|
Grevillea Oncogyne
''Grevillea oncogyne'' is a species of flowering plant in the family Proteaceae and is endemic to inland areas of Western Australia. It is an erect to spreading shrub with linear, sometimes lobed leaves, and clusters of red or pinkish red flowers. Description ''Grevillea oncogyne'' is an erect to spreading shrub that typically grows to a height of and sometimes forms a lignotuber. Its leaves are linear, mostly long and wide, sometimes with two to four linear lobes long. The edges of the leaves are rolled under, obscuring the lower surface. The flowers are arranged in leaf axils or on old wood on a silky-hairy rachis long. The flowers are red or pinkish red, the pistil long. Flowering mainly occurs from October to December and the fruit a follicle long with prominent ridges on one side. Taxonomy ''Grevillea oncogyne'' was first formally described in 1904 by Ludwig Diels in Ernst Georg Pritzel's ''Botanische Jahrbücher für Systematik, Pflanzengeschichte und Pflanzengeog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian National Botanic Gardens
The Australian National Botanic Gardens (ANBG) is a heritage-listed botanical garden located in , Canberra, in the Australian Capital Territory, Australia. Established in 1949, the Gardens is administered by the Australian Government's Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment. The botanic gardens was added to the Commonwealth Heritage List on 22 June 2004. The botanic gardens is the largest living collection of native Australian flora. The mission of the ANBG is to "study and promote Australia's flora". The gardens maintains a wide variety of botanical resources for researchers and cultivates native plants threatened in the wild. The herbarium code for the Australian National Botanic Gardens is ''CANB''. History When Canberra was being planned in the 1930s, the establishment of the gardens was recommended in a report in 1933 by the Advisory Council of Federal Capital Territory. In 1935, The Dickson Report set forth a framework for their development. A large site fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salmon Gums, Western Australia
Salmon Gums is a small town in Western Australia located 106 km north of Esperance on the Coolgardie-Esperance Highway. The name is derived from a prominent stretch of '' Eucalyptus salmonophloia'' (Salmon Gum) trees which formed a landmark in the town's early days. The town is part of the Shire of Esperance. At the 2016 census, Salmon Gums had a population of 191. The surrounding areas produce wheat and other cereal crops. The town is a receival site for Cooperative Bulk Handling. History The first potential use of a townsite was as a watering spot for the proposed Esperance to Norseman Railway, since Salmon Gums is roughly halfway between these two towns. Land for a town-site was set aside in 1912 and the name was recommended in 1916. This land lay within the tribal boundaries of the indigenous Kalaako. The town was gazetted in 1925, when the Esperance to Salmon Gums section of the railway was completed. Settlement of the area received a boost after the First World ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eudicots Of Western Australia
The eudicots, Eudicotidae, or eudicotyledons are a clade of flowering plants mainly characterized by having two seed leaves upon germination. The term derives from Dicotyledons. Traditionally they were called tricolpates or non-magnoliid dicots by previous authors. The botanical terms were introduced in 1991 by evolutionary botanist James A. Doyle and paleobotanist Carol L. Hotton to emphasize the later evolutionary divergence of tricolpate dicots from earlier, less specialized, dicots. Numerous familiar plants are eudicots, including many common food plants, trees, and ornamentals. Some common and familiar eudicots include sunflower, dandelion, forget-me-not, cabbage, apple, buttercup, maple, and macadamia. Most leafy trees of midlatitudes also belong to eudicots, with notable exceptions being magnolias and tulip trees which belong to magnoliids, and ''Ginkgo biloba'', which is not an angiosperm. Description The close relationships among flowering plants with tricolpate po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteales Of Australia
Proteales is an order of flowering plants consisting of three (or four) families. The Proteales have been recognized by almost all taxonomists. The representatives of the Proteales are very different from each other. The order contains plants that do not look alike at all. What they have in common is seeds with little or no endosperm. The ovules are often atropic. Families In the classification system of Dahlgren the Proteales were in the superorder Proteiflorae (also called Proteanae). The APG II system of 2003 also recognizes this order, and places it in the clade eudicots with this circumscription: * order Proteales :* family Nelumbonaceae :* family Proteaceae family Platanaceae">Platanaceae.html" ;"title=" family Platanaceae"> family Platanaceae with "+ ..." = optionally separate family (that may be split off from the preceding family). The APG III system of 2009 followed this same approach, but favored the narrower circumscription of the three families, firmly reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grevillea
''Grevillea'', commonly known as spider flowers, is a genus of about 360 species of evergreen flowering plants in the family Proteaceae. Plants in the genus ''Grevillea'' are shrubs, rarely trees, with the leaves arranged alternately along the branches, the flowers zygomorphic, arranged in racemes at the ends of branchlets, and the fruit a follicle that splits down one side only, releasing one or two seeds. Description Plants in the genus ''Grevillea'' are shrubs, rarely small trees with simple or compound leaves arranged alternately along the branchlets. The flowers are zygomorphic and typically arranged in pairs along a sometimes branched raceme at the ends of branchlets. The flowers are bisexual, usually with four tepals in a single whorl. There are four stamens and the gynoecium has a single carpel. The fruit is a thin-walled follicle that splits down only one side, releasing one or two seeds before the next growing season. Taxonomy The genus ''Grevillea'' was first forma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Grevillea Species
This is a list of ''Grevillea'' species accepted by Plants of the World Online as of December 2021: A *'' Grevillea acacioides'' C.A.Gardner ex McGill. (W.A.) *'' Grevillea acanthifolia'' A.Cunn. – Acanthus-leaved grevillea (N.S.W.) *:''Grevillea acanthifolia'' A.Cunn. subsp. ''acanthifolia'' *:''Grevillea acanthifolia'' subsp. ''paludosa'' Makinson & Albr. — bog grevillea *:''Grevillea acanthifolia'' subsp. ''stenomera'' (F.Muell. ex Benth.) McGill. *'' Grevillea acerata'' McGill. (N.S.W.) *'' Grevillea acrobotrya'' Meisn. (W.A.) *'' Grevillea acropogon'' Makinson (W.A.) *'' Grevillea acuaria'' F.Muell. ex Benth. (W.A.) *'' Grevillea adenotricha'' McGill. (W.A.) *'' Grevillea agrifolia'' A.Cunn. ex R.Br. — blue grevillea (W.A., N.T.) *:''Grevillea agrifolia'' A.Cunn. ex R.Br. subsp. ''agrifolia'' *:''Grevillea agrifolia'' subsp. ''microcarpa'' (Olde & Marriott) Makinson *'' Grevillea albiflora'' C.T.White – white spider flower (N.S.W., Qld., S.A., N.T.) *'' Grevillea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Department Of Biodiversity, Conservation And Attractions (Western Australia)
The Department of Biodiversity, Conservation and Attractions (DBCA) is the Government of Western Australia, Western Australian government department responsible for managing lands and waters described in the ''Conservation and Land Management Act 1984'', the ''Rottnest Island Authority Act 1987'', the ''Swan and Canning Rivers Management Act 2006'', the ''Botanic Gardens and Parks Authority Act 1998'', and the ''Zoological Parks Authority Act 2001'', and implementing the state's conservation and environment legislation and regulations. The Department reports to the Minister for Environment and the Minister for Tourism. DBCA was formed on 1 July 2017 by the merger of the Department of Parks and Wildlife (Western Australia), Department of Parks and Wildlife (DPaW), the Botanic Gardens and Parks Authority, the Zoological Parks Authority and the Rottnest Island Authority. The former DPaW became the Parks and Wildlife Service. Status Parks and Wildlife Service The Formerly the Depar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mallee Bioregion
Mallee, also known as Roe Botanical District, is a biogeographic region in southern Western Australia. Located between the Esperance Plains, Avon Wheatbelt and Coolgardie bioregions, it has a low, gently undulating topography, a semi-arid mediterranean climate, and extensive ''Eucalyptus'' mallee vegetation. It has an area of . About half of the region has been cleared for intensive agriculture. Recognised as a region under the Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA), it was first defined by John Stanley Beard in 1980. Geography and geology The Mallee region has a complex shape with tortuous boundaries, but may be roughly approximated as the triangular area south of a line from Bruce Rock to Eyre, but not within 40 kilometres (25 mi) of the south coast, except at its eastern limits. It has an area of about 79000 square kilometres (31000 mi²), making it about a quarter of the South West Botanic Province, 3% of the state, and 1% of Australia. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esperance Plains
Esperance Plains, also known as Eyre Botanical District, is a biogeographic region in southern Western Australia on the south coast between the Avon Wheatbelt and Hampton bioregions, and bordered to the north by the Mallee region. It is a plain punctuated by granite and quartz outcrops and ranges, with a semi-arid Mediterranean climate and vegetation consisting mostly of mallee-heath and proteaceous scrub. About half of the region has been cleared for intensive agriculture. Recognised as a bioregion under the Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA), it was first defined by John Stanley Beard in 1980. Geography and geology The Esperance Plains may be roughly approximated as the land within of the coast between Albany and Point Culver on the south coast of Western Australia. It has an area of about , making it about 9% of the South West Province, 1% of the state, and 0.3% of Australia. It is bounded to the north by the Mallee region, and to the west by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
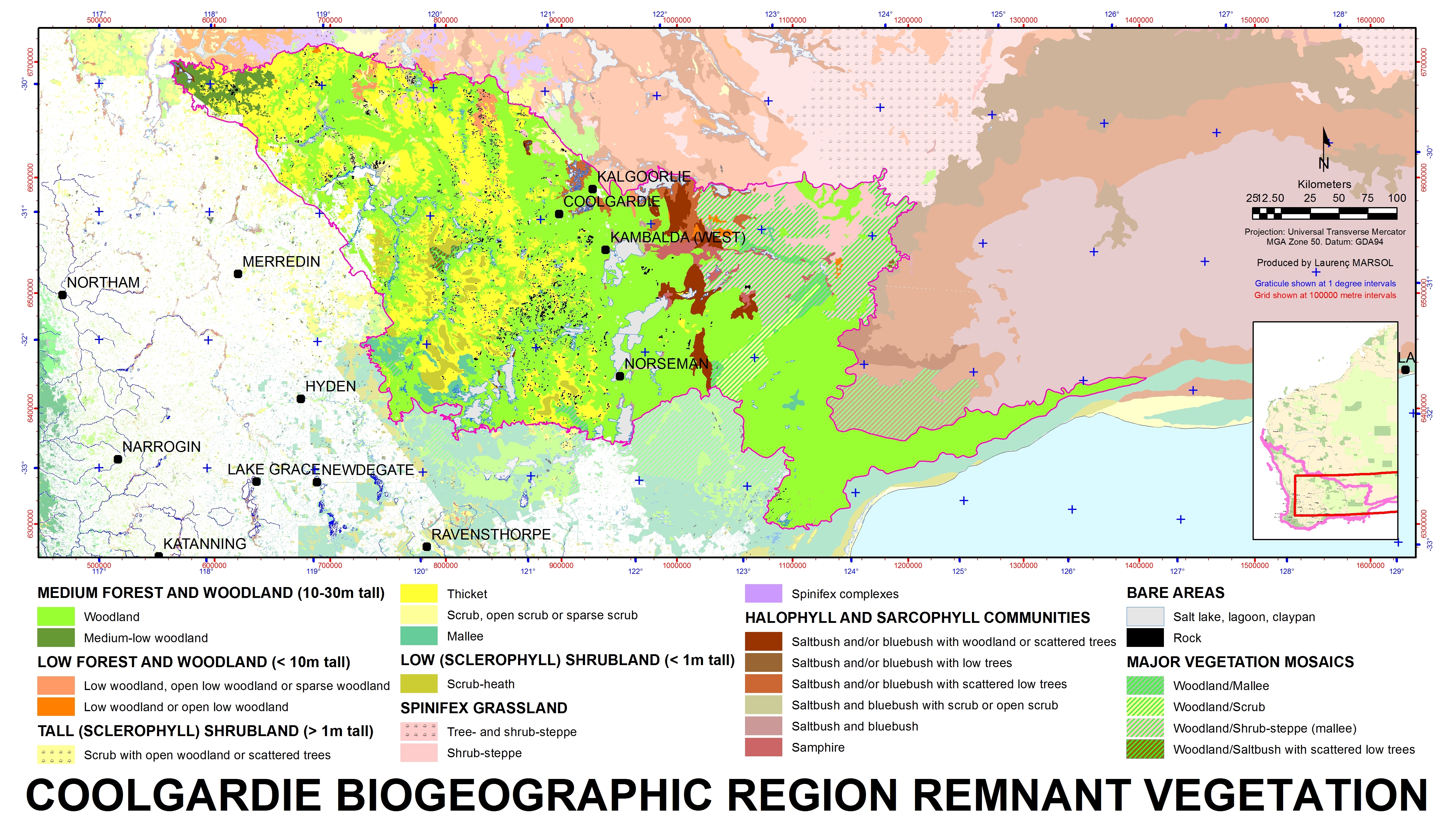
Coolgardie Bioregion
Coolgardie is an Australian bioregion consisting of an area of low hills and plains of infertile sandy soil in Western Australia. It has an area of . It includes much of the Great Western Woodlands. Location and description This is a transition zone between the Mediterranean climate of Australia's south-west coast and the country's dry interior. The poor soil makes it unsuitable for agriculture but Coolgardie has been a gold and nickel mining area. It is bounded on the north by the arid Murchison bioregion, characterised by open Mulga woodlands and steppe. The low shrublands of the arid Nullarbor Plain lie to the east. The Mallee bioregion adjoins Coolgardie on the south. The Avon Wheatbelt bioregion is to the west. The Coolgardie bioregion, together with the coastal Hampton bioregion to the southeast, constitute the Coolgardie woodlands ecoregion defined by the World Wildlife Fund. Flora and fauna The low hills are home to woodland of endemic species of eucalyptus whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avon Wheatbelt
The Avon Wheatbelt is a bioregion in Western Australia. It has an area of . It is considered part of the larger Southwest Australia savanna ecoregion. Geography The Avon Wheatbelt bioregion is mostly a gently undulating landscape with low relief. It lies on the Yilgarn Craton, an ancient block of crystalline rock, which was uplifted in the Tertiary and dissected by rivers. The craton is overlain by laterite deposits, which in places have decomposed into yellow sandplains, particularly on low hills. Steep-sided erosional gullies, known as breakaways, are common. Beecham, Brett (2001). "Avon Wheatbelt 2 (AW2 - Re-juvenated Drainage subregion)" in ''A Biodiversity Audit of Western Australia’s 53 Biogeographical Subregions in 2002''. Department of Conservation and Land Management, Government of Western Australia, November 2001. Accessed 15 May 2022/ref> In the south and west (the Katanning subregion), streams are mostly perennial, and feed rivers which drain westwards to empty in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyden, Western Australia
The town of Hyden is located east-southeast of Perth, Western Australia in the Shire of Kondinin. Hyden is home to Wave Rock, Mulka's Cave and Hippos Yawn, all popular local tourist attractions. The traditional owners of the area are the Aboriginal Australian group the Njakinjaki people, who have inhabited the region for thousands of years. The many granite outcrops, land formations, waterways as well as flora and fauna are still culturally significant to them. Sandalwood cutters were thought to be the earliest European visitors in the area. The land in the surrounding area was opened up for agriculture in the 1920s. A railway was built between Kondinin and Hyden Rock in 1930. The townsite was gazetted in 1932 following demand for land around the railway terminus. The first wheat crop was harvested in Hyden in 1927. The Hyden Progress Association was established prior to 1931 when the town was home to about 100 settlers. In 1931 the town had another large wheat crop, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |