|
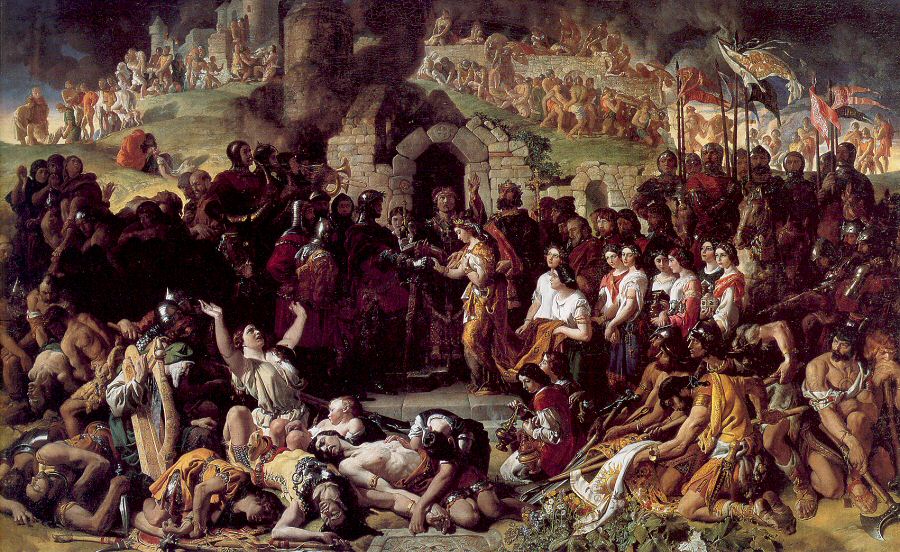
Gaelic Warfare
Gaelic warfare was the type of warfare practiced by the Gaels, Gaelic peoples (the Irish people, Irish, Scottish people, Scottish, and Manx people, Manx), in the pre-modern period. Indigenous Gaelic Warfare Weaponry Irish warfare was for centuries centered on the ''Ceithearn'', or Kern (soldier), Kern in English (and so pronounced in Gaelic), light skirmisher, skirmishing infantry who harried the enemy with missiles before charging. John Dymmok, serving under Elizabeth I's lord-lieutenant of Ireland, described the kerns as: "... A kind of footman, slightly armed with a sword, a target (round shield) of wood, or a bow and sheaf of arrows with barbed heads, or else three darts, which they cast with a wonderful facility and nearness..." For centuries the backbone of any Gaelic Irish army were these lightly armed Infantry in the Middle Ages, foot soldiers. Kern (soldier), Ceithearn were usually armed with a spear (''gae'') or sword (''claideamh''), dirk, long dagger (''scian'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallowglass - Dürer
The Gallowglass (also spelled galloglass, gallowglas or galloglas; from ga, gallóglaigh meaning foreign warriors) were a class of elite mercenary warriors who were principally members of the Norse-Gaels, Norse-Gaelic clans of Ireland between the Scotland in the High Middle Ages, mid 13th century and late 16th century. Originally applied to Scottish people, Scots, who shared a common background and language with the Irish people, Irish, but as they were descendants of 10th-century Norsemen, Norse settlers who had intermarried with the local population in Scottish Highlands, western Scotland, the Irish called them ("foreign Gaels"). An early family of gallowglasses was the Clan Sweeney, MacSweeneys, settled by the O'Donnell dynasty, O'Donnells in north Donegal. These were followed by MacDonnell of Antrim, MacDonnells, MacCabe (surname), MacCabes and several other groups settled by powerful Irish nobles in different areas. The gallowglasses were attractive as heavily armoured, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Archery
Archery, or the use of bow and arrows, was probably developed in Africa by the later Middle Stone Age (approx. 70,000 years ago). It is documented as part of warfare and hunting from the classical period (where it figures in the mythologies of many cultures) until the late medieval period when it was made obsolete by the increased use of firearms. Archers were a widespread if supplemental part of the military in the classical period, and bowmen fought on foot, in chariots or mounted on horses. Archery rose to prominence in Europe in the later medieval period, where victories such as the Battle of Agincourt cemented the longbow in military lore. Archery in both hunting and warfare was eventually replaced by firearms in Europe in the Late Middle Ages and early modern period. Firearms eventually diffused throughout Eurasia via the Gunpowder empires, gradually reducing the importance of archery in warfare throughout the world. Archery is still practiced today, for hunting and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poleaxe
The poleaxe (also pollaxe, pole-axe, pole axe, poleax, polax) is a European polearm that was widely used by medieval infantry. Etymology Most etymological authorities consider the ''poll''- prefix historically unrelated to "pole", instead meaning "head". However, some etymologists, including Eric Partridge, believe that the word is derived from "pole". Types of poleaxe The poleaxe design arose from the need to breach the plate armour of men at arms during the 14th and 15th centuries. Generally, the form consisted of a wooden haft some long, mounted with a steel head. It seems most schools of combat suggested a haft length comparable to the height of the wielder, but in some cases hafts appear to have been created up to in length. The design of the head varied greatly with a variety of interchangeable parts and rivets. Generally, the head bore an axe blade or hammer head upon the damaging 'face', with a spike, hammer, or fluke on the reverse. In addition, there was a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lance
A lance is a spear designed to be used by a mounted warrior or cavalry soldier ( lancer). In ancient and medieval warfare, it evolved into the leading weapon in cavalry charges, and was unsuited for throwing or for repeated thrusting, unlike similar weapons of the javelin and pike family typically used by infantry. Lances were often equipped with a vamplate, a small circular plate to prevent the hand sliding up the shaft upon impact, and beginning in the late 14th century were used in conjunction with a lance rest attached to the breastplate. Though best known as a military and sporting weapon carried by European knights and men-at-arms, the use of lances was widespread throughout Asia, the Middle East, and North Africa wherever suitable mounts were available. Lancers of the medieval period also carried secondary weapons such as swords, battle axes, war hammers, maces and daggers for use in hand-to-hand combat, since the lance was often a one-use-per-engagement weapon; assumi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knight
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of knighthood by a head of state (including the Pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the church or the country, especially in a military capacity. Knighthood finds origins in the Greek ''hippeis'' and '' hoplite'' (ἱππεῖς) and Roman '' eques'' and ''centurion'' of classical antiquity. In the Early Middle Ages in Europe, knighthood was conferred upon mounted warriors. During the High Middle Ages, knighthood was considered a class of lower nobility. By the Late Middle Ages, the rank had become associated with the ideals of chivalry, a code of conduct for the perfect courtly Christian warrior. Often, a knight was a vassal who served as an elite fighter or a bodyguard for a lord, with payment in the form of land holdings. The lords trusted the knights, who were skilled in battle on horseback. Knighthood in the Middle Ages was closely linked with horsemanship (and especially the joust) from its origins in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Men-at-arms
A man-at-arms was a soldier of the High Medieval to Renaissance periods who was typically well-versed in the use of arms and served as a fully-armoured heavy cavalryman. A man-at-arms could be a knight, or other nobleman, a member of a knight's or nobleman's retinue, or a mercenary in a company serving under a captain. Such men could serve for pay or through a feudal obligation. The terms ''knight'' and ''man-at-arms'' are often used interchangeably, but while all knights equipped for war were men-at-arms, not all men-at-arms were knights. Terminology Though in English the term man-at-arms is a fairly straightforward rendering of the French ''homme d'armes'', in the Middle Ages, there were numerous terms for this type of soldier, referring to the type of arms he would be expected to provide: In France, he might be known as a ''lance'' or ''glaive'', while in Germany, ''Spieß'', ''Helm'' or ''Gleve'', and in various places, a ''bascinet''. In Italy, the term '' barbuta'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Normans
The Anglo-Normans ( nrf, Anglo-Normaunds, ang, Engel-Norðmandisca) were the medieval ruling class in England, composed mainly of a combination of ethnic Normans, French, Anglo-Saxons, Flemings and Bretons, following the Norman conquest. A small number of Normans had earlier befriended future Anglo-Saxon king of England, Edward the Confessor, during his exile in his mother's homeland of Normandy in northern France. When he returned to England some of them went with him, and so there were Normans already settled in England prior to the conquest. Edward's successor, Harold Godwinson, was defeated by Duke William the Conqueror of Normandy at the Battle of Hastings, leading to William's accession to the English throne. The victorious Normans formed a ruling class in Britain, distinct from (although inter-marrying with) the native populations. Over time their language evolved from the continental Old Norman to the distinct Anglo-Norman language. Anglo-Normans quickly establishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norman Invasion Of Ireland
The Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland took place during the late 12th century, when Anglo-Normans gradually conquered and acquired large swathes of land from the Irish, over which the kings of England then claimed sovereignty, all allegedly sanctioned by the Papal bull ''Laudabiliter''. At the time, Gaelic Ireland was made up of several kingdoms, with a High King claiming lordship over most of the other kings. The Norman invasion was a watershed in Ireland's history, marking the beginning of more than 800 years of direct English and, later, British, involvement in Ireland. In May 1169, Anglo-Norman mercenaries landed in Ireland at the request of Diarmait mac Murchada (Dermot MacMurragh), the deposed King of Leinster, who sought their help in regaining his kingship. They achieved this within weeks and raided neighbouring kingdoms. This military intervention was sanctioned by King Henry II of England. In return, Diarmait had sworn loyalty to Henry and promised land to the Normans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallowglass
The Gallowglass (also spelled galloglass, gallowglas or galloglas; from ga, gallóglaigh meaning foreign warriors) were a class of elite mercenary warriors who were principally members of the Norse-Gaelic clans of Ireland between the mid 13th century and late 16th century. Originally applied to Scots, who shared a common background and language with the Irish, but as they were descendants of 10th-century Norse settlers who had intermarried with the local population in western Scotland, the Irish called them ("foreign Gaels"). An early family of gallowglasses was the MacSweeneys, settled by the O'Donnells in north Donegal. These were followed by MacDonnells, MacCabes and several other groups settled by powerful Irish nobles in different areas. The gallowglasses were attractive as heavily armoured, trained infantry to be relied upon as a strong defence for holding a position, unlike most Irish foot soldiers, who were less well armoured than the typical Irish noble who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norse–Gaels
The Norse–Gaels ( sga, Gall-Goídil; ga, Gall-Ghaeil; gd, Gall-Ghàidheil, 'foreigner-Gaels') were a people of mixed Gaelic and Norse ancestry and culture. They emerged in the Viking Age, when Vikings who settled in Ireland and in Scotland became Gaelicised and intermarried with Gaels. The Norse–Gaels dominated much of the Irish Sea and Scottish Sea regions from the 9th to 12th centuries. They founded the Kingdom of the Isles (which included the Hebrides and the Isle of Man), the Kingdom of Dublin, the Lordship of Galloway (which is named after them), and briefly (939–944 AD) ruled the Kingdom of York. The most powerful Norse–Gaelic dynasty were the Uí Ímair or House of Ivar. Over time, the Norse–Gaels became ever more Gaelicised and disappeared as a distinct group. However, they left a lasting influence, especially in the Isle of Man and Outer Hebrides, where most placenames are of Norse–Gaelic origin. Several Scottish clans have Norse–Gaelic roots, such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Scandinavian Dublin
:''This article is concerned with the History of Dublin between 795 and 902 CE and follows History of Dublin: Earliest times to 795.'' The First Viking Age in Ireland began in 795, when Vikings began carrying out hit-and-run raids on Gaelic Irish coastal settlements. Over the following decades the raiding parties became bigger and better organized; inland settlements were targeted as well as coastal ones; and the raiders built naval encampments known as longphorts to allow them to remain in Ireland throughout the winter. In the mid 9th century, Viking leader Turgeis or ''Thorgest'' founded a stronghold at Dublin, plundered Leinster and Meath, and raided other parts of Ireland. He was killed by the High King, Máel Sechnaill mac Máele Ruanaid, which was followed by several Irish victories against the Vikings and the seizure of Dublin in 849. Shortly after, a new group of Vikings known as the Dubgaill ("dark foreigners") came to Ireland and clashed with the earlier Viking set ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
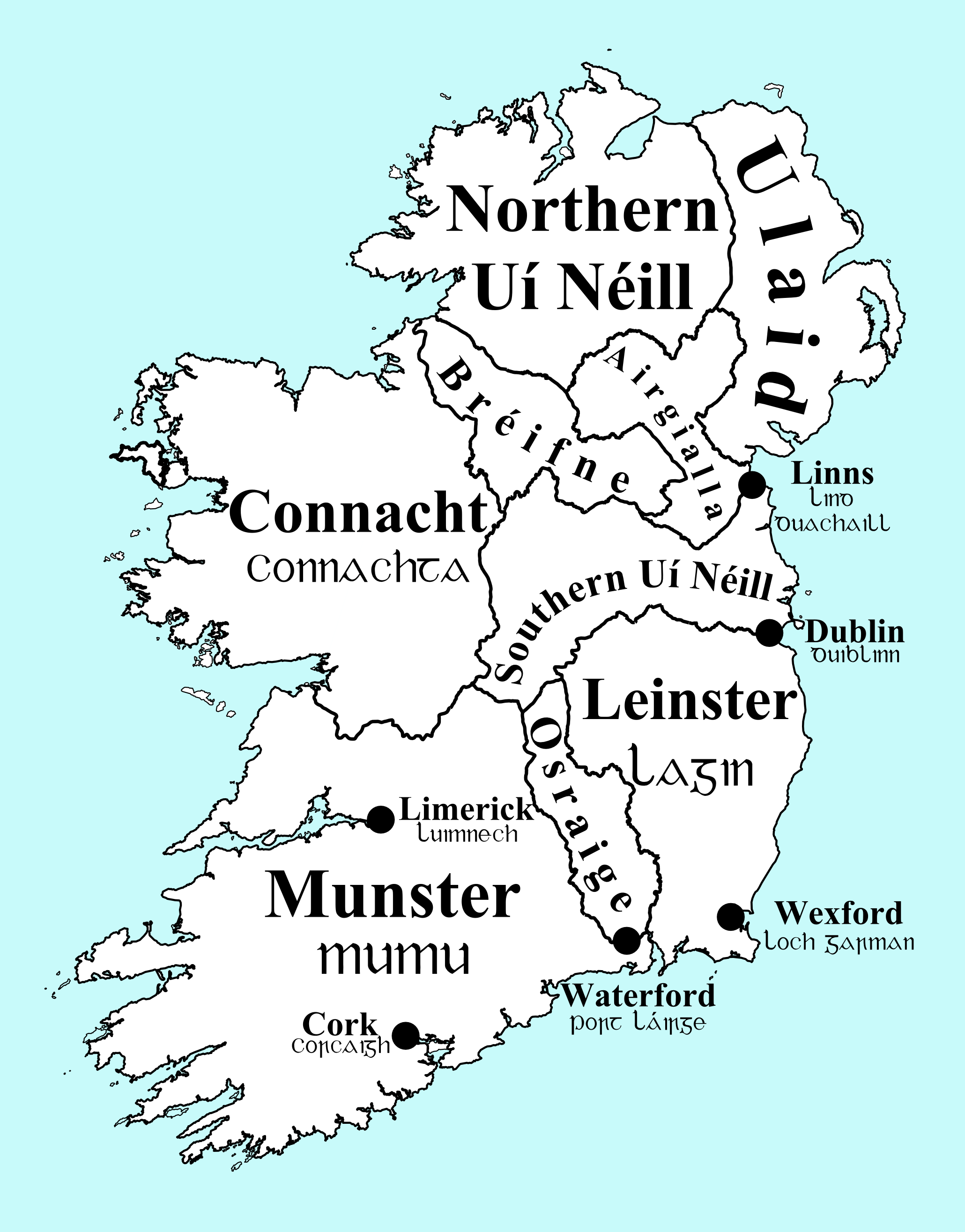
Gaelic Ireland
Gaelic Ireland ( ga, Éire Ghaelach) was the Gaelic political and social order, and associated culture, that existed in Ireland from the late prehistoric era until the early 17th century. It comprised the whole island before Anglo-Normans conquered parts of Ireland in the 1170s. Thereafter, it comprised that part of the country not under foreign dominion at a given time (i.e. the part beyond The Pale). For most of its history, Gaelic Ireland was a "patchwork" hierarchy of territories ruled by a hierarchy of kings or chiefs, who were chosen or elected through tanistry. Warfare between these territories was common. Occasionally, a powerful ruler was acknowledged as High King of Ireland. Society was made up of clans and, like the rest of Europe, was structured hierarchically according to class. Throughout this period, the economy was mainly pastoral and money was generally not used. A Gaelic Irish style of dress, music, dance, sport and art can be identified, with Irish art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |