|
Gustilo Open Fracture Classification
The Gustilo open fracture classification system is the most commonly used classification system for open fractures. It was created by Ramón Gustilo and Anderson, and then further expanded by Gustilo, Mendoza, and Williams. This system uses the amount of energy, the extent of soft-tissue injury and the extent of contamination for determination of fracture severity. Progression from grade 1 to 3C implies a higher degree of energy involved in the injury, higher soft tissue and bone damage and higher potential for complications. It is important to recognize that a Gustilo score of grade 3C implies vascular injury as well as bone and connective-tissue damage. Classification Reliability There are many discussions regarding the inter-observer reliability of this classification system. Different studies have shown inter-observer reliability of approximately 60% (ranging from 42% to 92%), representing poor-to-moderate agreement of scale grading between health-care professionals. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Fracture
An open fracture, also called a compound fracture, is a type of bone fracture in orthopedics that is frequently caused by high energy trauma. It is a bone fracture, also known as a broken bone, associated with a break in the skin continuity which can cause complications such as infection, malunion, and nonunion. Gustilo open fracture classification is the most commonly used method to classify open fractures, to guide treatment and to predict clinical outcomes. Advanced trauma life support is the first line of action in dealing with open fractures and to rule out other life-threatening condition in cases of trauma. Cephalosporins are generally the first line of antibiotics. The antibiotics are continued for 24 hours to minimize the risk of infections. Therapeutic irrigation, wound debridement, early wound closure and bone fixation are the main management of open fractures. All these actions aimed to reduce the risk of infections. Classification There are a number of classificat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunshot
A gunshot is a single discharge of a gun, typically a man-portable firearm, producing a visible flash, a powerful and loud shockwave and often chemical gunshot residue. The term can also refer to a ballistic wound caused by such a discharge. Multiple discharges of one or more firearms are referred to as gunfire. The word can connote either the sound of a gun firing, the projectiles that were fired, or both. For example, the statement "gunfire came from the next street" could either mean the sound of discharge, or it could mean the bullets that were discharged. It is better to be a bit more specific while writing however. "The sound of gunfire" or "we came under gunfire" would be more descriptive and prevent confusion. In the latter phrase, in particular, "fire" is used more (i.e. "under fire"), as both words hold the same general meaning within the proper context. Gunfire characteristics There are three primary attributes that characterize gunfire and hence enable the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prognosis
Prognosis (Greek: πρόγνωσις "fore-knowing, foreseeing") is a medical term for predicting the likely or expected development of a disease, including whether the signs and symptoms will improve or worsen (and how quickly) or remain stable over time; expectations of quality of life, such as the ability to carry out daily activities; the potential for complications and associated health issues; and the likelihood of survival (including life expectancy). A prognosis is made on the basis of the normal course of the diagnosed disease, the individual's physical and mental condition, the available treatments, and additional factors. A complete prognosis includes the expected duration, function, and description of the course of the disease, such as progressive decline, intermittent crisis, or sudden, unpredictable crisis. When applied to large statistical populations, prognostic estimates can be very accurate: for example the statement "45% of patients with severe septic shock w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Fixation
Internal fixation is an operation in orthopedics that involves the surgical implementation of implants for the purpose of repairing a bone, a concept that dates to the mid-nineteenth century and was made applicable for routine treatment in the mid-twentieth century. An internal fixator may be made of stainless steel, titanium alloy, or cobalt-chrome alloy. or plastics. Types of internal fixators include: * Plate and screws * Kirschner wires * Intramedullary nails Open reduction Open Reduction Internal Fixation (ORIF) involves the implementation of implants to guide the healing process of a bone, as well as the open reduction, or setting, of the bone. ''Open reduction'' refers to open surgery to set bones, as is necessary for some fractures. ''Internal fixation'' refers to fixation of screws and/or plates, intramedullary rods and other devices to enable or facilitate healing. Rigid fixation prevents micro-motion across lines of fracture to enable healing and prevent infec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis (OM) is an infection of bone. Symptoms may include pain in a specific bone with overlying redness, fever, and weakness. The long bones of the arms and legs are most commonly involved in children e.g. the femur and humerus, while the feet, spine, and hips are most commonly involved in adults. The cause is usually a bacterial infection, but rarely can be a fungal infection. It may occur by spread from the blood or from surrounding tissue. Risks for developing osteomyelitis include diabetes, intravenous drug use, prior removal of the spleen, and trauma to the area. Diagnosis is typically suspected based on symptoms and basic laboratory tests as C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).This is because plain radiographs are unremarkable in the first few days following acute infection. Diagnosis is further confirmed by blood tests, medical imaging, or bone biopsy. Treatment of bacterial osteomyelitis often involves both antimicrobials and sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Therapeutic Irrigation
In medicine, therapeutic irrigation or lavage ( or ) is cleaning or rinsing. Types Specific types include: * Antiseptic lavage * Bronchoalveolar lavage * Gastric lavage * Peritoneal lavage * Arthroscopic lavage * Ductal lavage * Nasal irrigation * Ear lavage *''Pulsed lavage'' is delivering an irrigant (usually normal saline) under direct pressure that is produced by an electrically powered device, and is useful in cleaning e.g. chronic wounds. See also * Vaginal douche * Enema An enema, also known as a clyster, is an injection of fluid into the lower bowel by way of the rectum.Cullingworth, ''A Manual of Nursing, Medical and Surgical'':155 The word enema can also refer to the liquid injected, as well as to a device ... References {{Medical placement and administration procedures Medical treatments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
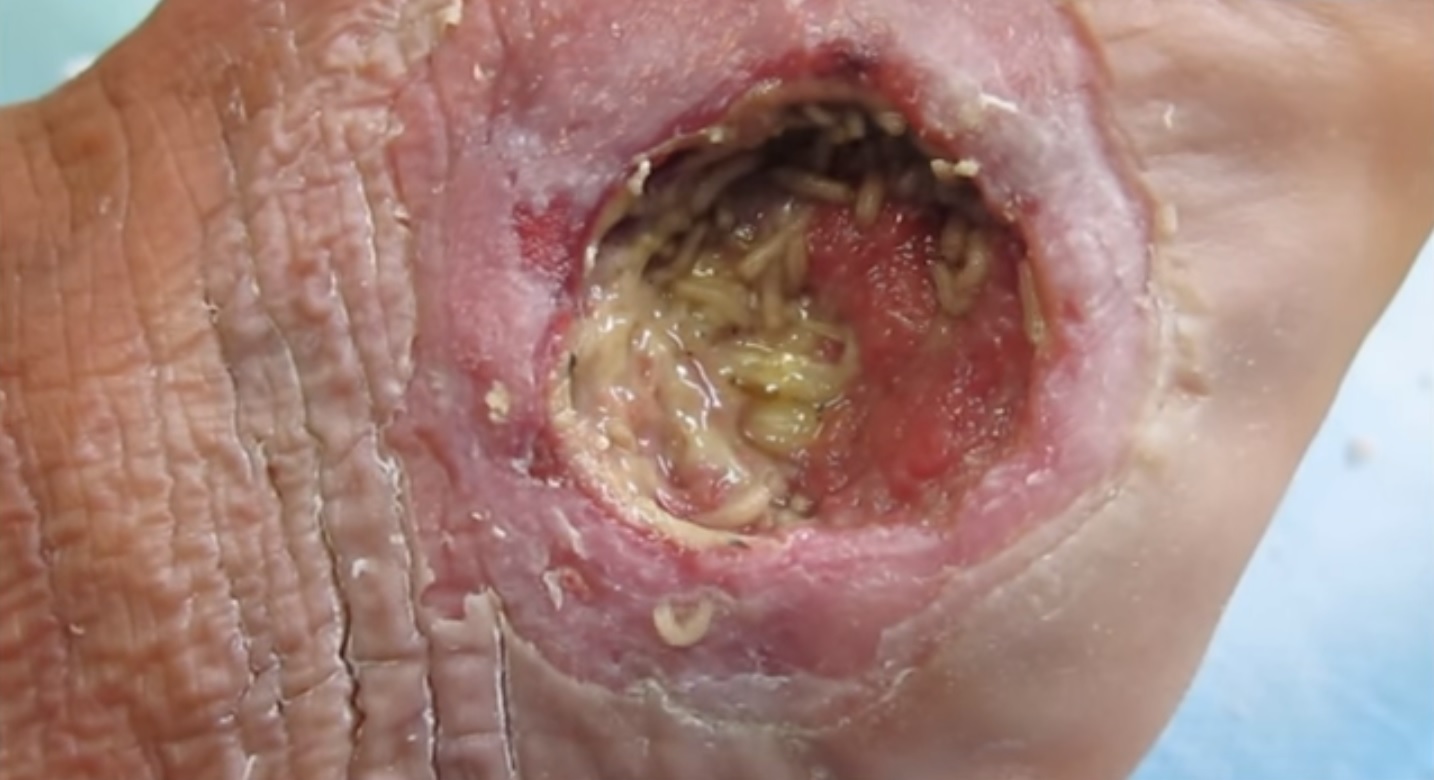
Debridement
Debridement is the medical removal of dead, damaged, or infected tissue to improve the healing potential of the remaining healthy tissue. Removal may be surgical, mechanical, chemical, autolytic (self-digestion), and by maggot therapy. In podiatry, practitioners such as chiropodists, podiatrists and foot health practitioners remove conditions such as calluses and verrucas. Debridement is an important part of the healing process for burns and other serious wounds; it is also used for treating some kinds of snake and spider bites. Sometimes the boundaries of the problem tissue may not be clearly defined. For example, when excising a tumor, there may be micrometastases along the edges of the tumor that are too small to be detected, but if not removed, could cause a relapse. In such circumstances, a surgeon may opt to debride a portion of the surrounding healthy tissue to ensure that the tumor is completely removed. Types There is lack of high quality evidence to compare th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tscherne Classification
The Tscherne classification is a system of categorization of soft tissue injuries An injury is any physiological damage to living tissue caused by immediate physical stress. An injury can occur intentionally or unintentionally and may be caused by blunt trauma, penetrating trauma, burning, toxic exposure, asphyxiation, or o .... Classification Reliability The intraobserver (observations at two different times by the same person) agreement for Tscherne classification is 85%; while for inter-observer agreement is 65%. History This classification system was developed by Harald Tscherne and Hans-Jörg Oestern in 1982 at the Hannover Medical School (Hanover, Germany) to classify both open and closed fractures. This classification system is based on the physiological concept that the higher the kinetic energy imparted on the bone, the higher the kinetic energy imparted on the soft tissue. It also serves as a tool to guide management and to predict clinical outcomes. It also serv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Fractures
A bone fracture (abbreviated FRX or Fx, Fx, or #) is a medical condition in which there is a partial or complete break in the continuity of any bone in the body. In more severe cases, the bone may be broken into several fragments, known as a ''comminuted fracture''. A bone fracture may be the result of high force impact or stress, or a minimal trauma injury as a result of certain medical conditions that weaken the bones, such as osteoporosis, osteopenia, bone cancer, or osteogenesis imperfecta, where the fracture is then properly termed a pathologic fracture. Signs and symptoms Although bone tissue contains no pain receptors, a bone fracture is painful for several reasons: * Breaking in the continuity of the periosteum, with or without similar discontinuity in endosteum, as both contain multiple pain receptors. * Edema and hematoma of nearby soft tissues caused by ruptured bone marrow evokes pressure pain. * Involuntary muscle spasms trying to hold bone fragments in place. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |