|
Guidepoint
Guidepoint is an expert network, providing business & government professionals with opportunities to communicate with industry and subject-matter experts to answer research questions. Guidepoint clients consult with these experts over the phone, in-person at conferences, at teleconferences, at custom events and workshops, or may gather their primary research data through surveys, polls, or web-based data offerings. History Guidepoint was founded by Albert Sebag, who had training and experience in chemotherapeutic drug development and intellectual property law and biotechnology litigation for generic pharmaceutical clients. This experience eventually led Sebag to begin a matching service for oncology patients called Clinical Advisors. Launched in 2003, Clinical Advisors matched cancer patients with the clinical trial that best suited their case. As Clinical Advisors expanded their network to include expertise in additional healthcare areas, the company progressed into other in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expert Network
Expert networks refer to a type of business that connects companies with expert resources or subject-matter experts, such as academics, C-levels, founders, and high-level officials to provide valuable information, data, or assistance. Background The phrase "expert network" was originally coined by Mark O'Connor of Yankee Group in presentations introducing his August 1997 Management Strategies report, ''Knowledge Management: People and the Process''. The first known published appearance of the phrase in this context is in the April 1999 Yankee Group white paper ''A Knowledge Perspective: The Knowledge Management Product and Service Domain.'' In the December 1999 publication, "Knowledge Evolution: Tools of the Trade," clients were advised to utilize Expert Networks to "Understand who the experts are throughout the organization (including the extended organization), and more appropriately employ that expertise within a broader range of business contexts for better decision making." ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expert Network
Expert networks refer to a type of business that connects companies with expert resources or subject-matter experts, such as academics, C-levels, founders, and high-level officials to provide valuable information, data, or assistance. Background The phrase "expert network" was originally coined by Mark O'Connor of Yankee Group in presentations introducing his August 1997 Management Strategies report, ''Knowledge Management: People and the Process''. The first known published appearance of the phrase in this context is in the April 1999 Yankee Group white paper ''A Knowledge Perspective: The Knowledge Management Product and Service Domain.'' In the December 1999 publication, "Knowledge Evolution: Tools of the Trade," clients were advised to utilize Expert Networks to "Understand who the experts are throughout the organization (including the extended organization), and more appropriately employ that expertise within a broader range of business contexts for better decision making." ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GG 14-001A Identity Vert Yellow
GG may refer to: Gaming * GG (gaming), an abbreviation used in video games meaning "good game" * GameGuard, a hacking protection program used in some MMORPGs * Game Gear, a handheld game console released by SEGA * Game Genie, a video game cheat cartridge * '' Guilty Gear'', a fighting game series by Arc System Works * ''The G.G. Shinobi'', a side-scrolling action game by Sega released for the Game Gear in 1991 Music * ''G. G.'' (album), a 1975 album by Gary Glitter * Girls' Generation, Korean girl group Television * ''Game Grumps'', a video gaming web series * '' Gossip Girl'', an American teen drama series * GG, the production code for the 1967 ''Doctor Who'' serial ''The Underwater Menace'' Transportation * GG (New York City Subway service) * Sky Lease Cargo's IATA designation * GG, a version of the Subaru Impreza station wagon * GG Duetto, a motorcycle+sidecar built by Swiss Grüter+Gut Motorradtechnik GmbH (GG) Other uses * .gg, the top-level domain country c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research And Analysis Firms Of The United States
Research is "creativity, creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge". It involves the collection, organization and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness to controlling sources of bias and error. These activities are characterized by accounting and controlling for biases. A research project may be an expansion on past work in the field. To test the validity of instruments, procedures, or experiments, research may replicate elements of prior projects or the project as a whole. The primary purposes of basic research (as opposed to applied research) are documentation, Discovery (observation), discovery, interpretation (philosophy), interpretation, and the research and development (R&D) of methods and systems for the advancement of human knowledge. Approaches to research depend on epistemology, epistemologies, which vary considerably both within and between humanities and sciences. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Companies Based In New York City
A company, abbreviated as co., is a legal entity representing an association of people, whether natural, legal or a mixture of both, with a specific objective. Company members share a common purpose and unite to achieve specific, declared goals. Companies take various forms, such as: * voluntary associations, which may include nonprofit organizations * business entities, whose aim is generating profit * financial entities and banks * programs or educational institutions A company can be created as a legal person so that the company itself has limited liability as members perform or fail to discharge their duty according to the publicly declared incorporation, or published policy. When a company closes, it may need to be liquidated to avoid further legal obligations. Companies may associate and collectively register themselves as new companies; the resulting entities are often known as corporate groups. Meanings and definitions A company can be defined as an "artificial per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business Intelligence Organizations
Business is the practice of making one's living or making money by producing or buying and selling products (such as goods and services). It is also "any activity or enterprise entered into for profit." Having a business name does not separate the business entity from the owner, which means that the owner of the business is responsible and liable for debts incurred by the business. If the business acquires debts, the creditors can go after the owner's personal possessions. A business structure does not allow for corporate tax rates. The proprietor is personally taxed on all income from the business. The term is also often used colloquially (but not by lawyers or by public officials) to refer to a company, such as a corporation or cooperative. Corporations, in contrast with sole proprietors and partnerships, are a separate legal entity and provide limited liability for their owners/members, as well as being subject to corporate tax rates. A corporation is more complicated and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telecommunication
Telecommunication is the transmission of information by various types of technologies over wire, radio, optical, or other electromagnetic systems. It has its origin in the desire of humans for communication over a distance greater than that feasible with the human voice, but with a similar scale of expediency; thus, slow systems (such as postal mail) are excluded from the field. The transmission media in telecommunication have evolved through numerous stages of technology, from beacons and other visual signals (such as smoke signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs), to electrical cable and electromagnetic radiation, including light. Such transmission paths are often divided into communication channels, which afford the advantages of multiplexing multiple concurrent communication sessions. ''Telecommunication'' is often used in its plural form. Other examples of pre-modern long-distance communication included audio messages, such as coded drumb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Media
Mass media refers to a diverse array of media technologies that reach a large audience via mass communication. The technologies through which this communication takes place include a variety of outlets. Broadcast media transmit information electronically via media such as films, radio, recorded music, or television. Digital media comprises both Internet and mobile mass communication. Internet media comprise such services as email, social media sites, websites, and Internet-based radio and television. Many other mass media outlets have an additional presence on the web, by such means as linking to or running TV ads online, or distributing QR codes in outdoor or print media to direct mobile users to a website. In this way, they can use the easy accessibility and outreach capabilities the Internet affords, as thereby easily broadcast information throughout many different regions of the world simultaneously and cost-efficiently. Outdoor media transmit information via such media ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technology
Technology is the application of knowledge to reach practical goals in a specifiable and reproducible way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in medicine, science, industry, communication, transportation, and daily life. Technologies include physical objects like utensils or machines and intangible tools such as software. Many technological advancements have led to societal changes. The earliest known technology is the stone tool, used in the prehistoric era, followed by fire use, which contributed to the growth of the human brain and the development of language in the Ice Age. The invention of the wheel in the Bronze Age enabled wider travel and the creation of more complex machines. Recent technological developments, including the printing press, the telephone, and the Internet have lowered communication barriers and ushered in the knowledge economy. While technology contributes to econom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
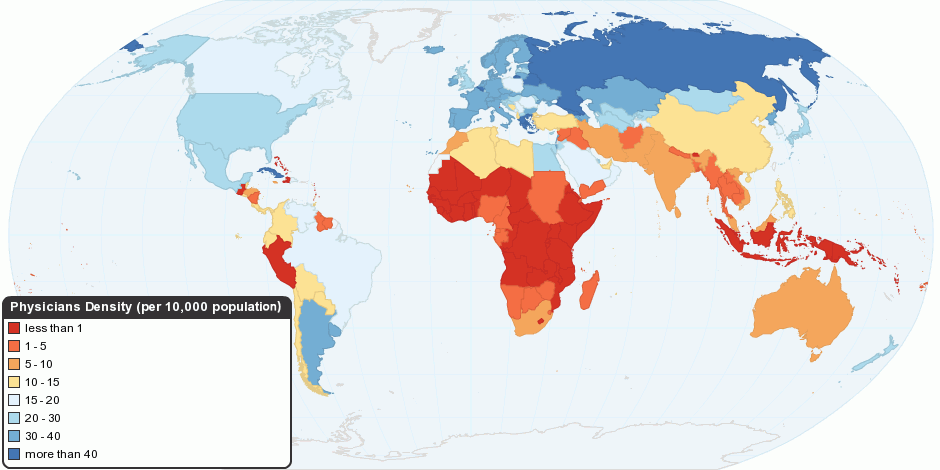
Healthcare
Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health professionals and allied health fields. Medicine, dentistry, pharmacy, midwifery, nursing, optometry, audiology, psychology, occupational therapy, physical therapy, athletic training, and other health professions all constitute health care. It includes work done in providing primary care, secondary care, and tertiary care, as well as in public health. Access to health care may vary across countries, communities, and individuals, influenced by social and economic conditions as well as health policies. Providing health care services means "the timely use of personal health services to achieve the best possible health outcomes". Factors to consider in terms of health care access include financial limitations (such as insurance coverage), geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J). Common forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, and the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system. All living organisms constantly take in and release energy. Due to mass–energy equivalence, any object that has mass whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |