|
Gymnoconia
Gymnoconia is a genus of rust fungi in the family Phragmidiaceae. '' G. nitens'' causes an orange rust of ''Rubus'' species. Gymnoconia interstitialis Importance ''Gymnoconia interstitialis'', otherwise known as "orange rust of raspberries", is a well-known disease of raspberries and blackberries throughout the eastern United States and southern Canada. It can stretch as far south as Florida, or as far west as California, and is also quite common in Europe and Asia (the disease cycles of this rust that are found in northern Europe are considered "long", as opposed to some of the "short" cycles found in the southern United States). Short cycles tend to attack cultivated varieties or blackberries, which has led to an economic setback in their production in the United States. This is not an issue in the European varieties, as the short cycle disease is not found in the Old World. Additionally, black raspberries of New York commonly are affected by orange rust, but the region north ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gymnoconia Potentillae
Gymnoconia is a genus of rust fungi in the family Phragmidiaceae. '' G. nitens'' causes an orange rust of ''Rubus'' species. Gymnoconia interstitialis Importance ''Gymnoconia interstitialis'', otherwise known as "orange rust of raspberries", is a well-known disease of raspberries and blackberries throughout the eastern United States and southern Canada. It can stretch as far south as Florida, or as far west as California, and is also quite common in Europe and Asia (the disease cycles of this rust that are found in northern Europe are considered "long", as opposed to some of the "short" cycles found in the southern United States). Short cycles tend to attack cultivated varieties or blackberries, which has led to an economic setback in their production in the United States. This is not an issue in the European varieties, as the short cycle disease is not found in the Old World. Additionally, black raspberries of New York commonly are affected by orange rust, but the region north ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gymnoconia Wildcat Canyon
Gymnoconia is a genus of rust fungi in the family Phragmidiaceae. '' G. nitens'' causes an orange rust of ''Rubus'' species. Gymnoconia interstitialis Importance ''Gymnoconia interstitialis'', otherwise known as "orange rust of raspberries", is a well-known disease of raspberries and blackberries throughout the eastern United States and southern Canada. It can stretch as far south as Florida, or as far west as California, and is also quite common in Europe and Asia (the disease cycles of this rust that are found in northern Europe are considered "long", as opposed to some of the "short" cycles found in the southern United States). Short cycles tend to attack cultivated varieties or blackberries, which has led to an economic setback in their production in the United States. This is not an issue in the European varieties, as the short cycle disease is not found in the Old World. Additionally, black raspberries of New York commonly are affected by orange rust, but the region north ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
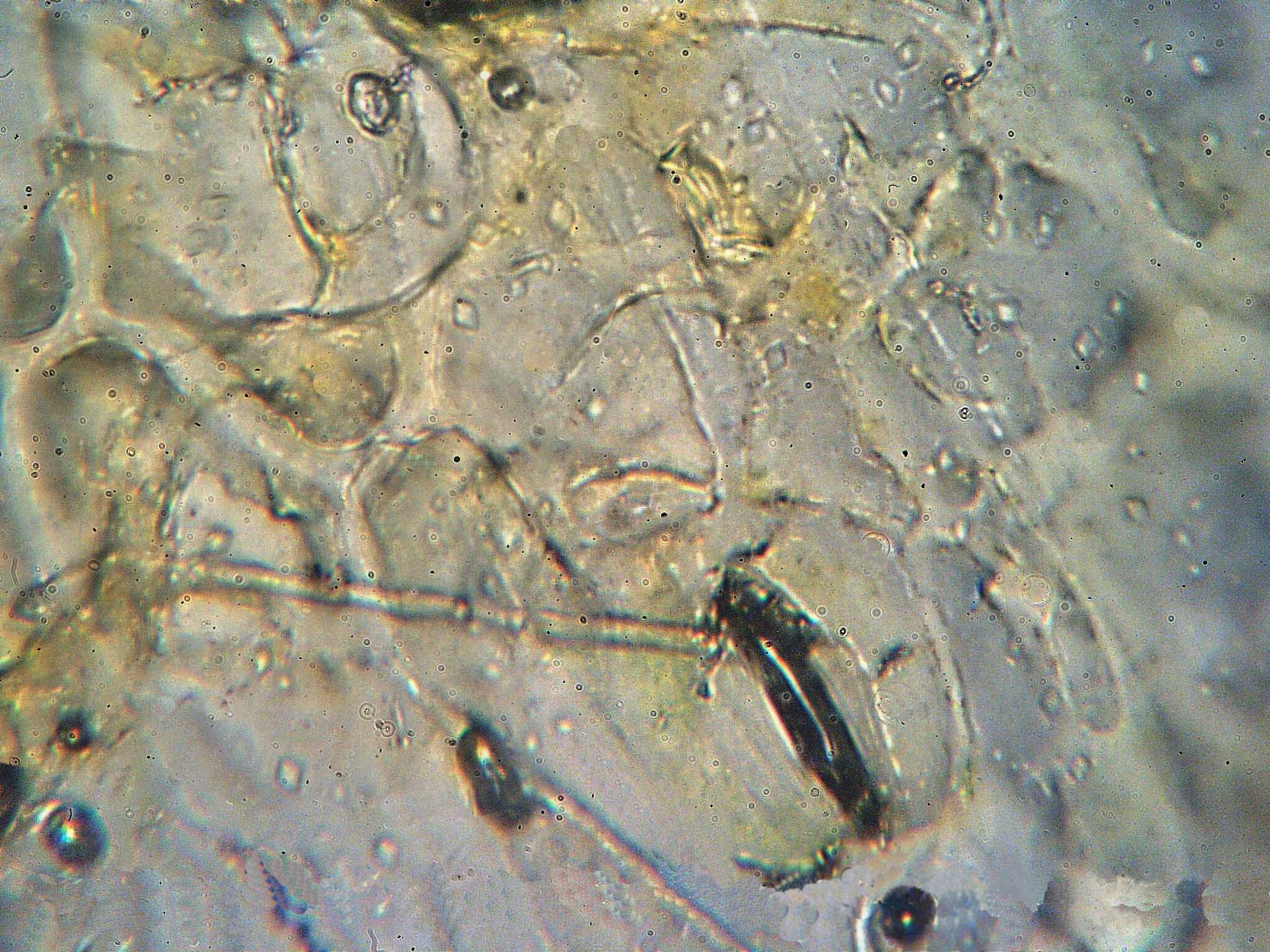
Gymnoconia Interstitialis
''Gymnoconia interstitialis'', otherwise known as orange rust of raspberries, is a well-known disease of raspberries and blackberries throughout the eastern United States and southern Canada. The disease targets the usefulness of the leaves, attacking them until they die and fall off of the plant. The disease returns annually, and this recurrence essentially makes the plants worthless—rarely do affected plants recover. Some strains have such a strong impact on the plants that the cultivation becomes unprofitable. Hesler & Whetzel (1917) claim, "Ten per cent rusty plants are frequently reported. Twenty-five per cent or more are recorded." Range It can stretch as far south as Florida, or as far west as California, and is also quite common in Europe and Asia (the disease cycles of this rust that are found in Europe are considered "long", as opposed to some of the "short" cycles found in the United States.) Black raspberries of New York commonly are affected by this disease, but th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gymnoconia Nitens
''Gymnoconia nitens'' is a species of rust fungus in the Phragmidiaceae family. It is a plant pathogen, and causes orange rust on various berries. The species was originally described in 1822 by mycologist Lewis David de Schweinitz Lewis David de Schweinitz (13 February 1780 – 8 February 1834) was a German-American botanist and mycologist. He is considered by some the "Father of North American Mycology", but also made significant contributions to botany. Education B ... as ''Aecidium luminatum''. References External links USDA ARS Fungal Database Fungal plant pathogens and diseases Pucciniales Fungi described in 1822 {{fungus-plant-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phragmidiaceae
The Phragmidiaceae are a family of rust fungi in the order Pucciniales. The family contains 14 genera and 164 species. Genera *'' Arthuriomyces'' *'' Frommeella'' *''Gerwasia'' *'' Gymnoconia'' *'' Hamaspora'' *'' Joerstadia'' *'' Kuehneola'' *'' Mainsia'' *'' Morispora'' *''Phragmidium ''Phragmidium '' is a genus of rust fungus that typically infects plant species in the family Rosaceae. It is characterised by having stalked teliospores borne on telia each having a row of four or more cells. All species have a caeoma which is ...'' *'' Physonema'' *'' Scutelliformis'' *'' Trachyspora'' *'' Xenodochus'' References External links * Pucciniales Basidiomycota families Taxa named by August Carl Joseph Corda Taxa described in 1837 {{Basidiomycota-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycelium
Mycelium (plural mycelia) is a root-like structure of a fungus consisting of a mass of branching, thread-like hyphae. Fungal colonies composed of mycelium are found in and on soil and many other substrates. A typical single spore germinates into a monokaryotic mycelium, which cannot reproduce sexually; when two compatible monokaryotic mycelia join and form a dikaryotic mycelium, that mycelium may form fruiting bodies such as mushrooms. A mycelium may be minute, forming a colony that is too small to see, or may grow to span thousands of acres as in '' Armillaria''. Through the mycelium, a fungus absorbs nutrients from its environment. It does this in a two-stage process. First, the hyphae secrete enzymes onto or into the food source, which break down biological polymers into smaller units such as monomers. These monomers are then absorbed into the mycelium by facilitated diffusion and active transport. Mycelia are vital in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems for their role ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parenchyma
Parenchyma () is the bulk of functional substance in an animal organ or structure such as a tumour. In zoology it is the name for the tissue that fills the interior of flatworms. Etymology The term ''parenchyma'' is New Latin from the word παρέγχυμα ''parenchyma'' meaning 'visceral flesh', and from παρεγχεῖν ''parenchyma'' meaning 'to pour in' from παρα- ''para-'' 'beside' + ἐν ''en-'' 'in' + χεῖν ''chyma'' 'to pour'. Originally, Erasistratus and other anatomists used it to refer to certain human tissues. Later, it was also applied to plant tissues by Nehemiah Grew. Structure The parenchyma is the ''functional'' parts of an organ, or of a structure such as a tumour in the body. This is in contrast to the stroma, which refers to the ''structural'' tissue of organs or of structures, namely, the connective tissues. Brain The brain parenchyma refers to the functional tissue in the brain that is made up of the two types of brain cell, neurons an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basidiomycete
Basidiomycota () is one of two large divisions that, together with the Ascomycota, constitute the subkingdom Dikarya (often referred to as the "higher fungi") within the kingdom Fungi. Members are known as basidiomycetes. More specifically, Basidiomycota includes these groups: mushrooms, puffballs, stinkhorns, bracket fungi, other polypores, jelly fungi, boletes, chanterelles, earth stars, smuts, bunts, rusts, mirror yeasts, and '' Cryptococcus'', the human pathogenic yeast. Basidiomycota are filamentous fungi composed of hyphae (except for basidiomycota-yeast) and reproduce sexually via the formation of specialized club-shaped end cells called basidia that normally bear external meiospores (usually four). These specialized spores are called basidiospores. However, some Basidiomycota are obligate asexual reproducers. Basidiomycota that reproduce asexually (discussed below) can typically be recognized as members of this division by gross similarity to others, by the for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorosis
In botany, chlorosis is a condition in which leaves produce insufficient chlorophyll. As chlorophyll is responsible for the green color of leaves, chlorotic leaves are pale, yellow, or yellow-white. The affected plant has little or no ability to manufacture carbohydrates through photosynthesis and may die unless the cause of its chlorophyll insufficiency is treated and this may lead to a plant diseases called rusts, although some chlorotic plants, such as the albino '' Arabidopsis thaliana'' mutant ''ppi2'', are viable if supplied with exogenous sucrose. The word ''chlorosis'' is derived from the Greek ''khloros'' meaning "greenish-yellow", "pale green", "pale", "pallid", or "fresh". In viticulture, the most common symptom of poor nutrition in grapevines is the yellowing of grape leaves caused by chlorosis and the subsequent loss of chlorophyll. This is often seen in vineyard soils that are high in limestone such as the Italian wine region of Barolo in the Piedmont, the Span ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubus
''Rubus'' is a large and diverse genus of flowering plants in the rose family, Rosaceae, subfamily Rosoideae, with over 1,350 species. Raspberries, blackberries, and dewberries are common, widely distributed members of the genus. Most of these plants have woody stems with prickles like roses; spines, bristles, and gland-tipped hairs are also common in the genus. The ''Rubus'' fruit, sometimes called a bramble fruit, is an aggregate of drupelets. The term "cane fruit" or "cane berry" applies to any ''Rubus'' species or hybrid which is commonly grown with supports such as wires or canes, including raspberries, blackberries, and hybrids such as loganberry, boysenberry, marionberry and tayberry. The stems of such plants are also referred to as canes. Description Most species in the genus are hermaphrodites, '' Rubus chamaemorus'' being an exception. ''Rubus'' species have a basic chromosome number of seven. Polyploidy from the diploid (14 chromosomes) to the tetrade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rust (fungus)
Rusts are plant diseases caused by pathogen In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a ger ...ic fungus, fungi of the order Pucciniales (previously known as Uredinales). An estimated 168 rust genera and approximately 7,000 species, more than half of which belong to the genus ''Puccinia'', are currently accepted. Rust fungi are highly specialized plant pathogens with several unique features. Taken as a group, rust fungi are diverse and affect many kinds of plants. However, each species has a very narrow range of hosts and cannot be transmitted to non-host plants. In addition, most rust fungi cannot be grown easily in pure culture. A single species of rust fungi may be able to infect two different plant hosts in different stages of its life cycle, and may produce up to five Morpholog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. '' Panthera leo'' (lion) and '' Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. phylogenetic analysis should c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |