|
Gunung Talang
Mount Talang ( id, Gunung Talang) () is an active stratovolcano in West Sumatra, Indonesia. Talang has two crater lakes on its flanks, the largest of which is wide and is called ''Lake Talang''. According to the Smithsonian Institution Global Volcanism Program, Mount Talang has had eight confirmed eruptions between 1833 and 1968. A minor eruption followed in April 2005, over 25,000 inhabitants of the local area being evacuated due to fears of further volcanic eruptions. Geologists say that the eruption in April 2005 is connected to the devastating December 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake. The pitcher plant ''Nepenthes talangensis'' is named after the mountain and is thought to be endemic to its upper slopes.Nerz, J. & A. Wistuba 1994Five new taxa of ''Nepenthes'' (Nepenthaceae) from North and West Sumatra. ''Carnivorous Plant Newsletter'' 23(4): 101–114.Clarke, C.M. 2001. ''Nepenthes of Sumatra and Peninsular Malaysia''. Natural History Publications (Borneo), Kota Kinabalu. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribu
A ribu is a mountain that reaches a topographic prominence of at least . "Ribu" is an Indonesian word meaning "thousand". In Indonesia and Malaysia, three categories of ribus are known according to the absolute height of the peak. The "Sangat Tinggi" (Indonesian for "very high") category is for peaks higher than 3,000 meters, "Tinggi Sedang" (Indonesian for "medium height") for peaks between 2,000 and 3,000 meters, and "Kurang Tinggi" (Indonesian for "less high") for peaks with an elevation of between 1,000 and 2,000 meters. Currently, a total of 270 ribus are known across the Indonesian archipelago, including those in Malaysia and East Timor. Some are popular hikes, such as Mount Rinjani, Mount Semeru, and Mount Kerinci, while others are much more obscure, and some do not even have official names. Some famous Indonesian mountains, such as Mount Bromo and Tangkuban Perahu, are not ribus because they are connected to higher peaks by high passes and therefore do not achieve enough to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnivorous Plant Newsletter
The ''Carnivorous Plant Newsletter'' is the official publication of the International Carnivorous Plant Society (ICPS), the largest such organization in the world. It is headquartered in Walnut Creek, California. History and editorship The newsletter has been published every year since its inception in 1972. It was first published as a stenciled product, with annual subscription priced at $1 for those in the contiguous United States, Mexico and Canada, and $2 for those living elsewhere. The first issue, from April 1972, opened with the following paragraph: In 1972 the newsletter had around 25 subscribers; this number quickly grew to more than 100 by June 29 of that year and reached 600 in July 1976. In 2018, the quarterly print run is 1400 copies. In volume 7 (1978), the newsletter started printing in a 6 by 9 inch format with colour covers, and limited colour reproduction in some articles. The publication was founded by Don Schnell and Joe Mazrimas. Additional early edit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Crater Lakes
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and most are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's plates, such as in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande rift in North America. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has been postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs from the core–mantle boundary, deep in the Earth. This results in hotspot volcanism, of which the Hawaiian hotspot is an example. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of Sumatra
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanoes Of Sumatra
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and most are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's plates, such as in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande rift in North America. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has been postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs from the core–mantle boundary, deep in the Earth. This results in hotspot volcanism, of which the Hawaiian hotspot is an example. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Volcanoes Of Indonesia
Active may refer to: Music * ''Active'' (album), a 1992 album by Casiopea * Active Records, a record label Ships * ''Active'' (ship), several commercial ships by that name * HMS ''Active'', the name of various ships of the British Royal Navy * USCS ''Active'', a US Coast Survey ship in commission from 1852 to 1861 * USCGC ''Active'', the name of various ships of the US Coast Guard * USRC ''Active'', the name of various ships of the US Revenue Cutter Service * USS ''Active'', the name of various ships of the US Navy Computers and electronics * Active Enterprises, a defunct video game developer * Sky Active, the brand name for interactive features on Sky Digital available in the UK and Ireland * Active (software), software used for open publishing by Indymedia; see Independent Media Center Sciences * Thermodynamic activity, measure of an effective concentration of a species in a mixture. * Activation, in chemistry the process whereby something is prepared for a su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subduction Volcanoes
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the heavier plate dives beneath the second plate and sinks into the mantle. A region where this process occurs is known as a subduction zone, and its surface expression is known as an arc-trench complex. The process of subduction has created most of the Earth's continental crust. Rates of subduction are typically measured in centimeters per year, with the average rate of convergence being approximately two to eight centimeters per year along most plate boundaries. Subduction is possible because the cold oceanic lithosphere is slightly denser than the underlying asthenosphere, the hot, ductile layer in the upper mantle underlying the cold, rigid lithosphere. Once initiated, stable subduction is driven mostly by the negative buoyancy of the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratovolcanoes Of Indonesia
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a conical volcano built up by many layers (strata) of hardened lava and tephra. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile with a summit crater and periodic intervals of explosive eruptions and effusive eruptions, although some have collapsed summit craters called calderas. The lava flowing from stratovolcanoes typically cools and hardens before spreading far, due to high viscosity. The magma forming this lava is often felsic, having high-to-intermediate levels of silica (as in rhyolite, dacite, or andesite), with lesser amounts of less-viscous mafic magma. Extensive felsic lava flows are uncommon, but have travelled as far as . Stratovolcanoes are sometimes called composite volcanoes because of their composite stratified structure, built up from sequential outpourings of erupted materials. They are among the most common types of volcanoes, in contrast to the less common shield volcanoes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
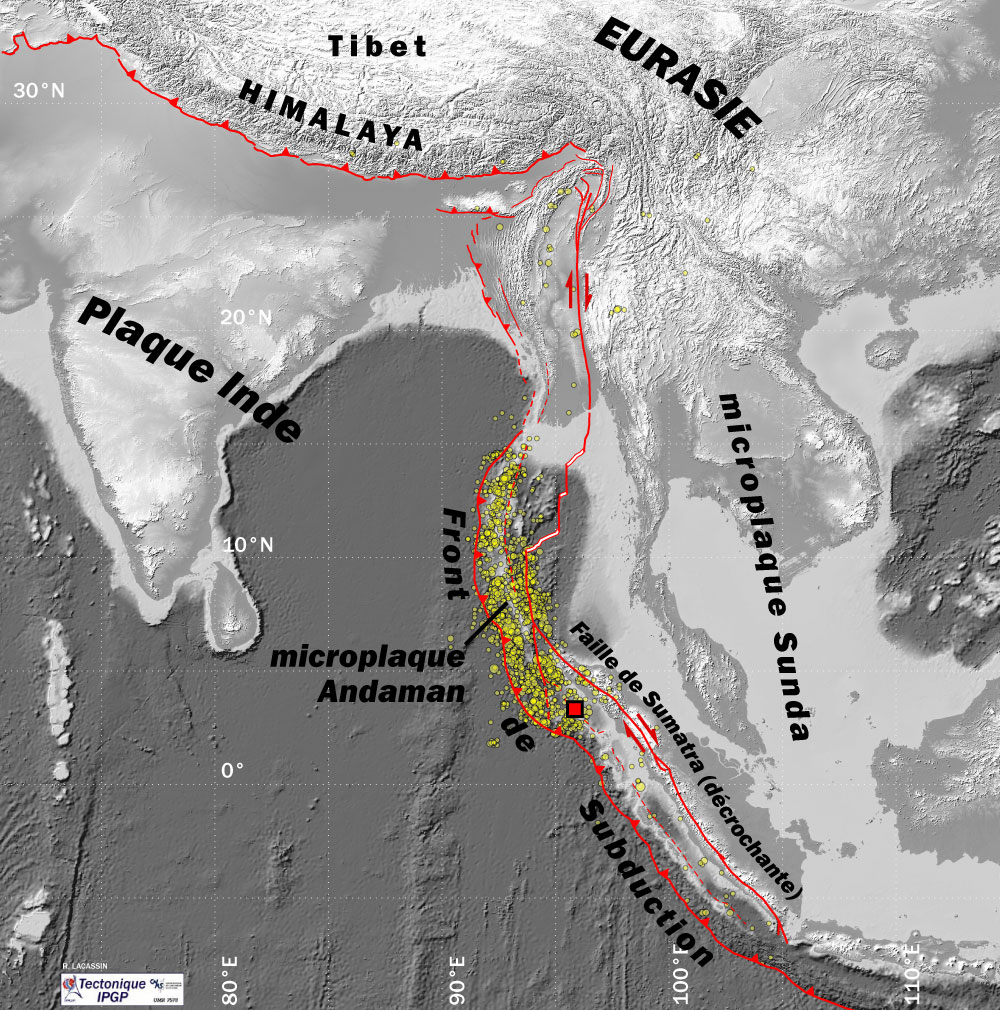
2004 Indian Ocean Earthquake And Tsunami
An earthquake and a tsunami, known as the Boxing Day Tsunami and, by the scientific community, the Sumatra–Andaman earthquake, occurred at 07:58:53 local time (UTC+7) on 26 December 2004, with an epicentre off the west coast of northern Sumatra, Indonesia. It was an undersea megathrust earthquake that registered a magnitude of 9.1–9.3 , reaching a Mercalli intensity up to IX in certain areas. The earthquake was caused by a rupture along the fault between the Burma Plate and the Indian Plate. A series of massive tsunami waves grew up to high once heading inland, after being created by the underwater seismic activity offshore. Communities along the surrounding coasts of the Indian Ocean were devastated, and the tsunamis killed an estimated 227,898 people in 14 countries, making it one of the deadliest natural disasters in recorded history. The direct results caused major disruptions to living conditions and commerce in coastal provinces of surrounded countries, including Ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Volcanoes In Indonesia
The geography of Indonesia is dominated by volcanoes that are formed due to subduction zones between the Eurasian plate and the Indo-Australian plate. Some of the volcanoes are notable for their eruptions, for instance, Krakatoa for its global effects in 1883, the Lake Toba Caldera for its supervolcanic eruption estimated to have occurred 74,000 years before present which was responsible for six years of volcanic winter, and Mount Tambora for the most violent eruption in recorded history in 1815. Volcanoes in Indonesia are part of the Pacific Ring of Fire. The 150 entries in the list below are grouped into six geographical regions, four of which belong to the volcanoes of the Sunda Arc trench system. The remaining two groups are volcanoes of Halmahera, including its surrounding volcanic islands, and volcanoes of Sulawesi and the Sangihe Islands. The latter group is in one volcanic arc together with the Philippine volcanoes. The most active volcano is Mount Merapi on Java. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nepenthes Of Sumatra And Peninsular Malaysia
''Nepenthes of Sumatra and Peninsular Malaysia'' is a monograph by Charles Clarke on the tropical pitcher plants of Sumatra, Peninsular Malaysia, and their minor surrounding islands. It was published in 2001 by Natural History Publications (Borneo). Clarke described it as "intermediate between an ecological monograph and a taxonomic one".Clarke, C.M. 2001. ''Nepenthes of Sumatra and Peninsular Malaysia''. Natural History Publications (Borneo), Kota Kinabalu. Background The work was conceived in late 1997Clarke, C.M. 2000. ''Proceedings of the 3rd Conference of the International Carnivorous Plant Society'': 9. and represents the culmination of 3 years of intensive research that included 15 field trips and numerous herbarium visits. The project encountered a number of difficulties and setbacks, including a "severe drought" in 1997 and political unrest in the following two years. Of the species covered in the book, Clarke observed all but three in the field. ''Nepenthes lavicola'' co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemism
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example '' Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. '' Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)