|
GNSS Positioning Calculation
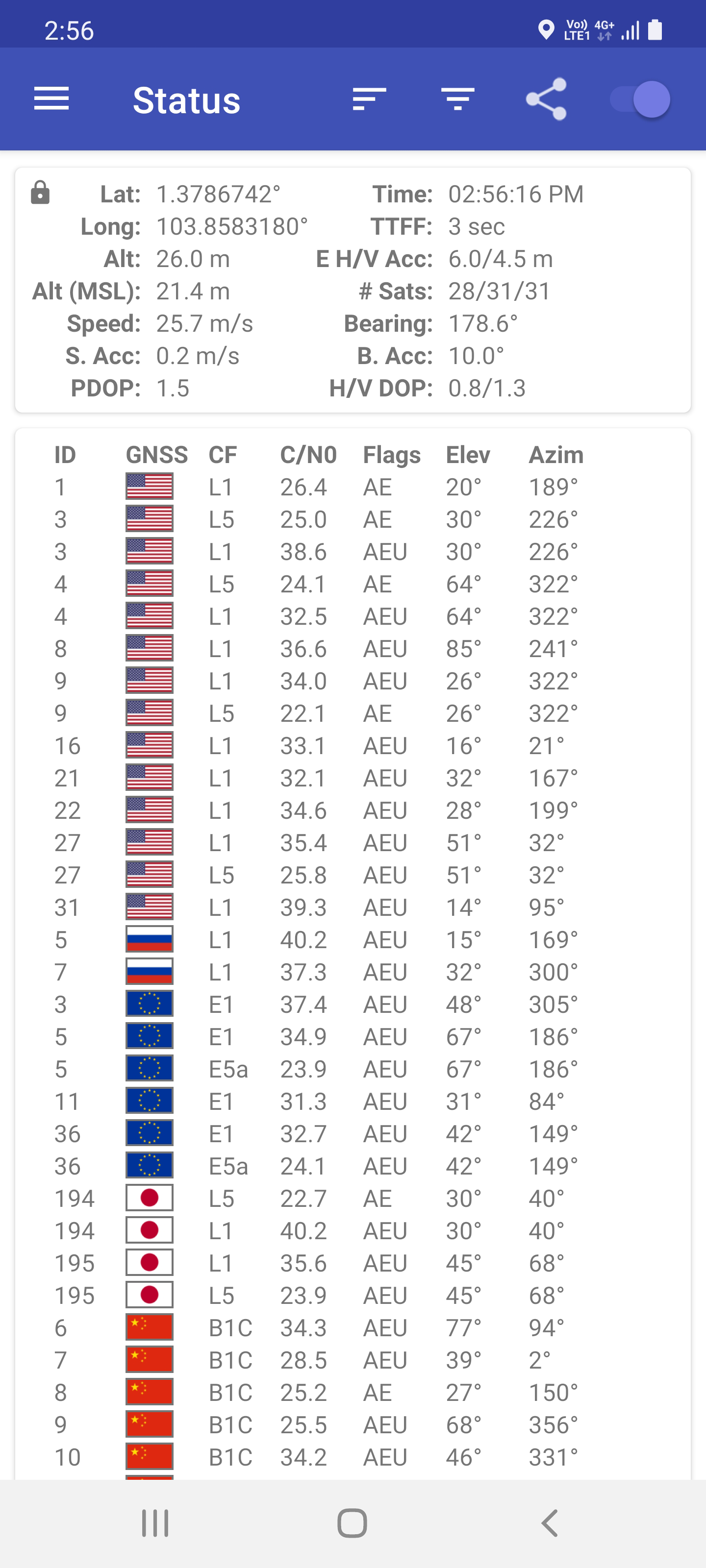
Satellite navigation solution for the receiver's position (geopositioning) involves an algorithm. In essence, a GNSS receiver measures the transmitting time of GNSS signals emitted from four or more GNSS satellites (giving the pseudorange) and these measurements are used to obtain its position (i.e., spatial coordinates) and reception time. Calculation steps # A global-navigation-satellite-system (GNSS) receiver measures the apparent transmitting time, \displaystyle \tilde_i, or "phase", of GNSS signals emitted from four or more GNSS satellites (\displaystyle i \;=\; 1,\, 2,\, 3,\, 4,\, ..,\, n ), simultaneously.Misra, P. and Enge, P., Global Positioning System: Signals, Measurements, and Performance, 2nd, Ganga-Jamuna Press, 2006. # GNSS satellites broadcast the messages of satellites' ephemeris, \displaystyle \boldsymbol_i (t), and intrinsic clock bias (i.e., clock advance), \displaystyle\delta t_ (t) as the functions of ( atomic) standard time, e.g., GPST. # The transmitting ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudorange
The pseudorange (from pseudo- and range) is the ''pseudo'' distance between a satellite and a navigation satellite receiver (see GNSS positioning calculation), for instance Global Positioning System (GPS) receivers. To determine its position, a satellite navigation receiver will determine the ranges to (at least) four satellites as well as their positions at time of transmitting. Knowing the satellites' orbital parameters, these positions can be calculated for any point in time. The pseudoranges of each satellite are obtained by multiplying the speed of light by the time the signal has taken from the satellite to the receiver. As there are accuracy errors in the time measured, the term ''pseudo''-ranges is used rather than ranges for such distances. Pseudorange and time error estimation Typically a quartz oscillator is used in the receiver to do the timing. The accuracy of quartz clocks in general is worse (i.e. more) than one part in a million; thus, if the clock hasn't been co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Navigation
A satellite navigation or satnav system is a system that uses satellites to provide autonomous geo-spatial positioning. It allows satellite navigation devices to determine their location (longitude, latitude, and altitude/elevation) to high precision (within a few centimetres to metres) using time signals transmitted along a line of sight by radio from satellites. The system can be used for providing position, navigation or for tracking the position of something fitted with a receiver (satellite tracking). The signals also allow the electronic receiver to calculate the current local time to a high precision, which allows time synchronisation. These uses are collectively known as Positioning, Navigation and Timing (PNT). One set of critical vulnerabilities in satellite communications are the signals that govern positioning, navigation and timing (PNT). Failure to properly secure these transmissions could not only disrupt satellite networks but wreak havoc on a host of dependent s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inertial Frame
In classical physics and special relativity, an inertial frame of reference (also called inertial reference frame, inertial frame, inertial space, or Galilean reference frame) is a frame of reference that is not undergoing any acceleration. It is a frame in which an isolated physical object — an object with zero net force acting on it — is perceived to move with a constant velocity (it might be a zero velocity) or, equivalently, it is a frame of reference in which Newton's first law of motion holds. All inertial frames are in a state of constant, rectilinear motion with respect to one another; in other words, an accelerometer moving with any of them would detect zero acceleration. It has been observed that celestial objects which are far away from other objects and which are in uniform motion with respect to the cosmic microwave background radiation maintain such uniform motion. Measurements in one inertial frame can be converted to measurements in another by a simple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Least-squares Problem
The method of least squares is a standard approach in regression analysis to approximate the solution of overdetermined systems (sets of equations in which there are more equations than unknowns) by minimizing the sum of the squares of the residuals (a residual being the difference between an observed value and the fitted value provided by a model) made in the results of each individual equation. The most important application is in data fitting. When the problem has substantial uncertainties in the independent variable (the ''x'' variable), then simple regression and least-squares methods have problems; in such cases, the methodology required for fitting errors-in-variables models may be considered instead of that for least squares. Least squares problems fall into two categories: linear or ordinary least squares and nonlinear least squares, depending on whether or not the residuals are linear in all unknowns. The linear least-squares problem occurs in statistical regression ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonlinear
In mathematics and science, a nonlinear system is a system in which the change of the output is not proportional to the change of the input. Nonlinear problems are of interest to engineers, biologists, physicists, mathematicians, and many other scientists because most systems are inherently nonlinear in nature. Nonlinear dynamical systems, describing changes in variables over time, may appear chaotic, unpredictable, or counterintuitive, contrasting with much simpler linear systems. Typically, the behavior of a nonlinear system is described in mathematics by a nonlinear system of equations, which is a set of simultaneous equations in which the unknowns (or the unknown functions in the case of differential equations) appear as variables of a polynomial of degree higher than one or in the argument of a function which is not a polynomial of degree one. In other words, in a nonlinear system of equations, the equation(s) to be solved cannot be written as a linear combination of the un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropospheric Delay
Radio propagation is the behavior of radio waves as they travel, or are propagated, from one point to another in vacuum, or into various parts of the atmosphere. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, like light waves, radio waves are affected by the phenomena of reflection, refraction, diffraction, absorption, polarization, and scattering. Understanding the effects of varying conditions on radio propagation has many practical applications, from choosing frequencies for amateur radio communications, international shortwave broadcasters, to designing reliable mobile telephone systems, to radio navigation, to operation of radar systems. Several different types of propagation are used in practical radio transmission systems. ''Line-of-sight propagation'' means radio waves which travel in a straight line from the transmitting antenna to the receiving antenna. Line of sight transmission is used for medium-distance radio transmission, such as cell phones, cordless phones, walk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionospheric Delay
The error analysis for the Global Positioning System is important for understanding how GPS works, and for knowing what magnitude of error should be expected. The GPS makes corrections for receiver clock errors and other effects but there are still residual errors which are not corrected. GPS receiver position is computed based on data received from the satellites. Errors depend on geometric dilution of precision and the sources listed in the table below. Overview User equivalent range errors (UERE) are shown in the table. There is also a numerical error with an estimated value, \ \sigma_ , of about . The standard deviations, \ \sigma_R, for the coarse/acquisition (C/A) and precise codes are also shown in the table. These standard deviations are computed by taking the square root of the sum of the squares of the individual components (i.e., RSS for root sum squares). To get the standard deviation of receiver position estimate, these range errors must be multiplied by the ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Delay
The error analysis for the Global Positioning System is important for understanding how GPS works, and for knowing what magnitude of error should be expected. The GPS makes corrections for receiver clock errors and other effects but there are still residual errors which are not corrected. GPS receiver position is computed based on data received from the satellites. Errors depend on geometric dilution of precision and the sources listed in the table below. Overview User equivalent range errors (UERE) are shown in the table. There is also a numerical error with an estimated value, \ \sigma_ , of about . The standard deviations, \ \sigma_R, for the coarse/acquisition (C/A) and precise codes are also shown in the table. These standard deviations are computed by taking the square root of the sum of the squares of the individual components (i.e., RSS for root sum squares). To get the standard deviation of receiver position estimate, these range errors must be multiplied by the app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equation
In mathematics, an equation is a formula that expresses the equality of two expressions, by connecting them with the equals sign . The word ''equation'' and its cognates in other languages may have subtly different meanings; for example, in French an ''équation'' is defined as containing one or more variables, while in English, any well-formed formula consisting of two expressions related with an equals sign is an equation. ''Solving'' an equation containing variables consists of determining which values of the variables make the equality true. The variables for which the equation has to be solved are also called unknowns, and the values of the unknowns that satisfy the equality are called solutions of the equation. There are two kinds of equations: identities and conditional equations. An identity is true for all values of the variables. A conditional equation is only true for particular values of the variables. An equation is written as two expressions, connected by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real-time Locating System
Real-time locating systems (RTLS), also known as real-time tracking systems, are used to automatically identify and track the location of objects or people in real time, usually within a building or other contained area. Wireless RTLS tags are attached to objects or worn by people, and in most RTLS, fixed reference points receive wireless signals from tags to determine their location. Examples of real-time locating systems include tracking automobiles through an assembly line, locating pallets of merchandise in a warehouse, or finding medical equipment in a hospital. The physical layer of RTLS technology is often radio frequency (RF) communication. Some systems use optical (usually infrared) or acoustic (usually ultrasound) technology with, or in place of, RF. RTLS tags and fixed reference points can be transmitters, receivers, or both, resulting in numerous possible technology combinations. RTLS are a form of local positioning system and do not usually refer to GPS or to mob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Navigation Satellite System
A satellite navigation or satnav system is a system that uses satellites to provide autonomous geo-spatial positioning. It allows satellite navigation devices to determine their location (longitude, latitude, and altitude/elevation) to high precision (within a few centimetres to metres) using time signals transmitted along a line of sight by radio from satellites. The system can be used for providing position, navigation or for tracking the position of something fitted with a receiver (satellite tracking). The signals also allow the electronic receiver to calculate the current local time to a high precision, which allows time synchronisation. These uses are collectively known as Positioning, Navigation and Timing (PNT). One set of critical vulnerabilities in satellite communications are the signals that govern positioning, navigation and timing (PNT). Failure to properly secure these transmissions could not only disrupt satellite networks but wreak havoc on a host of dependent sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |