|
Gromov Boundary
In mathematics, the Gromov boundary of a δ-hyperbolic space (especially a hyperbolic group) is an abstract concept generalizing the boundary sphere of hyperbolic space. Conceptually, the Gromov boundary is the set of all points at infinity. For instance, the Gromov boundary of the real line is two points, corresponding to positive and negative infinity. Definition There are several equivalent definitions of the Gromov boundary of a geodesic and proper δ-hyperbolic space. One of the most common uses equivalence classes of geodesic rays. Pick some point O of a hyperbolic metric space X to be the origin. A geodesic ray is a path given by an isometry \gamma: ,\infty)\rightarrow X such that each segment \gamma([0,t is a path of shortest length from O to \gamma(t). Two geodesics \gamma_1,\gamma_2 are defined to be equivalent if there is a constant K such that d(\gamma_1(t),\gamma_2(t))\leq K for all t. The equivalence class of \gamma is denoted gamma/math>. The Gromov boundary of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
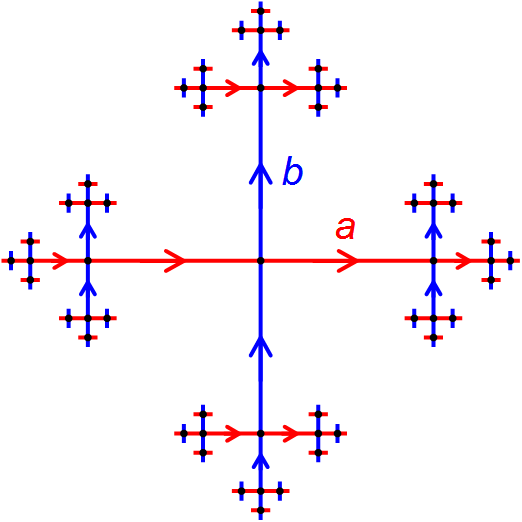
F2 Cayley Graph
F, or f, is the sixth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''ef'' (pronounced ), and the plural is ''efs''. History The origin of 'F' is the Semitic letter ''waw'' that represented a sound like or . Graphically it originally probably depicted either a hook or a club. It may have been based on a comparable Egyptian hieroglyph such as that which represented the word ''mace'' (transliterated as ḥ(dj)): T3 The Phoenician form of the letter was adopted into Greek as a vowel, ''upsilon'' (which resembled its descendant ' Y' but was also the ancestor of the Roman letters ' U', ' V', and ' W'); and, with another form, as a consonant, ''digamma'', which indicated the pronunciation , as in Phoenician. Latin 'F,' despite being pronounced differently, is ultimately descended from digamma and closely resembles it in form. After sound changes eliminated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quasi-isometry
In mathematics, a quasi-isometry is a function between two metric spaces that respects large-scale geometry of these spaces and ignores their small-scale details. Two metric spaces are quasi-isometric if there exists a quasi-isometry between them. The property of being quasi-isometric behaves like an equivalence relation on the class of metric spaces. The concept of quasi-isometry is especially important in geometric group theory, following the work of Gromov. Definition Suppose that f is a (not necessarily continuous) function from one metric space (M_1,d_1) to a second metric space (M_2,d_2). Then f is called a ''quasi-isometry'' from (M_1,d_1) to (M_2,d_2) if there exist constants A\ge 1, B\ge 0, and C\ge 0 such that the following two properties both hold:P. de la Harpe, ''Topics in geometric group theory''. Chicago Lectures in Mathematics. University of Chicago Press, Chicago, IL, 2000. #For every two points x and y in M_1, the distance between their images is up to the addit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acta Mathematica
''Acta Mathematica'' is a peer-reviewed open-access scientific journal covering research in all fields of mathematics. According to Cédric Villani, this journal is "considered by many to be the most prestigious of all mathematical research journals".. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 4.273, ranking it 5th out of 330 journals in the category "Mathematics". Publication history The journal was established by Gösta Mittag-Leffler in 1882 and is published by Institut Mittag-Leffler, a research institute for mathematics belonging to the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. The journal was printed and distributed by Springer from 2006 to 2016. Since 2017, Acta Mathematica has been published electronically and in print by International Press. Its electronic version is open access without publishing fees. Poincaré episode The journal's "most famous episode" (according to Villani) concerns Henri Poincaré, who won a prize offered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometric Group Action
In mathematics, specifically geometric group theory, a geometric group action is a certain type of action of a discrete group on a metric space. Definition In geometric group theory, a geometry is any proper, geodesic metric space. An action of a finitely-generated group ''G'' on a geometry ''X'' is geometric if it satisfies the following conditions: # Each element of ''G'' acts as an isometry of ''X''. # The action is cocompact, i.e. the quotient space ''X''/''G'' is a compact space. # The action is properly discontinuous, with each point having a finite stabilizer. Uniqueness If a group ''G'' acts geometrically upon two geometries ''X'' and ''Y'', then ''X'' and ''Y'' are quasi-isometric. Since any group acts geometrically on its own Cayley graph, any space on which ''G'' acts geometrically is quasi-isometric to the Cayley graph of ''G''. Examples Cannon's conjecture states that any hyperbolic group In group theory, more precisely in geometric group theory, a hyperbolic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikhail Gromov (mathematician)
Mikhael Leonidovich Gromov (also Mikhail Gromov, Michael Gromov or Misha Gromov; russian: link=no, Михаи́л Леони́дович Гро́мов; born 23 December 1943) is a Russian-French mathematician known for his work in geometry, analysis and group theory. He is a permanent member of IHÉS in France and a professor of mathematics at New York University. Gromov has won several prizes, including the Abel Prize in 2009 "for his revolutionary contributions to geometry". Biography Mikhail Gromov was born on 23 December 1943 in Boksitogorsk, Soviet Union. His Russian father Leonid Gromov and his Jewish mother Lea Rabinovitz were pathologists. His mother was the cousin of World Chess Champion Mikhail Botvinnik, as well as of the mathematician Isaak Moiseevich Rabinovich. Gromov was born during World War II, and his mother, who worked as a medical doctor in the Soviet Army, had to leave the front line in order to give birth to him. When Gromov was nine years old, his mother ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compact (topology)
In mathematics, specifically general topology, compactness is a property that seeks to generalize the notion of a closed and bounded subset of Euclidean space by making precise the idea of a space having no "punctures" or "missing endpoints", i.e. that the space not exclude any ''limiting values'' of points. For example, the open interval (0,1) would not be compact because it excludes the limiting values of 0 and 1, whereas the closed interval ,1would be compact. Similarly, the space of rational numbers \mathbb is not compact, because it has infinitely many "punctures" corresponding to the irrational numbers, and the space of real numbers \mathbb is not compact either, because it excludes the two limiting values +\infty and -\infty. However, the ''extended'' real number line ''would'' be compact, since it contains both infinities. There are many ways to make this heuristic notion precise. These ways usually agree in a metric space, but may not be equivalent in other topologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proper Metric Space
This is a glossary of some terms used in Riemannian geometry and metric geometry — it doesn't cover the terminology of differential topology. The following articles may also be useful; they either contain specialised vocabulary or provide more detailed expositions of the definitions given below. * Connection * Curvature * Metric space * Riemannian manifold See also: * Glossary of general topology * Glossary of differential geometry and topology * List of differential geometry topics Unless stated otherwise, letters ''X'', ''Y'', ''Z'' below denote metric spaces, ''M'', ''N'' denote Riemannian manifolds, , ''xy'', or , xy, _X denotes the distance between points ''x'' and ''y'' in ''X''. Italic ''word'' denotes a self-reference to this glossary. ''A caveat'': many terms in Riemannian and metric geometry, such as ''convex function'', ''convex set'' and others, do not have exactly the same meaning as in general mathematical usage. __NOTOC__ A Alexandrov space a gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neighborhood Basis
In topology and related areas of mathematics, the neighbourhood system, complete system of neighbourhoods, or neighbourhood filter \mathcal(x) for a point x in a topological space is the collection of all neighbourhoods of x. Definitions Neighbourhood of a point or set An of a point (or subset) x in a topological space X is any open subset U of X that contains x. A is any subset N \subseteq X that contains open neighbourhood of x; explicitly, N is a neighbourhood of x in X if and only if there exists some open subset U with x \in U \subseteq N. Equivalently, a neighborhood of x is any set that contains x in its topological interior. Importantly, a "neighbourhood" does have to be an open set; those neighbourhoods that also happen to be open sets are known as "open neighbourhoods." Similarly, a neighbourhood that is also a closed (respectively, compact, connected, etc.) set is called a (respectively, , , etc.). There are many other types of neighbourhoods that are used in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CAT(0) Space
In mathematics, a \mathbf(k) space, where k is a real number, is a specific type of metric space. Intuitively, triangles in a \operatorname(k) space are "slimmer" than corresponding "model triangles" in a standard space of constant curvature k. In a \operatorname(k) space, the curvature is bounded from above by k. A notable special case is k=0; complete \operatorname(0) spaces are known as "Hadamard spaces" after the French mathematician Jacques Hadamard. Originally, Aleksandrov called these spaces “\mathfrak_k domain”. The terminology \operatorname(k) was coined by Mikhail Gromov in 1987 and is an acronym for Élie Cartan, Aleksandr Danilovich Aleksandrov and Victor Andreevich Toponogov (although Toponogov never explored curvature bounded above in publications). Definitions For a real number k, let M_k denote the unique complete simply connected surface (real 2-dimensional Riemannian manifold) with constant curvature k. Denote by D_k the diameter of M_k, which is \i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complete Space
In mathematical analysis, a metric space is called complete (or a Cauchy space) if every Cauchy sequence of points in has a limit that is also in . Intuitively, a space is complete if there are no "points missing" from it (inside or at the boundary). For instance, the set of rational numbers is not complete, because e.g. \sqrt is "missing" from it, even though one can construct a Cauchy sequence of rational numbers that converges to it (see further examples below). It is always possible to "fill all the holes", leading to the ''completion'' of a given space, as explained below. Definition Cauchy sequence A sequence x_1, x_2, x_3, \ldots in a metric space (X, d) is called Cauchy if for every positive real number r > 0 there is a positive integer N such that for all positive integers m, n > N, d\left(x_m, x_n\right) < r. Complete space A metric space is complete if any of the following equivalent conditions are satisfied: :#Every |
Menger Sponge
In mathematics, the Menger sponge (also known as the Menger cube, Menger universal curve, Sierpinski cube, or Sierpinski sponge) is a fractal curve. It is a three-dimensional generalization of the one-dimensional Cantor set and two-dimensional Sierpinski carpet. It was first described by Karl Menger in 1926, in his studies of the concept of topological dimension. Construction The construction of a Menger sponge can be described as follows: # Begin with a cube. # Divide every face of the cube into nine squares, like Rubik's Cube. This sub-divides the cube into 27 smaller cubes. # Remove the smaller cube in the middle of each face, and remove the smaller cube in the center of the more giant cube, leaving 20 smaller cubes. This is a level-1 Menger sponge (resembling a void cube). # Repeat steps two and three for each of the remaining smaller cubes, and continue to iterate ''ad infinitum''. The second iteration gives a level-2 sponge, the third iteration gives a level-3 sponge, and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compact Riemann Surface
In mathematics, particularly in complex analysis, a Riemann surface is a connected one-dimensional complex manifold. These surfaces were first studied by and are named after Bernhard Riemann. Riemann surfaces can be thought of as deformed versions of the complex plane: locally near every point they look like patches of the complex plane, but the global topology can be quite different. For example, they can look like a sphere or a torus or several sheets glued together. The main interest in Riemann surfaces is that holomorphic functions may be defined between them. Riemann surfaces are nowadays considered the natural setting for studying the global behavior of these functions, especially multi-valued functions such as the square root and other algebraic functions, or the logarithm. Every Riemann surface is a two-dimensional real analytic manifold (i.e., a surface), but it contains more structure (specifically a complex structure) which is needed for the unambiguous definition of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)