|
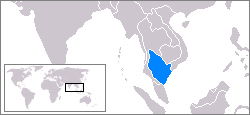
Gulf Of Siam
The Gulf of Thailand, also known as the Gulf of Siam, is a shallow inlet in the southwestern South China Sea, bounded between the southwestern shores of the Indochinese Peninsula and the northern half of the Malay Peninsula. It is around in length and up to in width, and has a surface area of . The gulf is surrounded on the north, west and southwest by the coastlines of Thailand (hence the name), on the northeast by Cambodia and the Mekong Delta region of Vietnam, and opens to the South China Sea in the southeast. Names The modern Thai name of the gulf is ''Ao Thai'' ( th, อ่าวไทย, , 'Thai Gulf') and "Gulf of Thailand" has been adopted as the official name of the body by the International Hydrographic Organization. Its name in Malay is he "Gulf of Siam", ''Teluk Siam'', and in km, ឈូងសមុទ្រសៀម'', Chhoung Samut Siem''. In Thai, the gulf is historically known as ''Ao Sayam'' ( th, อ่าวสยาม). In Vietnamese it is known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and north-west of mainland Australia. Southeast Asia is bordered to the north by East Asia, to the west by South Asia and the Bay of Bengal, to the east by Oceania and the Pacific Ocean, and to the south by Australia (continent), Australia and the Indian Ocean. Apart from the British Indian Ocean Territory and two out of atolls of Maldives, 26 atolls of Maldives in South Asia, Maritime Southeast Asia is the only other subregion of Asia that lies partly within the Southern Hemisphere. Mainland Southeast Asia is completely in the Northern Hemisphere. East Timor and the southern portion of Indonesia are the only parts that are south of the Equator. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval Arab Geographers
Medieval Islamic geography and cartography refer to the study of geography and cartography in the Muslim world during the Islamic Golden Age (variously dated between the 8th century and 16th century). Muslim scholars made advances to the map-making traditions of earlier cultures, particularly the Hellenistic geographers Ptolemy and Marinus of Tyre, combined with what explorers and merchants learned in their travels across the Old World (Afro-Eurasia). Islamic geography had three major fields: exploration and navigation, physical geography, and cartography and mathematical geography. Islamic geography reached its apex with Muhammad al-Idrisi in the 12th century. History Islamic geography began in the 8th century, influenced by Hellenistic geography, combined with what explorers and merchants learned in their travels across the Old World (Afro-Eurasia). Muslim scholars engaged in extensive exploration and navigation during the 9th-12th centuries, including journeys across the Muslim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal to ‰). Salinity is an important factor in determining many aspects of the chemistry of natural waters and of biological processes within it, and is a thermodynamic state variable that, along with temperature and pressure, governs physical characteristics like the density and heat capacity of the water. A contour line of constant salinity is called an ''isohaline'', or sometimes ''isohale''. Definitions Salinity in rivers, lakes, and the ocean is conceptually simple, but technically challenging to define and measure precisely. Conceptually the salinity is the quantity of dissolved salt content of the water. Salts are compounds like sodium chloride, magnesium sulfate, potassium nitrate, and sodium bicarbonate which dissolve into ions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pengkalan Chepa
Pengkalan Chepa is a town and parliamentary constituency in Kelantan, Malaysia. Pengkalan Chepa is where the Sultan Ismail Petra Airport is located. It is located about 8 km from Kota Bharu Kota Bharu, colloquially referred to as KB, is a town in Malaysia that serves as the state capital and royal seat of Kelantan. It is situated in the northeastern part of Peninsular Malaysia and lies near the mouth of the Kelantan River. The .... Kota Bharu District Towns in Kelantan {{Kelantan-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumpat District
Tumpat (Kelantanese: Ttupak) is a district (jajahan) in Kelantan, Malaysia. Tumpat is situated at the end of the '' East Coast Line'' railway line operated by Keretapi Tanah Melayu (Malayan Railways) which links Kelantan to the western part of Peninsular Malaysia. This strategic location makes it the transportation hub of Kelantan. Tumpat town is approximately 15 km from the state capital, Kota Bharu. Geography Tumpat is the northernmost constituency in Kelantan, bordering Thailand across the Golok River to the west, Kota Bharu across the Kelantan River to the east, and Pasir Mas to the south, and the Thai district of Tak Bai to the west. Demographics Tumpat has a population about 152,168 (2010), with the majority being the Malays with significant Siamese, Indian and Chinese population. Ranking Population of Jajahan Tumpat: Federal Parliament and State Assembly Seats List of LMS district representatives in the Federal Parliament (Dewan Rakyat) List of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mekong River
The Mekong or Mekong River is a trans-boundary river in East Asia and Southeast Asia. It is the world's twelfth longest river and the third longest in Asia. Its estimated length is , and it drains an area of , discharging of water annually. From the Tibetan Plateau the river runs through China, Myanmar, Laos, Thailand, Cambodia, and Vietnam. The extreme seasonal variations in flow and the presence of rapids and waterfalls in the Mekong make navigation difficult. Even so, the river is a major trade route between western China and Southeast Asia. Names The Mekong was originally called ''Mae Nam Khong'' from a contracted form of Tai shortened to ''Mae Khong''. In Thai and Lao, ''Mae Nam'' ("Mother of Water ) is used for large rivers and ''Khong'' is the proper name referred to as "River Khong". However, ''Khong'' is an archaic word meaning "river", loaned from Austroasiatic languages, such as Vietnamese ''sông'' (from *''krong'') and Mon ''kruŋ'' "river", which led to Chin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Bai Bung
A cape is a clothing accessory or a sleeveless outer garment which drapes the wearer's back, arms, and chest, and connects at the neck. History Capes were common in medieval Europe, especially when combined with a hood in the chaperon. They have had periodic returns to fashion - for example, in nineteenth-century Europe. Roman Catholic clergy wear a type of cape known as a ferraiolo, which is worn for formal events outside a ritualistic context. The cope is a liturgical vestment in the form of a cape. Capes are often highly decorated with elaborate embroidery. Capes remain in regular use as rainwear in various military units and police forces, in France for example. A gas cape was a voluminous military garment designed to give rain protection to someone wearing the bulky gas masks used in twentieth-century wars. Rich noblemen and elite warriors of the Aztec Empire would wear a tilmàtli; a Mesoamerican cloak/cape used as a symbol of their upper status. Cloth and clothing wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chao Phraya River
The Chao Phraya ( or ; th, แม่น้ำเจ้าพระยา, , or ) is the major river in Thailand, with its low alluvial plain forming the centre of the country. It flows through Bangkok and then into the Gulf of Thailand. Etymology On many old European maps, the river is named the ''Mae Nam'' (Thai: แม่น้ำ), the Thai word for "river" (literally, "motherly water"). James McCarthy, F.R.G.S., who served as Director-General of the Siamese Government Surveys prior to establishment of the Royal Survey Department, wrote in his account, "''Mae Nam'' is a generic term, ''mae'' signifying "mother" and ''Nam'' "water," and the epithet Chao P'ia signifies that it is the chief river in the kingdom of Siam." H. Warington Smyth, who served as Director of the Department of Mines in Siam from 1891 to 1896, refers to it in his book first published in 1898 as "the Mae Nam Chao Phraya". In the English-language media in Thailand, the name Chao Phraya River is oft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay Of Bangkok
The Bay of Bangkok ( th, อ่าวกรุงเทพ, , ), also known as the Bight of Bangkok, is the northernmost part of the Gulf of Thailand, roughly extending from Hua Hin District to the west and Sattahip District to the east. Three of the major rivers of central Thailand empty into the bay - the Chao Phraya and its distributary Tha Chin, the Mae Klong and the Bang Pakong River. There are some islands off the eastern shores of the bay, like Ko Sichang, Ko Lan and Ko Phai.Hydrographic Service of the Royal Thai Navy The Royal Thai Navy ( Abrv: RTN, ทร.; th, กองทัพเรือไทย, ) is the naval warfare force of Thailand. Established in 1906, it was modernised by the Admiral Prince Abhakara Kiartiwongse (1880–1923) who is known a ..., Chart 142 Environment The water quality of the Bay of Bangkok is rated as "very poor" by the Pollution Control Department. References {{thailand-geo-stub Bays of Thailand Gulf of Thailand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dragon Tail (peninsula)
The Dragon's Tail is a modern name for the phantom peninsula in southeast Asia which appeared in medieval Arabian and Renaissance European world maps. It formed the eastern shore of the Great Gulf (Gulf of Thailand) east of the Golden Chersonese (Malay Peninsula), replacing the " unknown lands" which Ptolemy and others had thought surrounded the "Indian Sea". Name The peninsula known to modern cartographers as the "Dragon's Tail" or "Tiger's Tail" appeared under various names on different maps. History Early history The peninsula does not appear in any surviving manuscript of Ptolemy's ''Geography'' or other Greek geographers. Instead, it is first attested in the Ptolemaic-influenced '' Book of the Description of the Earth'' compiled by al-Khwārizmī around 833 AD. Ptolemy's map ended at 180°E of the Fortunate Isles without being able to explain what might lie on the imagined eastern shore of the Indian Ocean or beyond the lands of the Sinae and of Serica in Asia. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese Explorers
Portuguese maritime exploration resulted in the numerous territories and maritime routes recorded by the Portuguese as a result of their intensive maritime journeys during the 15th and 16th centuries. Portuguese sailors were at the vanguard of European exploration, chronicling and mapping the coasts of Africa and Asia, then known as the East Indies, and Canada and Brazil (the West Indies), in what came to be known as the Age of Discovery. Methodical expeditions started in 1419 along West Africa's coast under the sponsorship of prince Henry the Navigator, with Bartolomeu Dias reaching the Cape of Good Hope and entering the Indian Ocean in 1488. Ten years later, in 1498, Vasco da Gama led the first fleet around Africa to India, arriving in Calicut and starting a maritime route from Portugal to India. Portuguese explorations then proceeded to southeast Asia, where they reached Japan in 1542, forty-four years after their first arrival in India. In 1500, the Portuguese nobleman Pedro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_-_img_05.jpg)

