|
Guevarism
Guevarism is a theory of communist revolution and a military strategy of guerrilla warfare associated with Marxist–Leninist revolutionary Ernesto "Che" Guevara, a leading figure of the Cuban Revolution who believed in the idea of Marxism–Leninism and embraced its principles. Overview After the 1959 triumph of the Cuban Revolution led by a militant foco under Fidel Castro, his Argentine-born, cosmopolitan and Marxist colleague, Guevara parlayed his ideology and experiences into a model for emulation (and at times, direct military intervention) around the globe. While exporting one such "focalist" revolution to Bolivia, leading an armed vanguard party there in October 1967, Guevara was captured and executed, becoming a martyr to both the world communist movement and socialism in general. His ideology promotes exporting revolution to any country whose leader is supported by the empire (United States) and has fallen out of favor with its citizens. Guevara talks about how con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
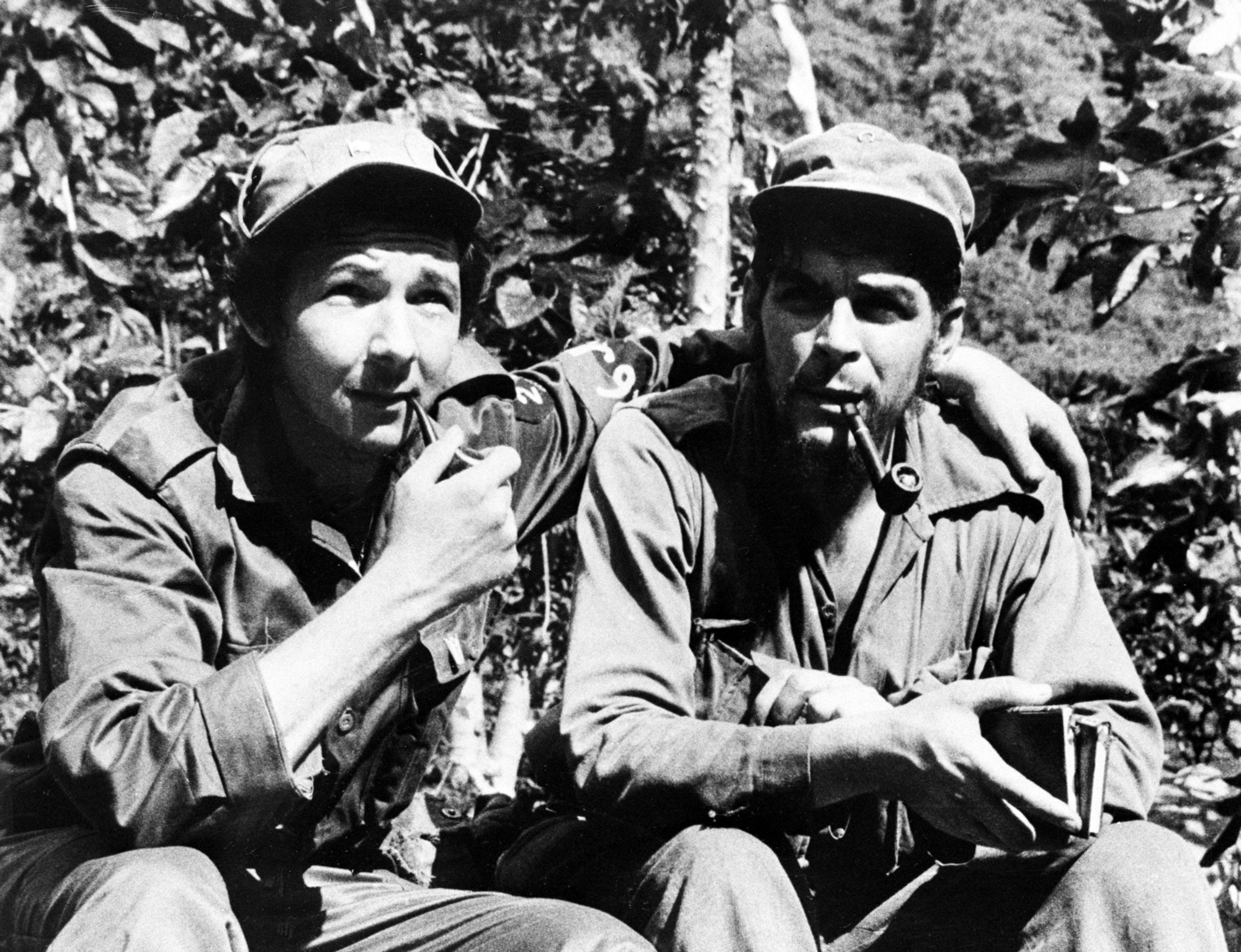
Che Guevara
Ernesto Che Guevara (; 14 June 1928The date of birth recorded on /upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/7/78/Ernesto_Guevara_Acta_de_Nacimiento.jpg his birth certificatewas 14 June 1928, although one tertiary source, (Julia Constenla, quoted by Jon Lee Anderson), asserts that he was actually born on 14 May of that year. Constenla alleges that she was told by Che's mother, Celia de la Serna, that she was already pregnant when she and Ernesto Guevara Lynch were married and that the date on the birth certificate of their son was forged to make it appear that he was born a month later than the actual date to avoid scandal. ( Anderson 1997, pp. 3, 769.) – 9 October 1967) was an Argentine Marxist revolutionary. A major figure of the Cuban Revolution, his stylized visage has become a ubiquitous countercultural symbol of rebellion and global insignia in popular culture. As a young medical student, Guevara traveled throughout South America and was radicalized by the poverty, hunger, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focalist
A guerilla foco is a small cadre of revolutionaries operating in a nation's countryside. This guerilla organization was popularized by Che Guevara in his book Guerilla Warfare, which was based on his experiences in the Cuban Revolution. Guevara would go on to argue that a foco was politically necessary for the success of a socialist revolution. Originally Guevara theorized that a foco was only useful in overthrowing personalistic military dictatorships and not liberal democratic capitalism where a peaceful overthrow was believed possible. Years later Guevara would revise his thesis and argue all nations in Latin America, including liberal democracies could be overthrown by a guerilla foco. Eventually the foco thesis would be that political conditions would not even need to be ripe for revolutions to be successful, since the sheer existence of a guerilla foco would create ripe conditions by itself. Guevara's theory of foco known as () was self-described as the application of Marxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foco
A guerilla foco is a small cadre of revolutionaries operating in a nation's countryside. This guerilla organization was popularized by Che Guevara in his book Guerilla Warfare, which was based on his experiences in the Cuban Revolution. Guevara would go on to argue that a foco was politically necessary for the success of a socialist revolution. Originally Guevara theorized that a foco was only useful in overthrowing personalistic military dictatorships and not liberal democratic capitalism where a peaceful overthrow was believed possible. Years later Guevara would revise his thesis and argue all nations in Latin America, including liberal democracies could be overthrown by a guerilla foco. Eventually the foco thesis would be that political conditions would not even need to be ripe for revolutions to be successful, since the sheer existence of a guerilla foco would create ripe conditions by itself. Guevara's theory of foco known as () was self-described as the application of Marxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foco
A guerilla foco is a small cadre of revolutionaries operating in a nation's countryside. This guerilla organization was popularized by Che Guevara in his book Guerilla Warfare, which was based on his experiences in the Cuban Revolution. Guevara would go on to argue that a foco was politically necessary for the success of a socialist revolution. Originally Guevara theorized that a foco was only useful in overthrowing personalistic military dictatorships and not liberal democratic capitalism where a peaceful overthrow was believed possible. Years later Guevara would revise his thesis and argue all nations in Latin America, including liberal democracies could be overthrown by a guerilla foco. Eventually the foco thesis would be that political conditions would not even need to be ripe for revolutions to be successful, since the sheer existence of a guerilla foco would create ripe conditions by itself. Guevara's theory of foco known as () was self-described as the application of Marxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marxism–Leninism
Marxism–Leninism is a communist ideology which was the main communist movement throughout the 20th century. Developed by the Bolsheviks, it was the state ideology of the Soviet Union, its satellite states in the Eastern Bloc, and various countries in the Non-Aligned Movement and Third World during the Cold War, as well as the Communist International after Bolshevisation. Today, Marxism–Leninism is the ideology of the ruling parties of China, Cuba, Laos and Vietnam (all one-party 'socialist republics'), as well as many other communist parties, while the state ideology of North Korea is derived from Marxism–Leninism. Marxist–Leninist states are commonly referred to as "communist states" by Western academics. Marxism–Leninism holds that a two-stage communist revolution is needed to replace capitalism. A vanguard party, organized through " democratic centralism", would seize power on behalf of the proletariat and establish a one-party socialist state, called the dict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paramilitary
A paramilitary is an organization whose structure, tactics, training, subculture, and (often) function are similar to those of a professional military, but is not part of a country's official or legitimate armed forces. Paramilitary units carry out duties that a country's military or police forces are unable or unwilling to handle. Other organizations may be considered paramilitaries by structure alone, despite being unarmed or lacking a combat role. Overview Though a paramilitary is, by definition, not a military, it is usually equivalent to a light infantry force in terms of strength, firepower, and organizational structure. Paramilitaries use "military" equipment (such as long guns and armored personnel carriers; usually military surplus resources), skills (such as battlefield medicine and bomb disposal), and tactics (such as urban warfare and close-quarters combat) that are compatible with their purpose, often combining them with skills from other relevant fields such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sino-Soviet Split
The Sino-Soviet split was the breaking of political relations between the People's Republic of China and the Soviet Union caused by doctrinal divergences that arose from their different interpretations and practical applications of Marxism–Leninism, as influenced by their respective geopolitics during the Cold War of 1947–1991. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, Sino-Soviet debates about the interpretation of orthodox Marxism became specific disputes about the Soviet Union's policies of national de-Stalinization and international peaceful coexistence with the Western Bloc, which Chinese founding father Mao Zedong decried as revisionism. Against that ideological background, China took a belligerent stance towards the Western world, and publicly rejected the Soviet Union's policy of peaceful coexistence between the Western Bloc and Eastern Bloc. In addition, Beijing resented the Soviet Union's growing ties with India due to factors such as the Sino-Indian border dispute, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbean Sea, Gulf of Mexico, and Atlantic Ocean meet. Cuba is located east of the Yucatán Peninsula (Mexico), south of both the American state of Florida and the Bahamas, west of Hispaniola ( Haiti/Dominican Republic), and north of both Jamaica and the Cayman Islands. Havana is the largest city and capital; other major cities include Santiago de Cuba and Camagüey. The official area of the Republic of Cuba is (without the territorial waters) but a total of 350,730 km² (135,418 sq mi) including the exclusive economic zone. Cuba is the second-most populous country in the Caribbean after Haiti, with over 11 million inhabitants. The territory that is now Cuba was inhabited by the Ciboney people from the 4th millennium BC with the Gua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viet Cong
, , war = the Vietnam War , image = FNL Flag.svg , caption = The flag of the Viet Cong, adopted in 1960, is a variation on the flag of North Vietnam. Sometimes the lower stripe was green. , active = 1954–1959 ''(as southern Viet Minh cadres)'' , ideology = , position = Far-left , leaders = Liberation Army: Central Office: Liberation Front:Burchett, Wilfred (1963):Liberation Front: Formation of the NLF, ''The Furtive War'', International Publishers, New York. Governance: , merged_into = Vietnamese Fatherland Front , clans = , headquarters = , area = Indochina, with a focus on South Vietnam , predecessor = Viet Minh , successor = Vietnam Fatherland Front , allies = , opponents = , battles = See full list The Viet Cong, ; contraction of (Vietnamese communist) was an armed communist organization in South Vietnam, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making it the world's sixteenth-most populous country. Vietnam borders China to the north, and Laos and Cambodia to the west. It shares maritime borders with Thailand through the Gulf of Thailand, and the Philippines, Indonesia, and Malaysia through the South China Sea. Its capital is Hanoi and its largest city is Ho Chi Minh City (commonly known as Saigon). Vietnam was inhabited by the Paleolithic age, with states established in the first millennium BC on the Red River Delta in modern-day northern Vietnam. The Han dynasty annexed Northern and Central Vietnam under Chinese rule from 111 BC, until the first dynasty emerged in 939. Successive monarchical dynasties absorbed Chinese influences through Confucianism and Buddhism, and expanded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin America
Latin America or * french: Amérique Latine, link=no * ht, Amerik Latin, link=no * pt, América Latina, link=no, name=a, sometimes referred to as LatAm is a large cultural region in the Americas where Romance languages — languages derived from Latin — are predominantly spoken. The term was coined in the nineteenth century, to refer to regions in the Americas that were ruled by the Spanish, Portuguese and French empires. The term does not have a precise definition, but it is "commonly used to describe South America, Central America, Mexico, and the islands of the Caribbean." In a narrow sense, it refers to Spanish America plus Brazil (Portuguese America). The term "Latin America" is broader than categories such as ''Hispanic America'', which specifically refers to Spanish-speaking countries; and ''Ibero-America'', which specifically refers to both Spanish and Portuguese-speaking countries while leaving French and British excolonies aside. The term ''Latin America'' was f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area and 20% of its land area.Sayre, April Pulley (1999), ''Africa'', Twenty-First Century Books. . With billion people as of , it accounts for about of the world's human population. Africa's population is the youngest amongst all the continents; the median age in 2012 was 19.7, when the worldwide median age was 30.4. Despite a wide range of natural resources, Africa is the least wealthy continent per capita and second-least wealthy by total wealth, behind Oceania. Scholars have attributed this to different factors including geography, climate, tribalism, colonialism, the Cold War, neocolonialism, lack of democracy, and corruption. Despite this low concentration of wealth, recent economic expansion and the large and young population make Afr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |