhedrin
The Sanhedrin (Hebrew and Aramaic: סַנְהֶדְרִין; Greek: , ''synedrion'', 'sitting together,' hence 'assembly' or 'council') was an assembly of either 23 or 71 elders (known as "rabbis" after the destruction of the Second Temple), appointed to sit as a tribunal in every city in the ancient Land of Israel. There were two classes of Rabbinite Jewish courts which were called Sanhedrin, the Great Sanhedrin and the Lesser Sanhedrin. A lesser Sanhedrin of 23 judges was appointed to sit as a tribunal in each city, but there was only supposed to be one Great Sanhedrin of 71 judges, which among other roles acted as the Supreme Court, taking appeals from cases which were decided by lesser courts. In general usage, ''the Sanhedrin'' without qualifier normally refers to the Great Sanhedrin, which was presided over by the ''Nasi'', who functioned as its head or representing president, and was a member of the court; the ''Av Beit Din'' or the chief of the court, who was second to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aramaic Language
The Aramaic languages, short Aramaic ( syc, ܐܪܡܝܐ, Arāmāyā; oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; tmr, אֲרָמִית), are a language family containing many varieties (languages and dialects) that originated in the ancient region of Syria. For over three thousand years, It is a sub-group of the Semitic languages. Aramaic varieties served as a language of public life and administration of ancient kingdoms and empires and also as a language of divine worship and religious study. Several modern varieties, namely the Neo-Aramaic languages, are still spoken in the present-day. The Aramaic languages belong to the Northwest group of the Semitic language family, which also includes the Canaanite languages such as Hebrew, Edomite, Moabite, and Phoenician, as well as Amorite and Ugaritic. Aramaic languages are written in the Aramaic alphabet, a descendant of the Phoenician alphabet, and the most prominent alphabet variant is the Syriac alphabet. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosh Yeshiva
Rosh yeshiva ( he, ראש ישיבה, pl. he, ראשי ישיבה, '; Anglicized pl. ''rosh yeshivas'') is the title given to the dean of a yeshiva, a Jewish educational institution that focuses on the study of traditional religious texts, primarily the Talmud and the Torah, and ''halakha'' (Jewish law). The general role of the rosh yeshiva is to oversee the Talmudic studies and practical matters. The rosh yeshiva will often give the highest ''shiur'' (class) and is also the one to decide whether to grant permission for students to undertake classes for rabbinical ordination, known as ''semicha''. The term is a compound of the Hebrew words ''rosh'' ("head") and ''yeshiva'' (a school of religious Jewish education). The rosh yeshiva is required to have a comprehensive knowledge of the Talmud and the ability to analyse and present new perspectives, called ''chidushim'' (novellae) verbally and often in print. In some institutions, such as YU's Rabbi Isaac Elchanan Theological Semin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaon (Hebrew)
Gaon (gā'ōn) ( he, גאון, , plural ''geonim'' — gĕ'ōnīm) may have originated as a shortened version of "Rosh Yeshivat Ge'on Ya'akov", although there are alternative explanations. In Biblical Hebrew, Ancient Hebrew, it referred to arrogance and haughty pride ( – "I abhor the pride of Jacob and detest his fortresses; I will deliver up the city and everything in it.") and later became known as a general term for pride, both the positive and negative forms ('Pride [of]'; Late Medieval and Modern Hebrew for 'genius'). Today, it may refer to: One of the Geonim during the period 589–1040. Prominent Geonim include: * Yehudai Gaon (Gaon 757–761) * Sar Shalom Ben Boaz (Gaon 838–848) * Natronai ben Hilai, Gaon of Sura (Gaon to 857) * Amram Gaon, Gaon of Sura (Gaon 857–875) * Saadia Gaon (882/892 – 942) * Zemah ben Hayyim (Gaon 889–895) * Sherira Gaon (906–1006) * Samuel ben Hofni (died 1034) * Hai Gaon (939–1038) An honorific title given to a few leading rabbis o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |