|
Gun Chronograph
A ballistic chronograph or gun chronograph is a measuring instrument used to measure the velocity of a projectile in flight, typically fired from a gun. History Benjamin Robins (1707–1751) invented the ballistic pendulum that measures the momentum of the projectile fired by a gun. Dividing the momentum by the projectile mass gives the velocity. Robbins published his results as ''New Principles of Gunnery'' in 1742. The ballistic pendulum could make only one measurement per firing because the device catches the projectile. The gun's accuracy also limited how far down range a measurement could be made. Alessandro Vittorio Papacino d'Antoni published results in 1765 using a wheel chronometer. This used a horizontal spinning wheel with a vertical paper mounted on the rim. The bullet was fired across the diameter of the wheel so that it pierced the paper on both sides, and the angular difference along with the rotation speed of the wheel was used to compute the bullet velocity. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measuring Instrument
A measuring instrument is a device to measure a physical quantity. In the physical sciences, quality assurance, and engineering, measurement is the activity of obtaining and comparing physical quantities of real-world objects and events. Established standard objects and events are used as units, and the process of measurement gives a number relating the item under study and the referenced unit of measurement. Measuring instruments, and formal test methods which define the instrument's use, are the means by which these relations of numbers are obtained. All measuring instruments are subject to varying degrees of instrument error and measurement uncertainty. These instruments may range from simple objects such as rulers and stopwatches to electron microscopes and particle accelerators. Virtual instrumentation is widely used in the development of modern measuring instruments. Time In the past, a common time measuring instrument was the sundial. Today, the usual measuring instrum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Military Academy, Woolwich
The Royal Military Academy (RMA) at Woolwich, in south-east London, was a British Army military academy for the training of commissioned officers of the Royal Artillery and Royal Engineers. It later also trained officers of the Royal Corps of Signals and other technical corps. RMA Woolwich was commonly known as "The Shop" because its first building was a converted workshop of the Woolwich Arsenal. History Origins in the Royal Arsenal An attempt had been made by the Board of Ordnance in 1720 to set up an academy within its Arsenal (then known as the Warren) to provide training and education for prospective officers of its new Regiment of Artillery and Corps of Engineers (both of which had been established there in 1716). A new building was being constructed in readiness for the Academy and funds had been secured, seemingly, through investment in the South Sea Company; but the latter's collapse led to plans for the Academy being placed on hold. After this false start, the acade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horology
Horology (; related to Latin '; ; , interfix ''-o-'', and suffix ''-logy''), . is the study of the measurement of time. Clocks, watches, clockwork, sundials, hourglasses, clepsydras, timers, time recorders, marine chronometers, and atomic clocks are all examples of instruments used to measure time. In current usage, horology refers mainly to the study of mechanical time-keeping devices, while chronometry more broadly includes electronic devices that have largely supplanted mechanical clocks for the best accuracy and precision in time-keeping. People interested in horology are called ''horologists''. That term is used both by people who deal professionally with timekeeping apparatuses (watchmakers, clockmakers), as well as aficionados and scholars of horology. Horology and horologists have numerous organizations, both professional associations and more scholarly societies. The largest horological membership organisation globally is the NAWCC, the National Association of Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doppler Radar
A Doppler radar is a specialized radar that uses the Doppler effect to produce velocity data about objects at a distance. It does this by bouncing a microwave signal off a desired target and analyzing how the object's motion has altered the frequency of the returned signal. This variation gives direct and highly accurate measurements of the radial component of a target's velocity relative to the radar. Concept Doppler effect The Doppler effect (or Doppler shift), named after Austrian physicist Christian Doppler who proposed it in 1842, is the difference between the observed frequency and the emitted frequency of a wave for an observer moving relative to the source of the waves. It is commonly heard when a vehicle sounding a siren approaches, passes and recedes from an observer. The received frequency is higher (compared to the emitted frequency) during the approach, it is identical at the instant of passing by, and it is lower during the recession. This variation of f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
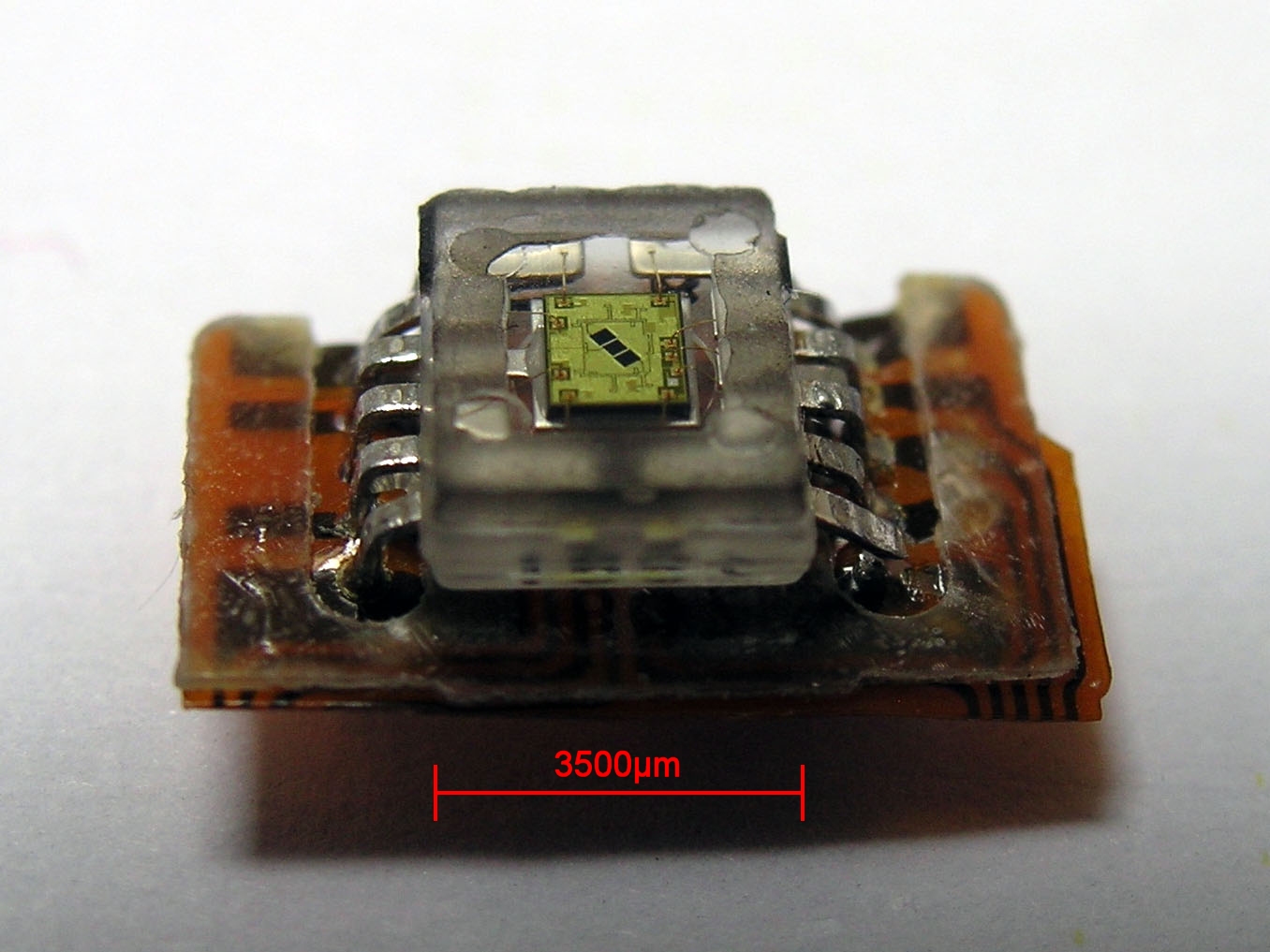
Photodetector
Photodetectors, also called photosensors, are sensors of light or other electromagnetic radiation. There is a wide variety of photodetectors which may be classified by mechanism of detection, such as Photoelectric effect, photoelectric or photochemical effects, or by various performance metrics, such as spectral response. Semiconductor-based photodetectors typically photo detector have a p–n junction that converts light photons into current. The absorbed photons make electron–hole pairs in the depletion region. Photodiodes and photo transistors are a few examples of photo detectors. Solar cells convert some of the light energy absorbed into electrical energy. Types Photodetectors may be classified by their mechanism for detection: * Photoemission or photoelectric effect: Photons cause electrons to transition from the conduction band of a material to free electrons in a vacuum or gas. * Thermal: Photons cause electrons to transition to mid-gap states then decay back to lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capacitor
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals. The effect of a capacitor is known as capacitance. While some capacitance exists between any two electrical conductors in proximity in a circuit, a capacitor is a component designed to add capacitance to a circuit. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term still encountered in a few compound names, such as the ''condenser microphone''. The physical form and construction of practical capacitors vary widely and many types of capacitor are in common use. Most capacitors contain at least two electrical conductors often in the form of metallic plates or surfaces separated by a dielectric medium. A conductor may be a foil, thin film, sintered bead of metal, or an electrolyte. The nonconducting dielectric acts to increase the capacitor's c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It has a great affinity towards oxygen, and forms a protective layer of oxide on the surface when exposed to air. Aluminium visually resembles silver, both in its color and in its great ability to reflect light. It is soft, non-magnetic and ductile. It has one stable isotope, 27Al; this isotope is very common, making aluminium the twelfth most common element in the Universe. The radioactivity of 26Al is used in radiodating. Chemically, aluminium is a post-transition metal in the boron group; as is common for the group, aluminium forms compounds primarily in the +3 oxidation state. The aluminium cation Al3+ is small and highly charged; as such, it is polarizing, and bonds aluminium forms tend towards covalency. The strong affinity towards ox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypersonic
In aerodynamics, a hypersonic speed is one that exceeds 5 times the speed of sound, often stated as starting at speeds of Mach 5 and above. The precise Mach number at which a craft can be said to be flying at hypersonic speed varies, since individual physical changes in the airflow (like molecular dissociation and ionization) occur at different speeds; these effects collectively become important around Mach 5-10. The hypersonic regime can also be alternatively defined as speeds where specific heat capacity changes with the temperature of the flow as kinetic energy of the moving object is converted into heat. Characteristics of flow While the definition of hypersonic flow can be quite vague and is generally debatable (especially due to the absence of discontinuity between supersonic and hypersonic flows), a hypersonic flow may be characterized by certain physical phenomena that can no longer be analytically discounted as in supersonic flow. The peculiarity in hypersonic flows ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown management f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Girl Gunners- The Work Of The Auxiliary Territorial Service At An Experimental Station, Shoeburyness, Essex, England, 1943 D12697
A girl is a young female human, usually a child or an adolescent. When a girl becomes an adult, she is accurately described as a ''woman''. However, the term ''girl'' is also used for other meanings, including ''young woman'',Dictionary.com, "Girl"'' Retrieved January 2, 2008. and is sometimes used as a synonym for ''daughter'', or ''girlfriend''. In certain contexts, the usage of ''girl'' for a woman may be derogatory. ''Girl'' may also be a term of endearment used by an adult, usually a woman, to designate adult female friends. ''Girl'' also appears in portmanteaus (compound words) like ''showgirl'', ''cowgirl'', and ''Student, schoolgirl''. The treatment and status of girls in any society is usually closely related to the women's rights, status of women in that culture. In cultures where women have a low societal position, girls may be unwanted by their parents, and the state may invest less in services for girls. Girls' upbringing ranges from being relatively the same a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Bashforth
Francis Bashforth (8 January 1819 – 12 February 1912) was an English Anglican priest and mathematician, who is known for his use of applied mathematics on ballistics. Early life and education Bashforth was born on 8 January 1819 in Thurnscoe, Yorkshire, England. Bashforth was the eldest son of John Bashforth, a farmer. He was educated at Doncaster Grammar School. In 1839, he matriculated into St John's College, Cambridge as a sizar. Having studied the Mathematical Tripos at the University of Cambridge, he graduated with a Bachelor of Arts (BA) degree in 1843 and was the Wrangler (University of Cambridge), Second Wrangler. Bashforth later returned to his alma-mater to undertake a Bachelor of Divinity (BD) degree, which he completed in 1853. Career Bashforth was elected a Fellow (Oxbridge), Fellow of St John's College, Cambridge in 1943. Bashforth was ordained in the Church of England as a Deacon#Anglicanism, deacon in 1850 and as a Priest#Anglican or Episcopalian, priest in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

_Mach_7_computational_fluid_dynamic_(CFD).jpg)
.jpg)