|
Ganges Canal (Rajasthan)
The Ganga Canal of Rajasthan (also called Gang Canal) is an irrigation system of canals laid down by Maharaja Ganga Singh of Bikaner in his princely state in the present district of Sri Ganganagar in the early twentieth century. It is fed from the Sutlej River near Firozpur, Punjab, close to the India–Pakistan border, and passes through the Faridkot and Muktsar districts. Faridkot's Jhok Sarkari village lies on its path. History The Bikaner state was one of the areas most affected by the Indian famine of 1899–1900. In order to get rid of this problem permanently, in 1903 Maharaja Ganga Singh obtained the services of A. W. E. Standley, chief engineer, who demonstrated the feasibility of the western area of the Bikaner State being brought under irrigation from the Satluj Waters. The plan of the Satluj Valley Project was drawn by then chief engineer of Punjab Mr. R. G. Kennedy, according to which the vast area of erstwhile Bikaner state could be brought under irrigation. Bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
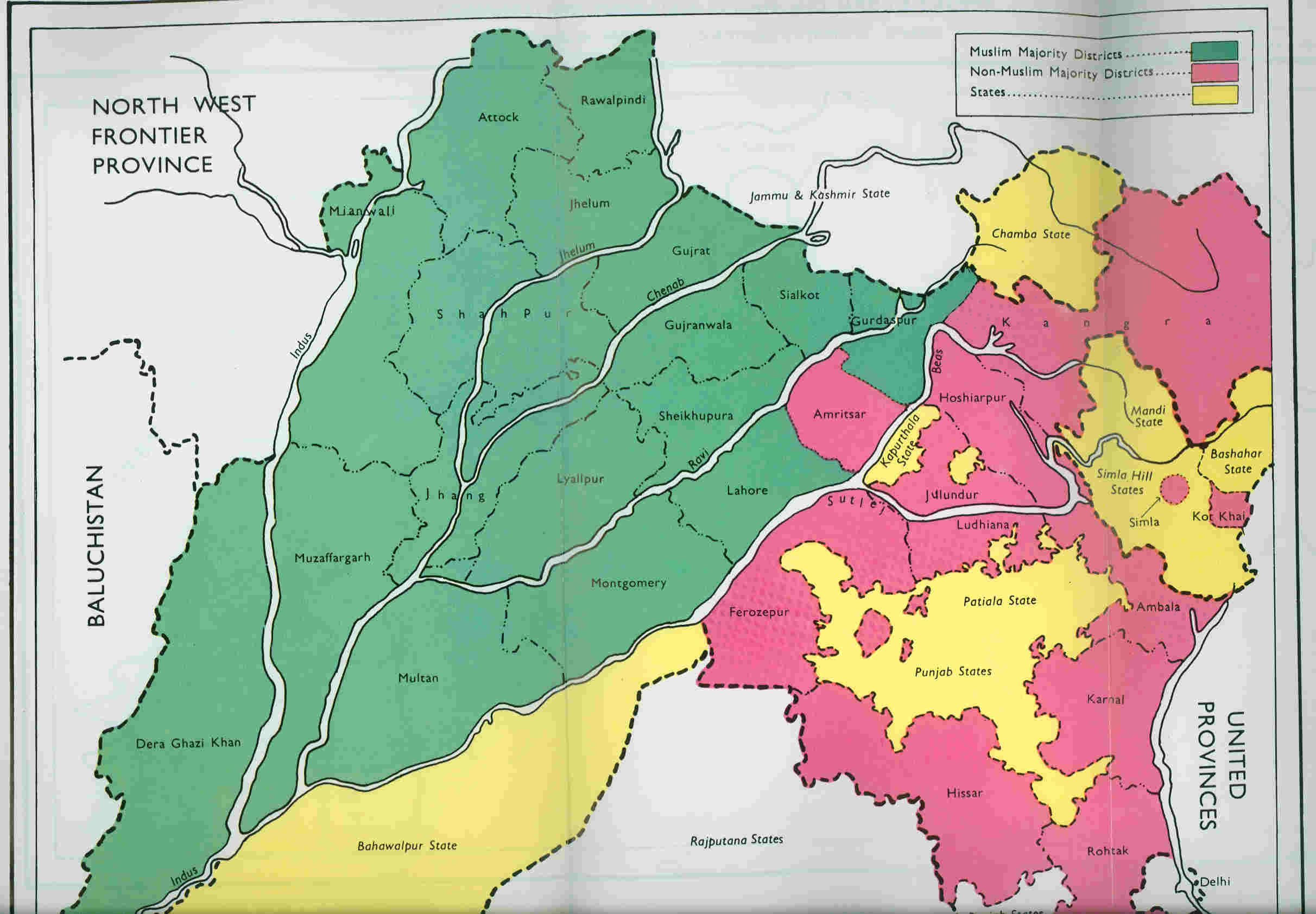
Punjab, British India
Punjab was a province of British India. Most of the Punjab region was annexed by the East India Company in 2 April 1849, and declared a province of British Rule, it was one of the last areas of the Indian subcontinent to fall under British control. In 1858, the Punjab, along with the rest of British India, came under the direct rule of the British Crown. It had an area of 358,354.5 km2. The province comprised four natural geographic regions – ''Indo-Gangetic Plain West'', ''Himalayan'', ''Sub-Himalayan'', and the ''North-West Dry Area'' – along with five administrative divisions – Delhi, Jullundur, Lahore, Multan, and Rawalpindi – and a number of princely states. In 1947, the Partition of India led to the province's division into East Punjab and West Punjab, in the newly independent dominions of India and Pakistan respectively. Etymology The region was originally called Sapta Sindhu,D. R. Bhandarkar, 1989Some Aspects of Ancient Indian Culture: Sir William Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Curzon, 1st Marquess Curzon Of Kedleston
George Nathaniel Curzon, 1st Marquess Curzon of Kedleston, (11 January 1859 – 20 March 1925), styled Lord Curzon of Kedleston between 1898 and 1911 and then Earl Curzon of Kedleston between 1911 and 1921, was a British Conservative statesman who served as Viceroy of India from 1899 to 1905. During the First World War, Curzon was Leader of the House of Lords and from December 1916 served in the small War Cabinet of Prime Minister David Lloyd George and in the War Policy Committee. He went on to serve as Secretary of State for Foreign Affairs at the Foreign Office from 1919 to 1924. In 1923, Curzon was a contender for the office of Prime Minister, but Bonar Law and some other leading Conservatives preferred Stanley Baldwin for the office. Early life Curzon was the eldest son and the second of the eleven children of Alfred Curzon, 4th Baron Scarsdale (1831–1916), who was the Rector of Kedleston in Derbyshire. George Curzon's mother was Blanche (1837–1875), the daugh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canals In Rajasthan
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface flow under atmospheric pressure, and can be thought of as artificial rivers. In most cases, a canal has a series of dams and locks that create reservoirs of low speed current flow. These reservoirs are referred to as ''slack water levels'', often just called ''levels''. A canal can be called a ''navigation canal'' when it parallels a natural river and shares part of the latter's discharges and drainage basin, and leverages its resources by building dams and locks to increase and lengthen its stretches of slack water levels while staying in its valley. A canal can cut across a drainage divide atop a ridge, generally requiring an external water source above the highest elevation. The best-known example of such a canal is the Panama Canal. Man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indira Gandhi Canal
The Indira Gandhi Canal (originally, Rajasthan Canal) is the longest canal in India. It starts at the Harike Barrage near Harike, a few kilometers downriver from the confluence of the Satluj and Beas rivers in Punjab state, and ends in irrigation facilities in the Thar Desert in the northwest of Rajasthan state. Previously known as the Rajasthan Canal, it was renamed the Indira Gandhi Canal on 2 November 1984 following the assassination of Prime Minister Indira Gandhi. The canal consists of the Rajasthan feeder canal with the first in Punjab and Haryana state and a further in Rajasthan. This is followed by the of the Rajasthan main canal, which is entirely within Rajasthan. The canal enters Haryana from Punjab near Lohgarh and runs through the western part of the Sirsa district before entering Rajasthan near Kharakhera village in the Tibbi tehsil of the Hanumangarh district. It traverses seven districts of Rajasthan: Barmer, Bikaner, Churu, Hanumangarh, Jaisalmer, Jodhpur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jawaharlal Nehru
Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru (; ; ; 14 November 1889 – 27 May 1964) was an Indian anti-colonial nationalist, secular humanist, social democrat— * * * * and author who was a central figure in India during the middle of the 20th century. Nehru was a principal leader of the Indian nationalist movement in the 1930s and 1940s. Upon India's independence in 1947, he served as the country's prime minister for 16 years. Nehru promoted parliamentary democracy, secularism, and science and technology during the 1950s, powerfully influencing India's arc as a modern nation. In international affairs, he steered India clear of the two blocs of the Cold War. A well-regarded author, his books written in prison, such as ''Letters from a Father to His Daughter'' (1929), '' An Autobiography'' (1936) and ''The Discovery of India'' (1946), have been read around the world. During his lifetime, the honorific Pandit was commonly applied before his name in India and even today too. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Mountbatten
Louis Francis Albert Victor Nicholas Mountbatten, 1st Earl Mountbatten of Burma (25 June 1900 – 27 August 1979) was a British naval officer, colonial administrator and close relative of the British royal family. Mountbatten, who was of German descent, was born in the United Kingdom to the prominent Battenberg family and was a maternal uncle of Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh, and a second cousin of King George VI. He joined the Royal Navy during the First World War and was appointed Supreme Allied Commander, South East Asia Command, in the Second World War. He later served as the last Viceroy of British India and briefly as the first Governor-General of the Dominion of India. Mountbatten attended the Royal Naval College, Osborne, before entering the Royal Navy in 1916. He saw action during the closing phase of the First World War, and after the war briefly attended Christ's College, Cambridge. During the interwar period, Mountbatten continued to pursue his naval career, spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferozpur District
Firozpur district, also known as Ferozepur district, is one of the twenty-three districts in the state of Punjab, India. Firozpur district comprises an area of . Firozpur (Ferozepur) is the capital city of the district. It is situated inside ten gates—Amritsari Gate, Wansi Gate, Makhu Gate, Zira Gate, Bagdadi Gate, Mori Gate, Delhi Gate, Magjani Gate, Multani Gate, and Kasuri Gate. Demographics According to the 2011 Census the undivided Firozpur district had a population of 2,029,074. This gives it a ranking of 230th in India (out of a total of 640). The district has a population density of . Its population growth rate over the decade 2001–2011 was 16.08%. Firozpur has a sex ratio of 893 females for every 1000 males, and a literacy rate of 69.8%. (This data is before the creation of Fazilka district). After bifurcation of Fazilika district, the residual district has a population of 1,001,931. Scheduled Castes made up 42.85% of the population. Religion Language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radcliffe Line
The Radcliffe Line was the boundary demarcated between the Indian and Pakistani portions of the Punjab Province and Bengal Presidency of British India. It was named after Cyril Radcliffe, who, as the joint chairman of the two boundary commissions for the two provinces, had the ultimate responsibility to equitably divide of territory with 88 million people. The demarcation line was published on 17 August 1947 upon the Partition of British India. Today, its western side of the line is part of the India–Pakistan border while its eastern side serves as the Bangladesh–India border. Background Events leading up to the Radcliffe Boundary Commissions On 18 July 1947, the Indian Independence Act 1947 of the Parliament of the United Kingdom stipulated that British rule in India would come to an end just one month later, on 15 August 1947. The Act also stipulated the partition of the Presidencies and provinces of British India into two new sovereign dominions: India and Pakistan. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyril Radcliffe
Cyril John Radcliffe, 1st Viscount Radcliffe, (30 March 1899 – 1 April 1977) was a British lawyer and Law Lord best known for his role in the Partition of India. He served as the first chancellor of the University of Warwick from its foundation in 1965 to 1977. Background, education and early career Radcliffe was born in Llanychan, Denbighshire, Wales, the son of an army captain. His maternal grandfather was President of the Law Society between 1890 and 1891. Radcliffe was educated at Haileybury College. He was then conscripted in World War I but his poor eyesight limited the options for service so he was allocated to the Labour Corps. After the War, he attended New College, Oxford as a scholar, and took a first in ''literae humaniores'' in 1921. In 1922 he was elected to a prize fellowship at All Souls College, Oxford. He won the Eldon Law Scholarship in 1923. He was called to the bar by the Inner Temple in 1924, and joined the chambers of Wilfred Greene, later the Mast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partition Of India
The Partition of British India in 1947 was the Partition (politics), change of political borders and the division of other assets that accompanied the dissolution of the British Raj in South Asia and the creation of two independent dominions: Dominion of India, India and Dominion of Pakistan, Pakistan. The Dominion of India is today the India, Republic of India, and the Dominion of Pakistan—which at the time comprised two regions lying on either side of India—is now the Pakistan, Islamic Republic of Pakistan and the Bangladesh, People's Republic of Bangladesh. The partition was outlined in the Indian Independence Act 1947. The change of political borders notably included the division of two provinces of British India, Bengal Presidency, Bengal and Punjab Province (British India), Punjab. The majority Muslim districts in these provinces were awarded to Pakistan and the majority non-Muslim to India. The other assets that were divided included the British Indian Army, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Bari Doab Canal
Madhopur Headworks is a barrage on the Ravi River, just 14km from Pathankot city in Pathankot district in the Indian state of Punjab. It is located on the border with Jammu and Kashmir. The Upper Bari Doab Canal (UBDC) off-taking from Madhopur irrigates agricultural lands in Punjab and provides water to the cities of Pathankot, Gurdaspur, Batala and Amritsar. The headworks was one of the first irrigation projects constructed in Punjab during the British Raj, within 10 years of the conquest of Punjab. It irrigated lands in the Gurdaspur, Amritsar and Lahore districts of the undivided Punjab. During the partition arrangements, Cyrill Radcliffe allocated three tehsils of Gurdaspur district to India in part to maintain the integrity of the canal system from Madhopur. After independence, India signed the Indus Waters Treaty with India obtaining the exclusive use of waters from the Ravi River. Subsequently, India rebuilt the Madhopur headwork as a full barrage. Pakistan continues to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanumangarh District
Hanumangarh district is a district in the state of Rajasthan in India. The city of Hanumangarh is the district headquarters and its largest city. District profile The district is located in the extreme north of Rajasthan. It has an area of 12,645 km2, a population of 1,774,692 (2011 census) and a population density of 184 persons/km2. It is bounded in the north by Punjab state, to the northeast by Haryana state, in the east and south by Churu District and in Bikaner District and on the west by Ganganagar District. The major livelihood of the district is farming; major crops include rice, millet, cotton, sonamukhi ( senna), wheat, and vegetables. It is called the food basket of Rajasthan along with Sri Ganganagar. It is the 31st district of Rajasthan. It was made as district on 12 July 1994 from Ganganagar district. Earlier it was one of the Tehsils of Sri Ganganagar district. The district contains the archaeological site of Kalibangan (Indus Valley civilisation), and P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |