|
Guy Richard Bisby
Guy Richard Bisby (1889–1958) was an American Canadian mycologist and botanist in plant pathology. He spent his early career working as a professor at the University of Minnesota and University of Manitoba in plant pathology, and his late career as Senior Assistant Mycologist at the Imperial Mycological Institute in Kew, England. He published around fifty books and papers in mycology that extensively contributed to the taxonomy and nomenclature of fungi. Biography Guy Richard Bisby was born on August 17, 1889, in Brookings, South Dakota. He grew up in South Dakota and earned a Bachelor of Science at South Dakota State College in 1912, and continued working at the college for a year after. He then worked as an assistant at the Brooklyn Botanic Garden in New York from 1913 to 1914, where he gained an interest in plant pathology. He studied at Columbia University in New York from 1914 to 1915. He also did work on potato diseases, working as a consulting pathologist to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guy Richard Bisby
Guy Richard Bisby (1889–1958) was an American Canadian mycologist and botanist in plant pathology. He spent his early career working as a professor at the University of Minnesota and University of Manitoba in plant pathology, and his late career as Senior Assistant Mycologist at the Imperial Mycological Institute in Kew, England. He published around fifty books and papers in mycology that extensively contributed to the taxonomy and nomenclature of fungi. Biography Guy Richard Bisby was born on August 17, 1889, in Brookings, South Dakota. He grew up in South Dakota and earned a Bachelor of Science at South Dakota State College in 1912, and continued working at the college for a year after. He then worked as an assistant at the Brooklyn Botanic Garden in New York from 1913 to 1914, where he gained an interest in plant pathology. He studied at Columbia University in New York from 1914 to 1915. He also did work on potato diseases, working as a consulting pathologist to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presque Isle, Maine
Presque Isle is the commercial center and largest city in Aroostook County, Maine, United States. The population was 8,797 at the 2020 Census. The city is home to the University of Maine at Presque Isle, Northern Maine Community College, Husson University Presque Isle, Northern Maine Fairgrounds, The Aroostook Centre Mall, and the Presque Isle International Airport. Presque Isle is the headquarters of the Aroostook Band of Micmac, a federally recognized tribe. History The first European settlers were British Loyalists who reached the area in 1819 hoping to obtain land for lumber. Border disputes between the United States and the United Kingdom over the area, however, made it impossible for pioneers to gain title to the land. In response, the government of the neighboring British colony of New Brunswick (now a Canadian province) gave out patents for pioneers to live on the land but not claim ownership or sell it. By 1825, surveyors traveling along the Aroostook River noted tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian National Mycological Herbarium
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their being ''Canadian''. Canada is a multilingual and multicultural society home to people of groups of many different ethnic, religious, and national origins, with the majority of the population made up of Old World immigrants and their descendants. Following the initial period of French and then the much larger British colonization, different waves (or peaks) of immigration and settlement of non-indigenous peoples took place over the course of nearly two centuries and continue today. Elements of Indigenous, French, British, and more recent immigrant customs, languages, and religions have combined to form the culture of Canada, and thus a Canadian identity. Canada has also been strongly influenced by its linguistic, geographic, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
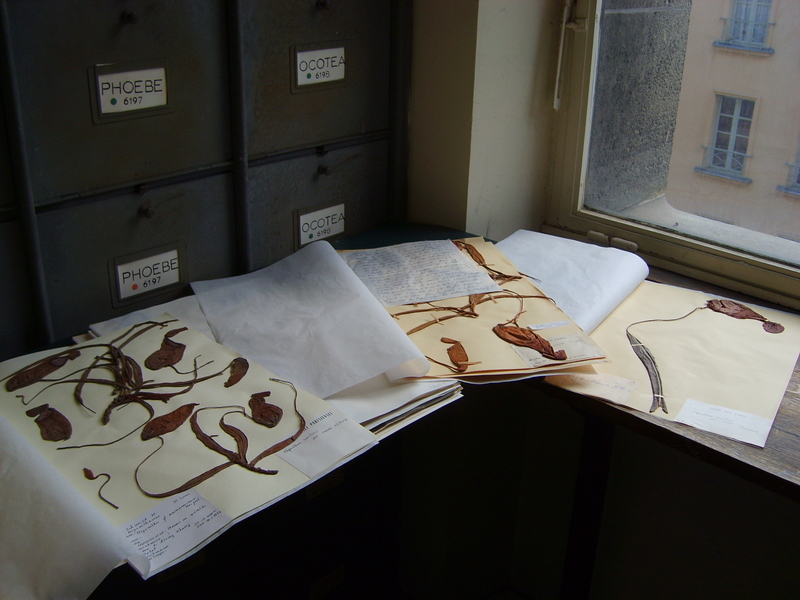
Herbarium
A herbarium (plural: herbaria) is a collection of preserved plant specimens and associated data used for scientific study. The specimens may be whole plants or plant parts; these will usually be in dried form mounted on a sheet of paper (called ''exsiccatum'', plur. ''exsiccata'') but, depending upon the material, may also be stored in boxes or kept in alcohol or other preservative. The specimens in a herbarium are often used as reference material in describing plant taxa; some specimens may be types. The same term is often used in mycology to describe an equivalent collection of preserved fungi, otherwise known as a fungarium. A xylarium is a herbarium specialising in specimens of wood. The term hortorium (as in the Liberty Hyde Bailey Hortorium) has occasionally been applied to a herbarium specialising in preserving material of horticultural origin. History The making of herbaria is an ancient phenomenon, at least six centuries old, although the techniques have changed l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edwin John Butler
Sir Edwin John Butler (13 August 1874 – 4 April 1943) was an Irish mycologist and plant pathologist. He became the Imperial Mycologist in India and later the first director of the Imperial Bureau of Mycology in England. He was knighted in 1939.''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'' http://www.oxforddnb.com/ During his twenty years in India, he began large scale surveys on fungi and plant pathology and published the landmark book ''Fungi and Disease in Plants: An Introduction to the Diseases of Field and Plantation Crops, especially those of India and the East'' (1918) and has been called the Father of Mycology and Plant Pathology in India. Background and education E.J. Butler was born in Kilkee, County Clare, Ireland the son of Thomas Butler, a resident magistrate. He initially went to school in Gainsborough, Lincolnshire but returned to Ireland in 1887 due to illness and studied under a tutor. A library in Cahersiveen where his father was transferred helped him deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Dearness
John Dearness (13 May 1852 – 6 December 1954) was a Canadian educator, botanist, and mycologist. Largely self taught he conducted scientific studies in plant pathology leading to B.T. Dickson of the McGill University called him the "Rostrup" of Canada, comparing him with the Danish plant pathologist Emil Rostrup (1831-1907). Dearness was born in Hamilton, Ontario and grew up on a farm near London, Ontario. At a young age he began a wildflower garden. At school he took an interest in natural history and at 19 he became principal of the Lucan village school and three years later principal of the Strathroy public school. In 1874 he became an inspector of public schools in East Middlesex. In 1881 he married Harriet Emma Wilkinson. He served as a professor of biology at Western University from 1888 to 1914. From the 1880s he began collecting and documenting plants and fungi, publishing on the latter with J.B. Ellis. He received a BA in 1902 and an MA in 1903 from the Western University. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Bureau Of Mycology
The International Mycological Institute was a non-profit organisation, based in England, that undertook research and disseminated information on fungi, particularly plant pathogenic species causing crop diseases. It was established as the Imperial Bureau of Mycology at Kew in 1920 and amalgamated with CAB International in 1998. History The Imperial Bureau of Mycology was established in 1920 as a centre for accumulating and disseminating information on plant pathogenic fungi in the British empire and for undertaking systematic research into such fungi. It was initially based in two houses at Kew, but in 1930 moved into a purpose-built building in the grounds of the Royal Botanic Gardens. In the same year, it became part of the Imperial Agricultural Bureaux and was renamed the Imperial Mycological Institute (IMI). IMI provided an identification service for pathogenic fungi from 1921 onwards and in 1922 started publishing abstracts of research literature in the ''Review of Appl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rust (fungus)
Rusts are plant diseases caused by pathogenic fungi of the order Pucciniales (previously known as Uredinales). An estimated 168 rust genera and approximately 7,000 species, more than half of which belong to the genus ''Puccinia'', are currently accepted. Rust fungi are highly specialized plant pathogens with several unique features. Taken as a group, rust fungi are diverse and affect many kinds of plants. However, each species has a very narrow range of hosts and cannot be transmitted to non-host plants. In addition, most rust fungi cannot be grown easily in pure culture. A single species of rust fungi may be able to infect two different plant hosts in different stages of its life cycle, and may produce up to five morphologically and cytologically distinct spore-producing structures viz., spermogonia, aecia, uredinia, telia, and basidia in successive stages of reproduction. Each spore type is very host specific, and can typically infect only one kind of plant. Rust fungi are o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycology
Mycology is the branch of biology concerned with the study of fungi, including their genetic and biochemical properties, their taxonomy and their use to humans, including as a source for tinder, traditional medicine, food, and entheogens, as well as their dangers, such as toxicity or infection. A biologist specializing in mycology is called a mycologist. Mycology branches into the field of phytopathology, the study of plant diseases, and the two disciplines remain closely related because the vast majority of plant pathogens are fungi. Overview Historically, mycology was a branch of botany because, although fungi are evolutionarily more closely related to animals than to plants, this was not recognized until a few decades ago. Pioneer mycologists included Elias Magnus Fries, Christian Hendrik Persoon, Anton de Bary, Elizabeth Eaton Morse, and Lewis David von Schweinitz. Beatrix Potter, author of ''The Tale of Peter Rabbit'', also made significant contributions to the fiel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winnipeg
Winnipeg () is the capital and largest city of the province of Manitoba in Canada. It is centred on the confluence of the Red and Assiniboine rivers, near the longitudinal centre of North America. , Winnipeg had a city population of 749,607 and a metropolitan population of 834,678, making it the sixth-largest city, and eighth-largest metropolitan area in Canada. The city is named after the nearby Lake Winnipeg; the name comes from the Western Cree words for "muddy water" - “winipīhk”. The region was a trading centre for Indigenous peoples long before the arrival of Europeans; it is the traditional territory of the Anishinabe (Ojibway), Ininew (Cree), Oji-Cree, Dene, and Dakota, and is the birthplace of the Métis Nation. French traders built the first fort on the site in 1738. A settlement was later founded by the Selkirk settlers of the Red River Colony in 1812, the nucleus of which was incorporated as the City of Winnipeg in 1873. Being far inland, the local cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Henry Reginald Buller
Arthur Henry Reginald Buller, (19 August 1874 – 3 July 1944) was a British-Canadian mycologist. He is mainly known as a researcher of fungi and wheat rust. Academic career Born in Moseley, Birmingham, England, he was educated at Queen's College, Taunton. He then studied at Mason College, which later became the University of Birmingham, (B.Sc. in 1896), the University of Leipzig (Ph.D.), and the University of Munich. He was awarded a D.Sc. by the University of Birmingham. He worked briefly for the Naples Zoological Station. From 1901 to 1904, he was a lecturer in Botany at the University of Birmingham. He came to Canada in 1904, founded the Botany Department and was the first Professor of Botany and Geology at the University of Manitoba, and served as Head of the Botany Department until his retirement in 1936. Poetry He also wrote limericks, some of which were published in ''Punch'', including this one on Einstein's special theory of relativity: [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Master Of Arts
A Master of Arts ( la, Magister Artium or ''Artium Magister''; abbreviated MA, M.A., AM, or A.M.) is the holder of a master's degree awarded by universities in many countries. The degree is usually contrasted with that of Master of Science. Those admitted to the degree have typically studied subjects within the scope of the humanities and social sciences, such as history, literature, languages, linguistics, public administration, political science, communication studies, law or diplomacy; however, different universities have different conventions and may also offer the degree for fields typically considered within the natural sciences and mathematics. The degree can be conferred in respect of completing courses and passing examinations, research, or a combination of the two. The degree of Master of Arts traces its origins to the teaching license or of the University of Paris, designed to produce "masters" who were graduate teachers of their subjects. Europe Czech Republic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)