|
Gujarati Literature
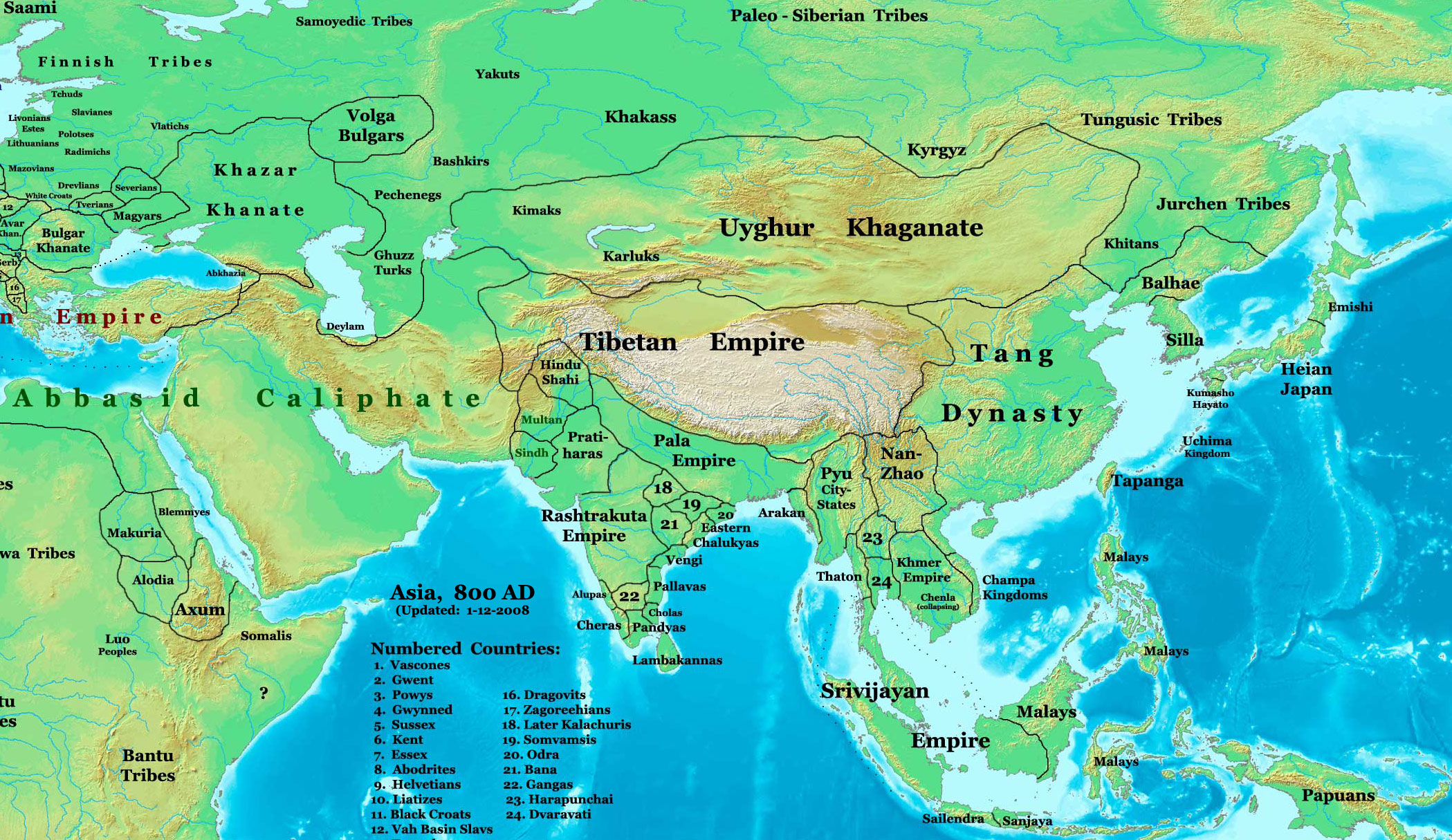
The history of Gujarat, Gujarati literature () may be traced to 1000 AD, and this literature has flourished since then to the present. It is unique in having almost no patronage from a ruling dynasty, other than its composers. Gujarat Vidhya Sabha, Gujarat Sahitya Sabha, Gujarat Sahitya Akademi and Gujarati Sahitya Parishad are Gujarat-based literary institutions promoting the Gujarati literature. History Such factors as the policies of the rulers, the living style of the people, and the worldwide influence on society are important for any literature to flourish. In Gujarat, due to the development of trade and commerce, the religious influence of Jainism as well as Hinduism, and also due to the safety and encouragement of rulers like Chaulukya dynasty, Chaulukya (Solanki) and Vaghela dynasty, Vaghela Rajputs, literary activities were in full force from the 11th century. * Gujarati literature ** Early literature (up to 1450 AD) *** Prāg-Narsinh Yug (1000 AD to 1450 AD) **** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gujarat
Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories of India by area, fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the List of states and union territories of India by population, ninth-most populous state, with a population of 60.4 million in 2011. It is bordered by Rajasthan to the northeast, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu to the south, Maharashtra to the southeast, Madhya Pradesh to the east, and the Arabian Sea and the Pakistani province of Sindh to the west. Gujarat's capital city is Gandhinagar, while its largest city is Ahmedabad. The Gujarati people, Gujaratis are indigenous to the state and their language, Gujarati language, Gujarati, is the state's official language. The state List of Indus Valley civilisation sites#List of Indus Valley sites discovered, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anhilwara
Patan () is the administrative seat of Patan district in the Indian state of Gujarat and is an administered municipality. It was the capital of Gujarat's Chavda and Chaulukya dynasties in medieval times and is also known as Anhilpur-Patan to distinguish it from Prabhas Patan. During the rule of Gujarat Sultanate, it was the capital from 1407 to 1411. Patan was established by the Chavda king Vanaraja. During the rule of several Hindu and Muslim dynasties, it thrived as a trading city and a regional capital of northern Gujarat. The city contains many Hindu and Jain temples as well as mosques, dargahs and rauzas. It is a historical place located on the bank of the now-extinct Saraswati River. Patan has an old market which is quite sizeable and is believed to have been in continuous operation since at least the rule of Vaghelas and gandhis. History Patan was established by the Chavda ruler Vanaraja in the ninth century as "Anahilapataka". During the 10th–13th centuries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhavai
Bhavai, also known as ''Vesha'' or ''Swang'', is a popular folk theatre form of western India, especially in Gujarat. Etymology ''Bhavai'' may derive from the Sanskrit word ''Bhava'', meaning expression or emotion. It is also associated with Hindu goddess Amba. ''Bhav'' means universe and ''Aai'' means mother, so it may be also considered an art form dedicated to the Mother of the Universe, Amba. Bhavai is also known as ''Vesha'' or ''Swang'', which literally means 'get-up'. History Bhavai is believed to have originated in the 14th century. Asaita Thakar is traditionally credited for its origin. Folklore In 14th century, Ganga, daughter of Unjha headman Hema Patel, was kidnapped by Muslim subedar. Their family priest, Asaita Thakar who was a brahmin, went to subedar claiming Ganga as his daughter. To prove, subedar asked him to dine with Ganga as during those time, brahmins did not dine with lower castes. He dined with her to save her but upon return, he was outcaste by B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanhadade Prabandha
''Kānhaḍade Prabandha'' is a book by Indian poet Padmanābha written in 1455, in a western Apabhramsha dialect. The book tells the story of Raval Kanhadade ( Kanhadadeva), the Chahamana ruler of Jalore. Textual history Padmanabha wrote ''Kanhadade Prabandha'' in 1455, in a western Apabhramsha dialect. The author was a court-poet of Akhairaja, the Chauhan Rajput king of Visalnagar. Akahiraja is said to be a descendant of the poem's hero Raval Kanhadade, through Viramade, Megalde, Ambaraja, and Khetsi. The German Indologist Georg Bühler was the first modern scholar to write about this treatise. He noticed its manuscript in a Jain library at Tharad. ''Kanhadade Prabandha'' has been praised as the finest work in Dingal (literary form of the Old Western Rajasthani or Old Gujarati), and one of the greatest Indian works written during the medieval period by eminent scholars like Muni Jinavijaya, K. M. Munshi, Dasharatha Sharma and K.B. Vyas. The work was tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merutunga
Merutuṅga was a medieval scholar from present-day Gujarat in India and was a Śvētāmbara Jain monk of the Achal Gaccha. He is presently most well-known for his Sanskrit text, the '' Prabandhacintāmaṇi'', composed in 1306 CE. He also wrote ''Vicāraśreṇī'' in 1350 CE which describes the chronology of Chāvḍā, Chaulukya and Vāghelā dynasties. Works ''Prabandhacintāmaṇi'' The ''Prabandhacintāmaṇi'' was composed in Vardhamāna (modern-day Wadhwan) in VS 1361 Phālguna Śukla 15, a Sunday. In the text itself, Merutuṅga states that Gaṇī Guṇacandra compiled the first version of the text and that Dharmadeva assisted Merutuṅga in the compilation of the final version. ''Therāvalī'' The ''Therāvalī'' of Merutuṅga is a Paṭṭāvalī that presents a chronology from Mahavira to the arrival of and invasion by the Sakas in India India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prabandha
Prabandha is a literary genre of medieval Indian Sanskrit literature. The ''prabandha''s contain semi-historical anecdotes about the lives of famous persons. They were written primarily by Jain scholars of western India (Gujarat and Malwa) from 13th century onwards. The ''prabandha''s feature colloquial Sanskrit with vernacular expressions, and contain elements of folklore. Definition The ''prabandha''s are semi-historical anecdotes about famous persons. The '' Prabandha Kosha'' of Rajashekhara Suri mentions two types of biographical narratives: ''charita''s and ''prabandha''s. It states that the ''charita''s are the life-stories of tirthankaras, kings and religious leaders up to Aryarakshita-Suri (who died in 30 CE). The biographies of persons born after Aryarakshita-Suri are called ''prabandha''s. It is not clear if this is Rajashekhara's own definition or if it is based on some other authority. However, several later texts do not abide by this definition. For example, there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasantavilas
''Vasantavilas'' ( The Joys of Spring) is a fagu poem by unknown author written in old Gujarati language, believed to be written in first half of the 14th-century. Its theme is the depiction of Shringara, an erotic sentiments. The poem has a significant historical value as it provides linguistic evidence of Old Gujarati. Overview Gujarati scholar Keshav Harshad Dhruv first discovered an illustrated manuscript of the ''Vasantavilas'' copied in 1455, and published it in ''Shalapatra''. The published version seemed unsatisfied to him as the version needed many editing, he published it again with notes in ''Haji Muhammad Smarak Granth'' (1923). In the meanwhile, he found another manuscript from the Bhandarkar Oriental Research Institute, Pune, and with its help, he re-edited the text. In 1943, another scholar Kantilal B. Vyas published another carefully edited edition of the poem, which aroused interest among scholars in India and abroad. Vyas published its English translation in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasanta (Ritu)
Vasanta (), also referred to as Basant, refers to the Indian spring. One of the main festivals of the Vasanta season is celebrated on '' Vasanta Panchami'' (), which in Indian society is a cultural and religious festival, celebrated annually on the first day of spring, the fifth day (Panchami) of the Hindu month '' Magha'' (January–February). Origin In Sanskrit ''Vasanta'' means ''spring''. Panchami is the fifth day of ''Shukla Paksha'', the fortnight of the waxing moon in the Hindu month of Magha, (January – February). Vasanta Panchami, which marks the end of the winter and heralds in spring, is dedicated to goddess Saraswati. She is a goddess of water and of a river bearing her name. Her water originates in the Himalayas, flows southeast and meets the Ganges at Prayag near its confluence with the Yamuna (Triveni). Saraswati is also a goddess of speech and learning who blesses the world with ''vach'' (words), hymns, Sanskrit and the wealth of knowledge. It is auspici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khambhat
Khambhat (, ), also known as Cambay, is a city and the surrounding urban agglomeration in Anand district in the Indian state of Gujarat. It was once an important trading center, but its harbour gradually silted up, and the maritime trade moved to Surat. Khambat lies on an alluvial plain at the north end of the Gulf of Khambhat, noted for the extreme rise and fall of its tides, which can vary as much as thirty feet in the vicinity of Khambat. Khambat is known for its halvasan sweet, sutarfeni, akik stone and kites (patang), and for sources of oil and gas. Khambat is perhaps the only place in India where the Harappan craft of agate bead making is found in the living tradition. Surprisingly Khambat has no stone deposits; the craft has survived mainly through acquiring stones from the Rajpipla hills, about 200 km away from the city. In the folklore of Khambat, the beginning of the craft is attributed to Baba Ghor, a 1500 AD saint from Ethiopia ( Habash) who had led a large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaisalmer
Jaisalmer , nicknamed ''The Golden city'', is a city in the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan, located west of the state capital Jaipur, in the heart of the Thar Desert. It serves as the administrative headquarters of Jaisalmer district. It is a former medieval trading center and the historic capital of the kingdom of Jaisalmer, founded in 1156 by Rawal Jaisal of the Bhati clan of Rajputs. Jaisalmer stands on a ridge of yellowish sandstone and is crowned by the World Heritage Site, Jaisalmer Fort, a sprawling hilltop citadel supported by 99 bastions. This fort contains a royal palace and several ornate Jain temples. Many of the houses and temples of both the fort and of the town below are built of finely sculptured yellow sandstone. The town has a population, including the residents of the fort, of about 78,000. Jaisalmer ranked 9th on Booking.com's Top 10 The Most Welcoming cities in the world. It is the only Indian city on the list. Etymology Jaisalmer was founded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad ( ), also spelled Amdavad (), is the most populous city in the Indian state of Gujarat. It is the administrative headquarters of the Ahmedabad district and the seat of the Gujarat High Court. Ahmedabad's population of 5,570,585 (per the 2011 population census) makes it the fifth-most populous city in India, and the encompassing urban agglomeration population was estimated at 8,854,444 (as of 2024) is the seventh-most populous in India. Ahmedabad is located near the banks of the Sabarmati River, from the capital of Gujarat, Gandhinagar, also known as its twin city. Ahmedabad has emerged as an important economic and industrial hub in India. It is the second-largest producer of cotton in India, due to which it was known as the 'Manchester of India' along with Kanpur. Ahmedabad's stock exchange (before it was shut down in 2018) was the country's second oldest. Cricket is a popular sport in Ahmedabad; a newly built stadium, called Narendra Modi Stadium, at Mote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patan, Gujarat
Patan () is the administrative seat of Patan district in the Indian state of Gujarat and is an administered municipality. It was the capital of Gujarat's Chavda dynasty, Chavda and Chaulukya dynasties in medieval times and is also known as Anhilpur-Patan to distinguish it from Prabhas Patan. During the rule of Gujarat Sultanate, it was the capital from 1407 to 1411. Patan was established by the Chavda king Vanaraja Chavda, Vanaraja. During the rule of several Hindu and Muslim dynasties, it thrived as a trading city and a regional capital of northern Gujarat. The city contains many Hindu and Jain temples as well as mosques, dargahs and rauzas. It is a historical place located on the bank of the now-extinct Saraswati River, Gujarat, Saraswati River. Patan has an old market which is quite sizeable and is believed to have been in continuous operation since at least the rule of Vaghelas and gandhis. History Patan was established by the Chavda dynasty, Chavda ruler Vanaraja in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |