|
Gwalleuk
Gwalleuk was a Korean Buddhist monk from the kingdom of Baekje who lived during the time of King Wideok. In 602, he travelled to Japan and is known for helping to spread the teachings of Taoism and Buddhism to Japan. In particular, he brought over ''fangshu'' texts related to the likes of geomancy and ''onmyōdō'' (yinyang-based sorcery and divination), as well as a calendar, according to the Nihon Shoki. In 624, he was made a high priest (僧正 ''sōjō''), possibly of Gangō-ji, for the rest of his life. He is mentioned several times in Buddhist records in Japan, where he was known as ''Kanroku'', the Japanese reading of his name.Kōjien entry for ''Kanroku'' (觀勒) Asteroid The asteroid 4963 Kanroku discovered on 18 February 1977 by Hiroki Kosai and Kiichirō Furukawa of the Tokyo Astronomical Observatory was named after him. References See also *List of Baekje-related topics *Korean Buddhism *Three Kingdoms of Korea Samhan or the Three Kingdoms of Korea () r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Baekje-related Topics
Articles about Baekje-related people, places, things, and concepts include: A * Abe no Hirafu * Ajikgi * Asin of Baekje B * Baekje * Battle of Baekgang * Battle of Hwangsanbeol * Beop of Baekje * Biryu of Baekje * Biyu of Baekje * Gwisil Boksin * Bunseo of Baekje * Buyeo County * Buyeo National Museum * Buyeo Pung * Buyeo Yung C * Chaekgye of Baekje * Chiljido * Chogo of Baekje D * Daifang commandery * Daru of Baekje * Dongseong of Baekje G * Gaero of Baekje * Gaeru of Baekje * Geunchogo of Baekje * Geungusu of Baekje * Gilt-bronze Incense Burner of Baekje * Giru of Baekje * Goi of Baekje * Guisin of Baekje * Gusu of Baekje * Gwalleuk, Buddhist monk who traveled to Japan. * Gye of Baekje * Gyeon Hwon H * Hye of Baekje J * Jeonji of Baekje * Jinsa of Baekje M * Mahan confederacy * Mu of Baekje * Munju of Baekje * Muryeong of Baekje N * Neungsan-ri O * Onjo of Baekje P * Pungnap Toseong S * Saban of Baekje * Sabi * Samgeun of Baekje * Seong of Baekje U * U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onmyōdō
is a system of natural science, astronomy, almanac, divination and Magic (supernatural), magic that developed independently in Japan based on the Chinese philosophies of yin and yang and Wuxing (Chinese philosophy), wuxing (five elements). The philosophy of yin and yang and wu xing was introduced to Japan at the beginning of the 6th century, and, influenced by Taoism, Buddhism, and Confucianism, evolved into the earliest system of ''Onmyōdō'' around the late 7th century. In 701, the Taiho Code established the departments and posts of ''onmyōji'' who practiced ''Onmyōdō'' in the Imperial Court, and ''Onmyōdō'' was institutionalized. From around the 9th century during the Heian period, ''Onmyōdō'' interacted with Shinto and in Japan, and developed into a system unique to Japan. Abe no Seimei, who was active during Heian period, is the most famous ''onmyōji'' (''Onmyōdō'' practitioner) in Japanese history and has appeared in various Japanese literature in later years. '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia via the Silk Road. It is the world's fourth-largest religion, with over 520 million followers (Buddhists) who comprise seven percent of the global population. The Buddha taught the Middle Way, a path of spiritual development that avoids both extreme asceticism and hedonism. It aims at liberation from clinging and craving to things which are impermanent (), incapable of satisfying ('), and without a lasting essence (), ending the cycle of death and rebirth (). A summary of this path is expressed in the Noble Eightfold Path, a training of the mind with observance of Buddhist ethics and meditation. Other widely observed practices include: monasticism; " taking refuge" in the Buddha, the , and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korean Buddhist Missionaries
Korean may refer to: People and culture * Koreans, ethnic group originating in the Korean Peninsula * Korean cuisine * Korean culture * Korean language **Korean alphabet, known as Hangul or Chosŏn'gŭl **Korean dialects and the Jeju language **See also: North–South differences in the Korean language Places * Korean Peninsula, a peninsula in East Asia * Korea, a region of East Asia * North Korea, the Democratic People's Republic of Korea * South Korea, the Republic of Korea Other uses *Korean Air, flag carrier and the largest airline of South Korea See also *Korean War, 1950–1953 war between North Korea and South Korea *Names of Korea, various country names used in international contexts *History of Korea, the history of Korea up to 1945 * {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asuka Period Buddhist Clergy
Asuka may refer to: People * Asuka (name), a list of people * Asuka (wrestler), professional wrestler * Asuka (wrestler, born 1998), professional wrestler also known as Veny outside of Japan Places In Japan * , an area in Yamato Province (now Nara Prefecture) in Japan, where imperial palaces and centers of government were built in the 6th and 7th centuries * , a village in Nara Prefecture in Japan, in the same area as ancient ** , also known as , a Buddhist temple in Asuka, Nara * , a park in Kita, Tokyo, Japan Outside of Japan * Asuka, Estonia, a village in Saaremaa Parish, Saare County, Estonia * Asuka Station (Antarctica) Ships * (now MS ''Amadea''), a cruise ship operated by Nippon Yusen Kaisha from 1991 to 2006 * , a cruise ship operated by Nippon Yusen Kaisha from 2006 onwards * , an experimental ship of the Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force commissioned in 1995 Popular media * ''Asuka'' (album), by the traditional/pop-rock group Rin' * ''Asuka'' (magazine), a Japane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
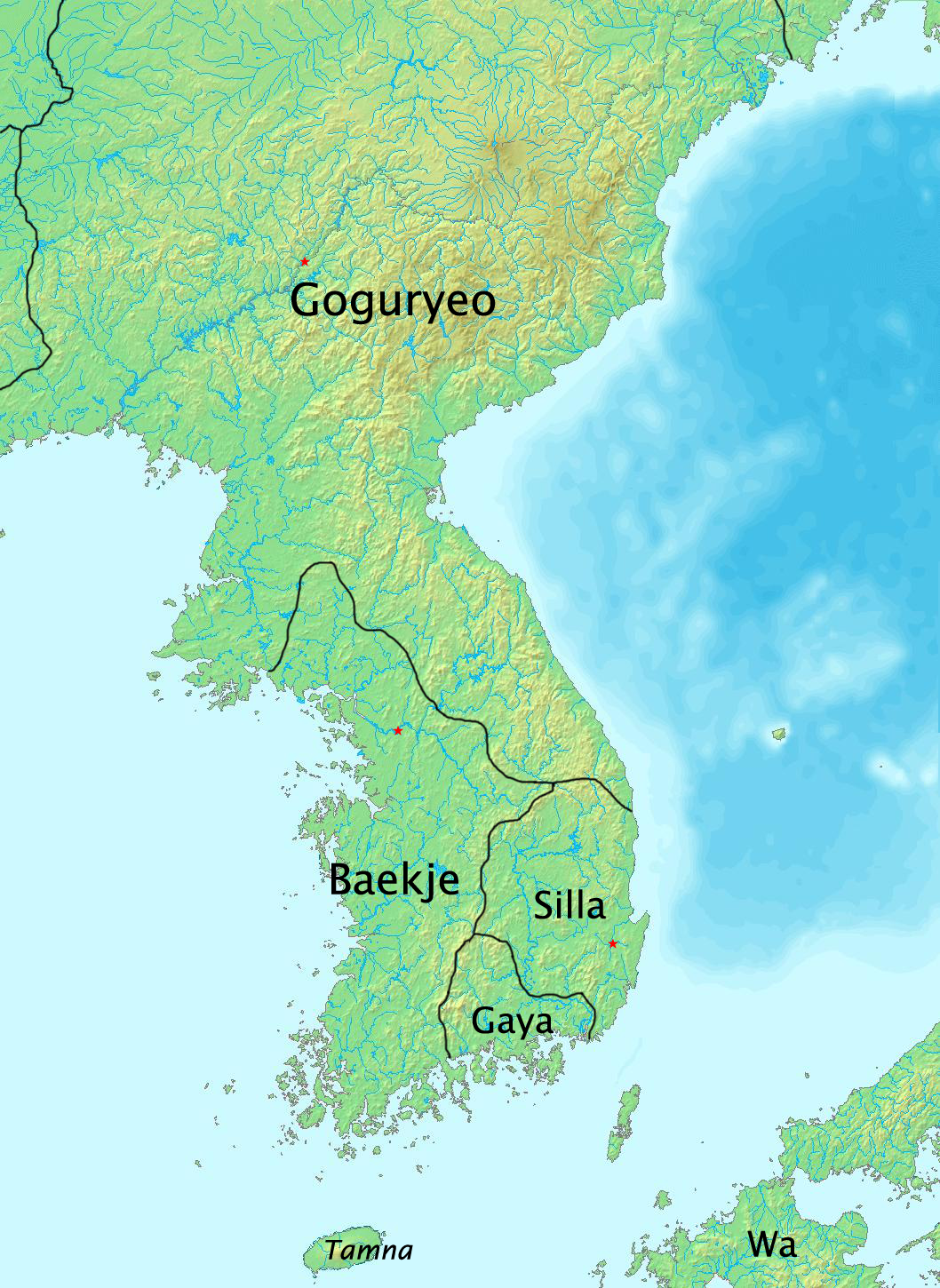
Baekje Buddhist Monks
Baekje or Paekche (, ) was a Korean kingdom located in southwestern Korea from 18 BC to 660 AD. It was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, together with Goguryeo and Silla. Baekje was founded by Onjo of Baekje, Onjo, the third son of Goguryeo's founder King Dongmyeong of Goguryeo, Jumong and So Seo-no, at Wiryeseong (present-day southern Seoul). Baekje, like Goguryeo, claimed to succeed Buyeo kingdom, Buyeo, a state established in present-day Manchuria around the time of Gojoseon's fall. Baekje alternately battled and allied with Goguryeo and Silla as the three kingdoms expanded control over the peninsula. At its peak in the 4th century, Baekje controlled most of the western Korean peninsula, as far north as Pyongyang, and may have even held territories in Timeline of Chinese history#3rd century, China, such as in Liaoxi Commandery, Liaoxi, though this view is controversial. It became a significant regional sea power, with political and trade relations with China and Japan. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th-century Births
The 6th century is the period from 501 through 600 in line with the Julian calendar. In the West, the century marks the end of Classical Antiquity and the beginning of the Middle Ages. The collapse of the Western Roman Empire late in the previous century left Europe fractured into many small Germanic kingdoms competing fiercely for land and wealth. From the upheaval the Franks rose to prominence and carved out a sizeable domain covering much of modern France and Germany. Meanwhile, the surviving Eastern Roman Empire began to expand under Emperor Justinian, who recaptured North Africa from the Vandals and attempted fully to recover Italy as well, in the hope of reinstating Roman control over the lands once ruled by the Western Roman Empire. In its second Golden Age, the Sassanid Empire reached the peak of its power under Khosrau I in the 6th century.Roberts, J: "History of the World.". Penguin, 1994. The classical Gupta Empire of Northern India, largely overrun by the Huna, ended i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baekje People
Baekje or Paekche (, ) was a Korean kingdom located in southwestern Korea from 18 BC to 660 AD. It was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, together with Goguryeo and Silla. Baekje was founded by Onjo, the third son of Goguryeo's founder Jumong and So Seo-no, at Wiryeseong (present-day southern Seoul). Baekje, like Goguryeo, claimed to succeed Buyeo, a state established in present-day Manchuria around the time of Gojoseon's fall. Baekje alternately battled and allied with Goguryeo and Silla as the three kingdoms expanded control over the peninsula. At its peak in the 4th century, Baekje controlled most of the western Korean peninsula, as far north as Pyongyang, and may have even held territories in China, such as in Liaoxi, though this view is controversial. It became a significant regional sea power, with political and trade relations with China and Japan. Baekje was a great maritime power; its nautical skill, which made it the Phoenicia of East Asia, was instrumental in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three Kingdoms Of Korea
Samhan or the Three Kingdoms of Korea () refers to the three kingdoms of Goguryeo (고구려, 高句麗), Baekje (백제, 百濟), and Silla (신라, 新羅). Goguryeo was later known as Goryeo (고려, 高麗), from which the modern name ''Korea'' is derived. The Three Kingdoms period is defined as being from 57 BC to 668 AD (but there existed Gaya confederacy in the southern region of the Korean Peninsula and relatively large states like Okjeo, Buyeo, and Dongye in its northern part and Manchuria of modern China). The "Korean Three Kingdoms" (Goguryeo, Baekje and Silla) contributed to what would become Korea; and the Goguryeo, Baekje and Silla peoples became what we know as the Korean people. The Book of Sui (Volume 81) recorded: "The customs, laws and clothes of Goguryeo, Baekje and Silla are generally identical." The three kingdoms occupied the entire peninsula of Korea and roughly half of Manchuria, located mostly in present-day China, along with smaller parts from present- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korean Buddhism
Korean Buddhism is distinguished from other forms of Buddhism by its attempt to resolve what its early practitioners saw as inconsistencies within the Mahayana Buddhist traditions that they received from foreign countries. To address this, they developed a new holistic approach to Buddhism that became a distinct form, an approach characteristic of virtually all major Korean thinkers. The resulting variation is called ''Tongbulgyo'' ("interpenetrated Buddhism"), a form that sought to harmonize previously arising disputes among scholars (a principle called ''hwajaeng'' 和諍). Centuries after Buddhism originated in India, the Mahayana tradition arrived in China through the Silk Road in the 1st century CE via Tibet; it then entered the Korean peninsula in the 3rd century during the Three Kingdoms Period, from where it was transmitted to Japan. In Korea, it was adopted as the state religion of 3 constituent polities of the Three Kingdoms Period, first by the Goguryeo (also know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiichirō Furukawa
『新訂 現代日本人名録94 4. ひろ - わ』、247頁 was a Japanese astronomer and discoverer of minor planets at the Tokyo Astronomical Observatory. Furukawa was also associated with Nagoya University Department of Astrophysics. Awards and honors Asteroid 3425 Hurukawa, a member of the Eos family and discovered by Karl Reinmuth at Heidelberg in 1929, was named in his honor. The official naming citation was published by the Minor Planet Center (MPC) on 16 December 1986 (). Discoveries Kiichirō Furukawa was a prolific discoverer of asteroids, credited by the MPC under the name K. Hurukawa with a total of 92 co-discovered numbered minor planets, all of them in collaboration with astronomer Hiroki Kosai is a Japanese astronomer with the Kiso Observatory. He is best known for helping to popularize astronomy in Japan and for his observations of comets and asteroids, most notably with his co-discovery the comet 1976 XVI. He is credited by the M .... List of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |