|
Gaius Octavius Appius Suetrius Sabinus
Gaius Octavius Appius Suetrius Sabinus (fl. 3rd century) was a Roman senator and military officer who was appointed consul twice, firstly in AD 214, and secondly in AD 240. Biography Originating from the town of Histonium, and the son of a senator, Suetrius Sabinus began his senatorial career under the reign of the emperor Septimius Severus. His first role was as a member of the ''Decemviri Stlitibus Iudicandis'' which he filled around AD 193 or 194. He then stood as one of the imperial candidates for the office of Quaestor in AD 201, before again standing for the office of Plebeian Tribune in AD 203. He was eventually elected to the office of '' praetor de liberalibus causis'' in AD 206. Suetrius Sabinus was next sent as a Legatus to Africa before returning to Rome to act as ''curator viarum viae Latinae novae'' (or curator of the Via Latina) from AD 209 to 210. His next posting was as '' iuridicus per Aemiliam et Liguriam'', which he held from AD 210 to 211. Suetrius Sabinus th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. From the accession of Caesar Augustus as the first Roman emperor to the military anarchy of the 3rd century, it was a Principate with Italia as the metropole of its provinces and the city of Rome as its sole capital. The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire. The city of Rome remained the nominal capital of both parts until AD 476 when the imperial insignia were sent to Constantinople following the capture of the Western capital of Ravenna by the Germanic barbarians. The adoption of Christianity as the state church of the Roman Empire in AD 380 and the fall of the Western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caracalla
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (born Lucius Septimius Bassianus, 4 April 188 – 8 April 217), better known by his nickname "Caracalla" () was Roman emperor from 198 to 217. He was a member of the Severan dynasty, the elder son of Emperor Septimius Severus and Empress Julia Domna. Proclaimed co-ruler by his father in 198, he reigned jointly with his brother Geta, co-emperor from 209, after their father's death in 211. His brother was murdered by the Praetorian Guard later that year, under orders from Caracalla himself, who then reigned afterwards as sole ruler of the Roman Empire. Caracalla found administration to be mundane, leaving those responsibilities to his mother. Caracalla's reign featured domestic instability and external invasions by the Germanic peoples. Caracalla's reign became notable for the Antonine Constitution ( la, Constitutio Antoniniana), also known as the Edict of Caracalla, which granted Roman citizenship to all free men throughout the Roman Empire. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praefectus
''Praefectus'', often with a further qualification, was the formal title of many, fairly low to high-ranking, military or civil officials in the Roman Empire, whose authority was not embodied in their person (as it was with elected Magistrates) but conferred by delegation from a higher authority. They did have some authority in their prefecture such as controlling prisons and in civil administration. Praetorian prefects The Praetorian prefect (''Praefectus praetorio'') began as the military commander of a general's guard company in the field, then grew in importance as the Praetorian Guard became a potential kingmaker during the Empire. From the Emperor Diocletian's tetrarchy (c. 300) they became the administrators of the four Praetorian prefectures, the government level above the (newly created) dioceses and (multiplied) provinces. Police and civil prefects *''Praefectus urbi'', or ''praefectus urbanus'': city prefect, in charge of the administration of Rome. *''Praefectus vigilu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucius Valerius Messalla Apollinaris
Lucius Valerius Messalla (fl. 3rd century) was a Roman senator. Life Messalla, a member of the third century gens Valeria, was possibly the son of Lucius Valerius Messalla Thrasea Priscus and speculatively his wife Coelia Balbina, since the ''cognomen'' Balbinus appears in their great-grandson's name. He apparently did not suffer any repercussions following the purge that saw his father put to death on the orders of the emperor Caracalla in 212, and in fact he was appointed '' consul prior'' in 214, alongside Gaius Octavius Appius Suetrius Sabinus. It is believed this Messalla was the Valerius Messalla who was the proconsul of Asia sometime between 236 and 238. If so, there must have been some political circumstance that resulted in such a lengthy gap between his consulship and the proconsular governorship. Christian Settipani has speculated, due to the combination of both's ''nomina'' and ''cognomina'', that Messalla married Claudia Acilia Priscilliana, daughter of Tiberius Cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
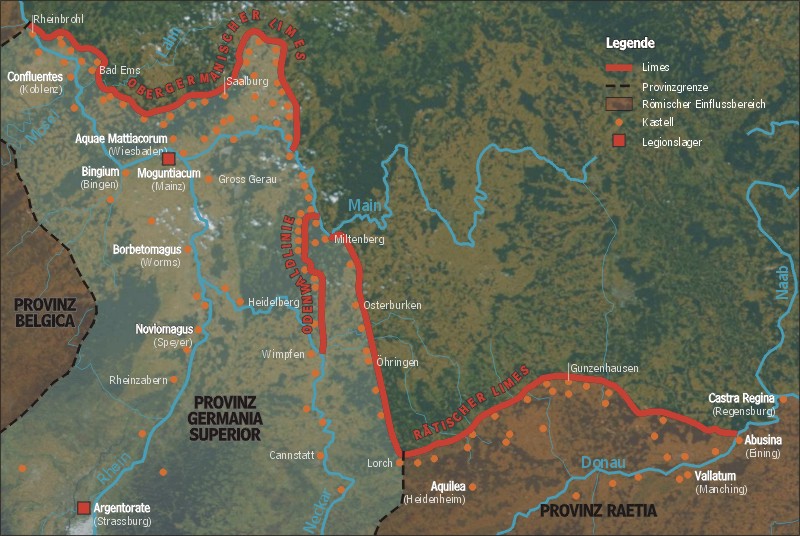
Raetia
Raetia ( ; ; also spelled Rhaetia) was a province of the Roman Empire, named after the Rhaetian people. It bordered on the west with the country of the Helvetii, on the east with Noricum, on the north with Vindelicia, on the south-west with Transalpine Gaul and on the south with Venetia et Histria, a region of Roman Italy. It thus comprised the districts occupied in modern times by eastern and central Switzerland (containing the Upper Rhine and Lake Constance), southern Germany (Bavaria and most of Baden-Württemberg), Vorarlberg and the greater part of Tyrol in Austria, and part of northern Lombardy in Italy. The region of Vindelicia (today eastern Württemberg and western Bavaria) was annexed to the province at a later date than the others. The northern border of Raetia during the reigns of emperors Augustus and Tiberius was the River Danube. Later the Limes Germanicus marked the northern boundary, stretching for 166 km north of the Danube. Raetia linked to Italy ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was ruled by a Roman appointed as governor. For centuries it was the largest administrative unit of the foreign possessions of ancient Rome. With the administrative reform initiated by Diocletian, it became a third level administrative subdivision of the Roman Empire, or rather a subdivision of the imperial dioceses (in turn subdivisions of the imperial prefectures). Terminology The English word ''province'' comes from the Latin word ''provincia''. In early Republican times, the term was used as a common designation for any task or set of responsibilities assigned by the Roman Senate to an individual who held ''imperium'' (right of command), which was often a military command within a specified theatre of operations. In time, the term became t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legatus Augusti Pro Praetore
A ''legatus Augusti pro praetore'' (literally: "envoy of the emperor – acting for the praetor") was the official title of the governor or general of some Imperial provincess of the Roman Empire during the Principate era, normally the larger ones or those where legions were based. Provinces were denoted imperial if their governor was selected by the emperor, in contrast to senatorial provinces, whose governors (called proconsuls) were elected by the Roman Senate. A ''legatus Augusti'' was always a senator of consular or praetorian rank (i.e., who had previously held the office of consul or praetor). However, the position of the governor of Egypt (''praefectus Aegypti'') was unparalleled, for though an '' eques'' (Roman knight) he had legions under his command. Some smaller imperial provinces where no legions were based (e.g. Mauretania, Thrace, Rhaetia, Noricum, and Judaea) were administered by equestrian ''praefecti'' (prefects) later designated ''procuratores'' (procurators) w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germania
Germania ( ; ), also called Magna Germania (English: ''Great Germania''), Germania Libera (English: ''Free Germania''), or Germanic Barbaricum to distinguish it from the Roman province of the same name, was a large historical region in north-central Europe during the Roman era, which was associated by Roman authors with the Germanic peoples. The region stretched roughly from the Middle and Lower Rhine in the west to the Vistula in the east. It also extended as far south as the Upper and Middle Danube and Pannonia, and to the known parts of Scandinavia in the north. Archaeologically, these peoples correspond roughly to the Roman Iron Age of those regions. While apparently dominated by Germanic peoples, Magna Germania was also inhabited by Celts. The Latin name ''Germania'' means "land of the Germani", but the etymology of the name ''Germani'' itself is uncertain. During the Gallic Wars of the 1st century BC, the Roman general Julius Caesar encountered peoples originating from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comes
''Comes'' ( ), plural ''comites'' ( ), was a Roman title or office, and the origin Latin form of the medieval and modern title "count". Before becoming a word for various types of title or office, the word originally meant "companion", either individually or as a member of a collective denominated a "''Comitatus (classical meaning), comitatus''", especially the suite of a magnate, being in some instances sufficiently large and/or formal to justify specific denomination, e.g. a "''cohors amicorum''". "''Comes''" derives from "''com-''" ("with") and "''ire''" ("go"). Ancient Roman religion ''Comes'' was a common epithet or title that was added to the name of a hero or god in order to denote relation with another god. The coinage of Constantine I (emperor), Roman Emperor Constantine I declared him "''comes''" to Sol Invictus ("Unconquered Sun") ''qua'' god. Imperial Roman curial titles and offices styled ''Comites'' Historically more significant, "''comes''" became a secular ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legio XI Claudia
Legio XI Claudia ("Claudius' Eleventh Legion") was a legion of the Imperial Roman army. The legion was levied by Julius Caesar for his campaign against the Nervii. XI ''Claudia'' dates back to the two legions (the other was the XIIth) recruited by Julius Caesar to invade Gallia in 58 BC, and it existed at least until the early 5th century, guarding lower Danube in Durostorum (modern Silistra, Bulgaria). History Founding and Service in the Late Republic Legio XI Claudia, along with Legio XII Fulminata, was a Roman Legion levied by Julius Caesar in 58 BC in Cisalpine Gaul, for his war against the Nervii. They likely were present at the Siege of Alesia. After his campaigns in Gaul, civil war broke out between Julius Caesar and Pompey, both of whom were triumvirs, and in January, 49 BC, Caesar invaded Italy with Legio XI serving in his army. They fought in 48 BC at Dyrrhachium and Pharsalus, but were disbanded in 45 BC and settled in Central Italy around the area of Bovianum Undec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vexillarius
left, A reenactor, equipped as a ''vexillifer'', with a ''vexillum'' standard Vexillarius is a term referring to one of several distinct types of Roman soldier. A vexillarius or vexillifer was one of the ''signiferi'' in a Roman legion. His duty was to carry the vexillum, a military standard displaying the name and emblem of the legion. This standard consisted of a woven fabric banner, hung on a crossbar attached to a pole or lance. It was used by both infantry and cavalry. It could designate a vexillation (Latin: ''vexillatio''), a detachment from a larger unit, though it was most likely also a standard for regular complete or component units (such as legions, cohorts, ''alae''). The term vexillarius may also refer to specially re-enlisted veterans. These soldiers were so named because they served in a company (''vexillatio'') under their own vexillum standard within the legion, separate from the ordinary legionaries in the cohorts of that same legion. They had privileged statu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germania Superior
Germania Superior ("Upper Germania") was an imperial province of the Roman Empire. It comprised an area of today's western Switzerland, the French Jura and Alsace regions, and southwestern Germany. Important cities were Besançon ('' Vesontio''), Strasbourg (''Argentoratum''), Wiesbaden ('' Aquae Mattiacae''), and Germania Superior's capital, Mainz (''Mogontiacum''). It comprised the Middle Rhine, bordering on the ''Limes Germanicus'', and on the Alpine province of Raetia to the south-east. Although it had been occupied militarily since the reign of Augustus, Germania Superior (along with Germania Inferior) was not made into an official province until c. 85 AD. Origin Initial Roman involvement The terms, "Upper Germania" and "Lower Germania" do not appear in the ''Commentarii de Bello Gallico'' of Julius Caesar, yet he writes about reports that the people who lived in those regions were referred to as "Germani" locally, a term used for a tribe that the Romans called the Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |