|
Guy De Pourtalès
Guy de Pourtalès (4 August 1881 Berlin – 12 June 1941 Lausanne) was a Swiss author. Early life and education He was the son of Hermann de Pourtalès, Herman Alexander de Pourtalès (1847–1904) and his first wife, Marguerite "Daisy" Marcet (1857–1888). Guy was born in Berlin, where his father at that time was an officer in the service of the Prussian king Wilhelm I of Germany, Wilhelm I. When he was six years old, the family returned to Switzerland, where they lived first at Malagny near Versoix in the Canton of Geneva and then, after his father's second marriage (with Hélène de Pourtalès, Hélène Barbey) in 1891, at Mies, Switzerland, Mies in the Canton de Vaud. Guy de Pourtalès went to schools in Geneva and in Vevey and then to the Gymnasium (school), gymnasium in Neuchâtel. After his matura in 1899, he studied in Germany. In Karlsruhe, he began to study Chemistry, which he abandoned soon in favor of musical studies, which he continued from 1902 to 1905 at the Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constituent states, Berlin is surrounded by the State of Brandenburg and contiguous with Potsdam, Brandenburg's capital. Berlin's urban area, which has a population of around 4.5 million, is the second most populous urban area in Germany after the Ruhr. The Berlin-Brandenburg capital region has around 6.2 million inhabitants and is Germany's third-largest metropolitan region after the Rhine-Ruhr and Rhine-Main regions. Berlin straddles the banks of the Spree, which flows into the Havel (a tributary of the Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the city's main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel and Dahme, the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee. Due to its l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, fashion, gastronomy, and science. For its leading role in the arts and sciences, as well as its very early system of street lighting, in the 19th century it became known as "the City of Light". Like London, prior to the Second World War, it was also sometimes called the capital of the world. The City of Paris is the centre of the Île-de-France region, or Paris Region, with an estimated population of 12,262,544 in 2019, or about 19% of the population of France, making the region France's primate city. The Paris Region had a GDP of €739 billion ($743 billion) in 2019, which is the highest in Europe. According to the Economist Intelli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measure For Measure
''Measure for Measure'' is a play by William Shakespeare, believed to have been written in 1603 or 1604 and first performed in 1604, according to available records. It was published in the ''First Folio'' of 1623. The play's plot features its protagonist, Duke Vincentio of Vienna, stepping out from public life to observe the affairs of the city under the governance of his deputy, Angelo. Angelo's harsh and ascetic public image is compared to his abhorrent personal conduct once in office, in which he exploits his power to procure a sexual favour from Isabella, whom he considers enigmatically beautiful. The tension in the play is eventually resolved through Duke Vincentio's intervention, which is considered an early use of the deus ex machina in English literature. ''Measure for Measure'' was printed as a comedy in the First Folio and continues to be classified as one. Though it shares features with other Shakespearean comedies, such as the use of wordplay and irony, and the emp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques Copeau
Jacques Copeau (; 4 February 1879 – 20 October 1949) was a French theatre director, producer, actor, and dramatist. Before he founded the Théâtre du Vieux-Colombier in Paris, he wrote theatre reviews for several Parisian journals, worked at the Georges Petit Gallery where he organized exhibits of artists' works and helped found the ''Nouvelle Revue Française'' in 1909, along with writer friends, such as André Gide and Jean Schlumberger. Twentieth century French theatre is marked by Copeau's outlook. According to Albert Camus, "in the history of the French theatre, there are two periods: before Copeau and after Copeau." Early life and formative years The child of a well-off middle-class family, the Paris-born Copeau was raised in Paris and attended the best schools. At the Lycée Condorcet, he was a talented but nonchalant student whose interest in theatre already consumed him. His first staged play, ''Brouillard du matin'' ("Morning Fog"), was presented on 27 Marc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
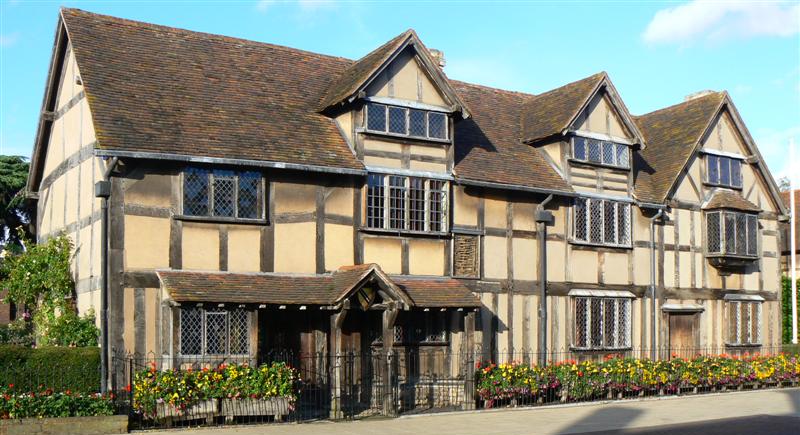
Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 26 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's national poet and the " Bard of Avon" (or simply "the Bard"). His extant works, including collaborations, consist of some 39 plays, 154 sonnets, three long narrative poems, and a few other verses, some of uncertain authorship. His plays have been translated into every major living language and are performed more often than those of any other playwright. He remains arguably the most influential writer in the English language, and his works continue to be studied and reinterpreted. Shakespeare was born and raised in Stratford-upon-Avon, Warwickshire. At the age of 18, he married Anne Hathaway, with whom he had three children: Susanna Hall, Susanna, and twins Hamnet Shakespeare, Hamnet and Judith Quiney, Judith. Sometime between 1585 and 1592, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nouvelle Revue Française
''La Nouvelle Revue Française'' (; "The New French Review") is a literary magazine based in France. In France, it is often referred to as the ''NRF''. History and profile The magazine was founded in 1909 by a group of intellectuals including André Gide, Jacques Copeau, and Jean Schlumberger. It was established 'in opposition to other, more established, cultural institutions, most notably the Académie Française and its associated networks'.:4 In 1911, Gaston Gallimard became editor of the ''Revue'', which led to the founding of the publishing house, Éditions Gallimard. During World War I its publication stopped. The magazine was relaunched in 1919. Established writers such as Paul Bourget and Anatole France contributed to the magazine from its early days. The magazine's influence grew until, during the interwar period, it became the leading literary journal, occupying a unique role in French culture. The first published works by André Malraux and Jean-Paul Sartre were in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanticism
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic, literary, musical, and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century, and in most areas was at its peak in the approximate period from 1800 to 1850. Romanticism was characterized by its emphasis on emotion and individualism, clandestine literature, paganism, idealization of nature, suspicion of science and industrialization, and glorification of the past with a strong preference for the medieval rather than the classical. It was partly a reaction to the Industrial Revolution, the social and political norms of the Age of Enlightenment, and the scientific rationalization of nature. It was embodied most strongly in the visual arts, music, and literature, but had a major impact on historiography, education, chess, social sciences, and the natural sciences. It had a significant and complex effect on politics, with romantic thinkers influencing conservatism, libe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Étoy, Switzerland
Étoy is a municipality of the canton of Vaud, Switzerland, located in the district of Morges. History Etoy is first mentioned in 1145 as ''Stuie''. In 1228 it was mentioned as ''Estue''. Geography Etoy has an area, , of . Of this area, or 67.2% is used for agricultural purposes, while or 6.7% is forested. Of the rest of the land, or 26.5% is settled (buildings or roads), or 0.2% is either rivers or lakes.Swiss Federal Statistical Office-Land Use Statistics 2009 data accessed 25 March 2010 Of the built up area, industrial buildings made up 3.9% of the total area while housing and buildings made up 9.8% and transportation infrastructure made up 10.8%. while parks, green belts and sports fields made up 1.2%. Out of the forested land, all of the fore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as latent tuberculosis. Around 10% of latent infections progress to active disease which, if left untreated, kill about half of those affected. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with blood-containing mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. It was historically referred to as consumption due to the weight loss associated with the disease. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms. Tuberculosis is spread from one person to the next through the air when people who have active TB in their lungs cough, spit, speak, or sneeze. People with Latent TB do not spread the disease. Active infection occurs more often in people with HIV/AIDS and in those who smoke. Diagnosis of active TB is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
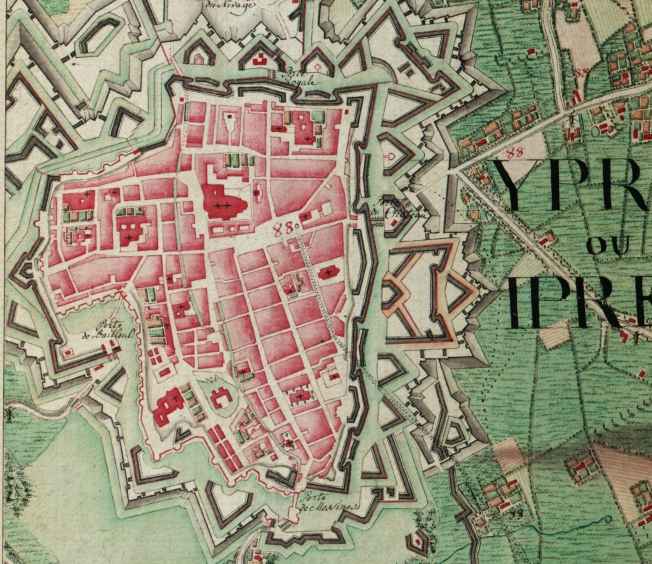
Ypres
Ypres ( , ; nl, Ieper ; vls, Yper; german: Ypern ) is a Belgian city and municipality in the province of West Flanders. Though the Dutch name is the official one, the city's French name is most commonly used in English. The municipality comprises the city of Ypres/Ieper and the villages of Boezinge, Brielen, Dikkebus, Elverdinge, Hollebeke, Sint-Jan, Vlamertinge, Voormezele, Zillebeke, and Zuidschote. Together, they are home to about 34,900 inhabitants. During the First World War, Ypres (or "Wipers" as it was commonly known by the British troops) was the centre of the Battles of Ypres between German and Allied forces. History Origins before First World War Ypres is an ancient town, known to have been raided by the Romans in the first century BC. It is first mentioned by name in 1066 and is probably named after the river Ieperlee on the banks of which it was founded. During the Middle Ages, Ypres was a prosperous Flemish city with a population of 40,000 in 1200 AD, renow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising France, Russia, and Britain) and the Triple Alliance (containing Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy). Tensions in the Balkans came to a head on 28 June 1914, following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edict Of Nantes
The Edict of Nantes () was signed in April 1598 by King Henry IV and granted the Calvinist Protestants of France, also known as Huguenots, substantial rights in the nation, which was in essence completely Catholic. In the edict, Henry aimed primarily to promote civil unity. The edict separated civil from religious unity, treated some Protestants for the first time as more than mere schismatics and heretics and opened a path for secularism and tolerance. In offering a general freedom of conscience to individuals, the edict offered many specific concessions to the Protestants, such as amnesty and the reinstatement of their civil rights, including the right to work in any field, even for the state, and to bring grievances directly to the king. It marked the end of the French Wars of Religion, which had afflicted France during the second half of the 16th century. The Edict of St. Germain, promulgated 36 years earlier by Catherine de Médici, had granted limited tolerance to Hugu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |