|
Gyroelongated Square Bipyramid
In geometry, the gyroelongated square bipyramid, heccaidecadeltahedron, or tetrakis square antiprism is one of the Johnson solids (). As the name suggests, it can be constructed by gyroelongating an octahedron (square bipyramid) by inserting a square antiprism between its congruent halves. It is one of the eight strictly-convex deltahedra. The dual of the gyroelongated square bipyramid is a square truncated trapezohedron with 10 faces: 8 pentagons and 2 square. See also * Gyroelongated bipyramid * Gyroelongated square pyramid In geometry, the gyroelongated square pyramid is one of the Johnson solids (). As its name suggests, it can be constructed by taking a square pyramid and "gyroelongating" it, which in this case involves joining a square antiprism to its base. ... External links * Johnson solids Deltahedra Pyramids and bipyramids {{Polyhedron-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyroelongated Bipyramid
In geometry, a Johnson solid is a strictly convex polyhedron each face of which is a regular polygon. There is no requirement that each face must be the same polygon, or that the same polygons join around each vertex. An example of a Johnson solid is the square-based pyramid with equilateral sides ( ); it has 1 square face and 4 triangular faces. Some authors require that the solid not be uniform (i.e., not Platonic solid, Archimedean solid, uniform prism, or uniform antiprism) before they refer to it as a “Johnson solid”. As in any strictly convex solid, at least three faces meet at every vertex, and the total of their angles is less than 360 degrees. Since a regular polygon has angles at least 60 degrees, it follows that at most five faces meet at any vertex. The pentagonal pyramid () is an example that has a degree-5 vertex. Although there is no obvious restriction that any given regular polygon cannot be a face of a Johnson solid, it turns out that the faces of John ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octahedron
In geometry, an octahedron (plural: octahedra, octahedrons) is a polyhedron with eight faces. The term is most commonly used to refer to the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex. A regular octahedron is the dual polyhedron of a cube. It is a rectified tetrahedron. It is a square bipyramid in any of three orthogonal orientations. It is also a triangular antiprism in any of four orientations. An octahedron is the three-dimensional case of the more general concept of a cross polytope. A regular octahedron is a 3-ball in the Manhattan () metric. Regular octahedron Dimensions If the edge length of a regular octahedron is ''a'', the radius of a circumscribed sphere (one that touches the octahedron at all vertices) is :r_u = \frac a \approx 0.707 \cdot a and the radius of an inscribed sphere (tangent to each of the octahedron's faces) is :r_i = \frac a \approx 0.408\cdot a while the midradius, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johnson Solids
In geometry, a Johnson solid is a strictly convex polyhedron each face of which is a regular polygon. There is no requirement that each face must be the same polygon, or that the same polygons join around each vertex. An example of a Johnson solid is the square-based pyramid with equilateral sides ( ); it has 1 square face and 4 triangular faces. Some authors require that the solid not be uniform (i.e., not Platonic solid, Archimedean solid, uniform prism, or uniform antiprism) before they refer to it as a “Johnson solid”. As in any strictly convex solid, at least three faces meet at every vertex, and the total of their angles is less than 360 degrees. Since a regular polygon has angles at least 60 degrees, it follows that at most five faces meet at any vertex. The pentagonal pyramid () is an example that has a degree-5 vertex. Although there is no obvious restriction that any given regular polygon cannot be a face of a Johnson solid, it turns out that the faces of Johns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyroelongated Square Pyramid
In geometry, the gyroelongated square pyramid is one of the Johnson solids (). As its name suggests, it can be constructed by taking a square pyramid and "gyroelongating" it, which in this case involves joining a square antiprism to its base. Applications The ''Gyroelongated square pyramid'' represents the capped square antiprismatic molecular geometry: : Dual polyhedron The dual of the gyroelongated square pyramid has 9 faces: 4 kites, 1 square and 4 pentagonal. See also * Gyroelongated square bipyramid In geometry, the gyroelongated square bipyramid, heccaidecadeltahedron, or tetrakis square antiprism is one of the Johnson solids (). As the name suggests, it can be constructed by gyroelongating an octahedron (square bipyramid) by inserting a s ... External links * Johnson solids Pyramids and bipyramids {{Polyhedron-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square Truncated Trapezohedron
In geometry, the square truncated trapezohedron is the second in an infinite series of truncated trapezohedra. It has 8 pentagon and 2 square faces. This polyhedron can be constructed by taking a tetragonal trapezohedron and truncating the polar axis vertices. The kite faces of the trapezohedron become pentagons. The vertices exist as 4 squares in four parallel planes, with alternating orientation in the middle creating the pentagons. A ''truncated trapezohedron'' has all valence-3 vertices. This means that the dual polyhedrona gyroelongated square dipyramid has all triangular faces. It represents the dual polyhedron to the Johnson solid, gyroelongated square dipyramid In geometry, the gyroelongated square bipyramid, heccaidecadeltahedron, or tetrakis square antiprism is one of the Johnson solids (). As the name suggests, it can be constructed by gyroelongating an octahedron (square bipyramid) by inserting a ... (), with specific proportions: Polyhedra {{Polyhed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deltahedra
In geometry, a deltahedron (plural ''deltahedra'') is a polyhedron whose faces are all equilateral triangles. The name is taken from the Greek upper case delta (Δ), which has the shape of an equilateral triangle. There are infinitely many deltahedra, all having an even number of faces by the handshaking lemma. Of these only eight are convex, having 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16 and 20 faces. The number of faces, edges, and vertices is listed below for each of the eight convex deltahedra. The eight convex deltahedra There are only eight strictly-convex deltahedra: three are regular polyhedra, and five are Johnson solids. The three regular convex polyhedra are indeed Platonic solids. In the 6-faced deltahedron, some vertices have degree 3 and some degree 4. In the 10-, 12-, 14-, and 16-faced deltahedra, some vertices have degree 4 and some degree 5. These five irregular deltahedra belong to the class of Johnson solids: convex polyhedra with regular polygons for faces. Deltahedra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
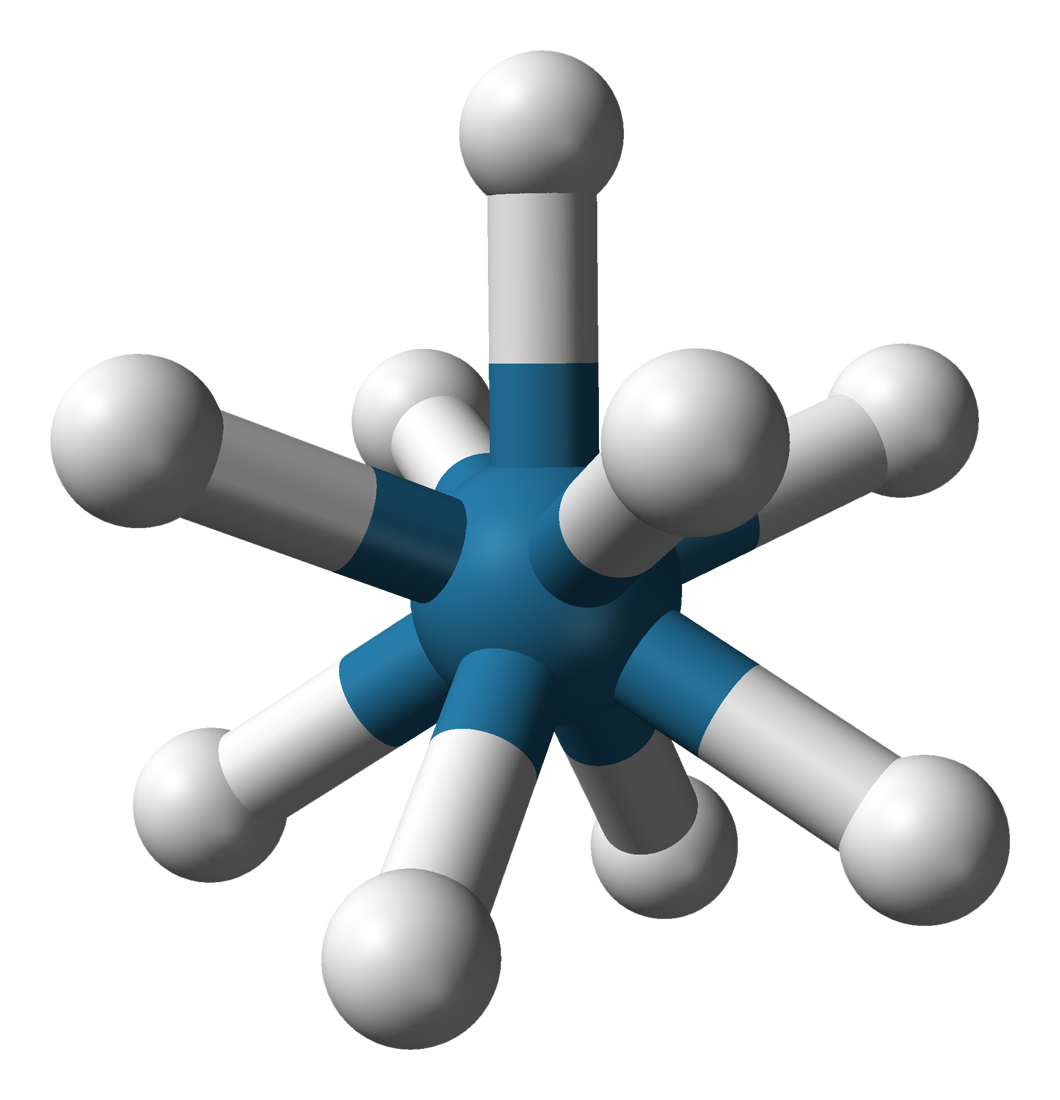
Square Antiprism
In geometry, the square antiprism is the second in an infinite family of antiprisms formed by an even-numbered sequence of triangle sides closed by two polygon caps. It is also known as an ''anticube''. If all its faces are regular, it is a semiregular polyhedron or uniform polyhedron. A nonuniform ''D''4-symmetric variant is the cell of the noble square antiprismatic 72-cell. Points on a sphere When eight points are distributed on the surface of a sphere with the aim of maximising the distance between them in some sense, the resulting shape corresponds to a square antiprism rather than a cube. Specific methods of distributing the points include, for example, the Thomson problem (minimizing the sum of all the reciprocals of distances between points), maximising the distance of each point to the nearest point, or minimising the sum of all reciprocals of squares of distances between points. Molecules with square antiprismatic geometry According to the VSEPR theory of molecul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bipyramid
A (symmetric) -gonal bipyramid or dipyramid is a polyhedron formed by joining an -gonal pyramid and its mirror image base-to-base. An -gonal bipyramid has triangle faces, edges, and vertices. The "-gonal" in the name of a bipyramid does not refer to a face but to the internal polygon base, lying in the mirror plane that connects the two pyramid halves. (If it were a face, then each of its edges would connect three faces instead of two.) "Regular", right bipyramids A ''"regular"'' bipyramid has a ''regular'' polygon base. It is usually implied to be also a ''right'' bipyramid. A ''right'' bipyramid has its two apices ''right'' above and ''right'' below the center or the ''centroid'' of its polygon base. A "regular" right (symmetric) -gonal bipyramid has Schläfli symbol . A right (symmetric) bipyramid has Schläfli symbol , for polygon base . The "regular" right (thus face-transitive) -gonal bipyramid with regular vertices is the dual of the -gonal uniform (thus right) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometry
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is called a ''geometer''. Until the 19th century, geometry was almost exclusively devoted to Euclidean geometry, which includes the notions of point, line, plane, distance, angle, surface, and curve, as fundamental concepts. During the 19th century several discoveries enlarged dramatically the scope of geometry. One of the oldest such discoveries is Carl Friedrich Gauss' ("remarkable theorem") that asserts roughly that the Gaussian curvature of a surface is independent from any specific embedding in a Euclidean space. This implies that surfaces can be studied ''intrinsically'', that is, as stand-alone spaces, and has been expanded into the theory of manifolds and Riemannian geometry. Later in the 19th century, it appeared that geometries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johnson Solid
In geometry, a Johnson solid is a strictly convex polyhedron each face of which is a regular polygon. There is no requirement that isohedral, each face must be the same polygon, or that the same polygons join around each Vertex (geometry), vertex. An example of a Johnson solid is the square-based Pyramid (geometry), pyramid with equilateral sides (square pyramid, ); it has 1 square face and 4 triangular faces. Some authors require that the solid not be uniform polyhedron, uniform (i.e., not Platonic solid, Archimedean solid, prism (geometry), uniform prism, or uniform antiprism) before they refer to it as a “Johnson solid”. As in any strictly convex solid, at least three faces meet at every vertex, and the total of their angles is less than 360 degrees. Since a regular polygon has angles at least 60 degrees, it follows that at most five faces meet at any vertex. The pentagonal pyramid () is an example that has a degree-5 vertex. Although there is no obvious restriction tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
J17 Gyroelongated Square Bipyramid
{{Letter-Number Combination Disambiguation ...
J17 may refer to: Vehicles Locomotives * GSR Class J17, an Irish steam locomotive * LNER Class J17, a British steam locomotive class Ships * , a ''Halcyon''-class minesweeper of the Royal Navy * , a ''Sandhayak''-class survey ship of the Indian Navy Other uses * County Route J17 (California) * Gyroelongated square bipyramid, a Johnson solid (J17) * ''Just Seventeen'', a British magazine * Small nucleolar RNA snR60/Z15/Z230/Z193/J17 * Pneumonia Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deltahedron
In geometry, a deltahedron (plural ''deltahedra'') is a polyhedron whose face (geometry), faces are all equilateral triangles. The name is taken from the Greek language, Greek upper case delta (letter), delta (Δ), which has the shape of an equilateral triangle. There are infinitely many deltahedra, all having an even number of faces by the handshaking lemma. Of these only eight are Convex polyhedron, convex, having 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16 and 20 faces. The number of faces, edges, and vertex (geometry), vertices is listed below for each of the eight convex deltahedra. The eight convex deltahedra There are only eight strictly-convex deltahedra: three are regular polyhedra, and five are Johnson solids. The three regular convex polyhedra are indeed Platonic solids. In the 6-faced deltahedron, some vertices have degree 3 and some degree 4. In the 10-, 12-, 14-, and 16-faced deltahedra, some vertices have degree 4 and some degree 5. These five irregular deltahedra belong to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |