|
Greater Bengal
Greater Bangladesh ( bn, বৃহত্তর বাংলাদেশ, Brihôttôr Bangladesh; among other names, see below) is a theory that the People's Republic of Bangladesh has aspirations of territorial expansion, to include the Indian states of West Bengal, Tripura and Assam's Barak valley, Hojai and Undivided Goalpara as part of its own territory. Some proponents also claim that Sheikh Hasina, Prime minister of Bangladesh and Mamata Banerjee, Chief minister of West Bengal, are involved in trying to create Greater Bangladesh. Names It is known by various names in Bengali. bn, বৃহত্তর বাংলাদেশ, Brihôttôr Bangladesh;Col. Ved Prakash, ''Terrorism in India's north-east: a gathering storm'' (Volume 1),Kalpaz Publications, 2008, bn, বৃহৎ বাংলাদেশ, Brihôt Bangladesh; bn, মহাবাংলাদেশ, Môhabangladesh; bn, বড় বাঙ্গালা, Boro Bangala and bn, বিশাল বাংলা, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
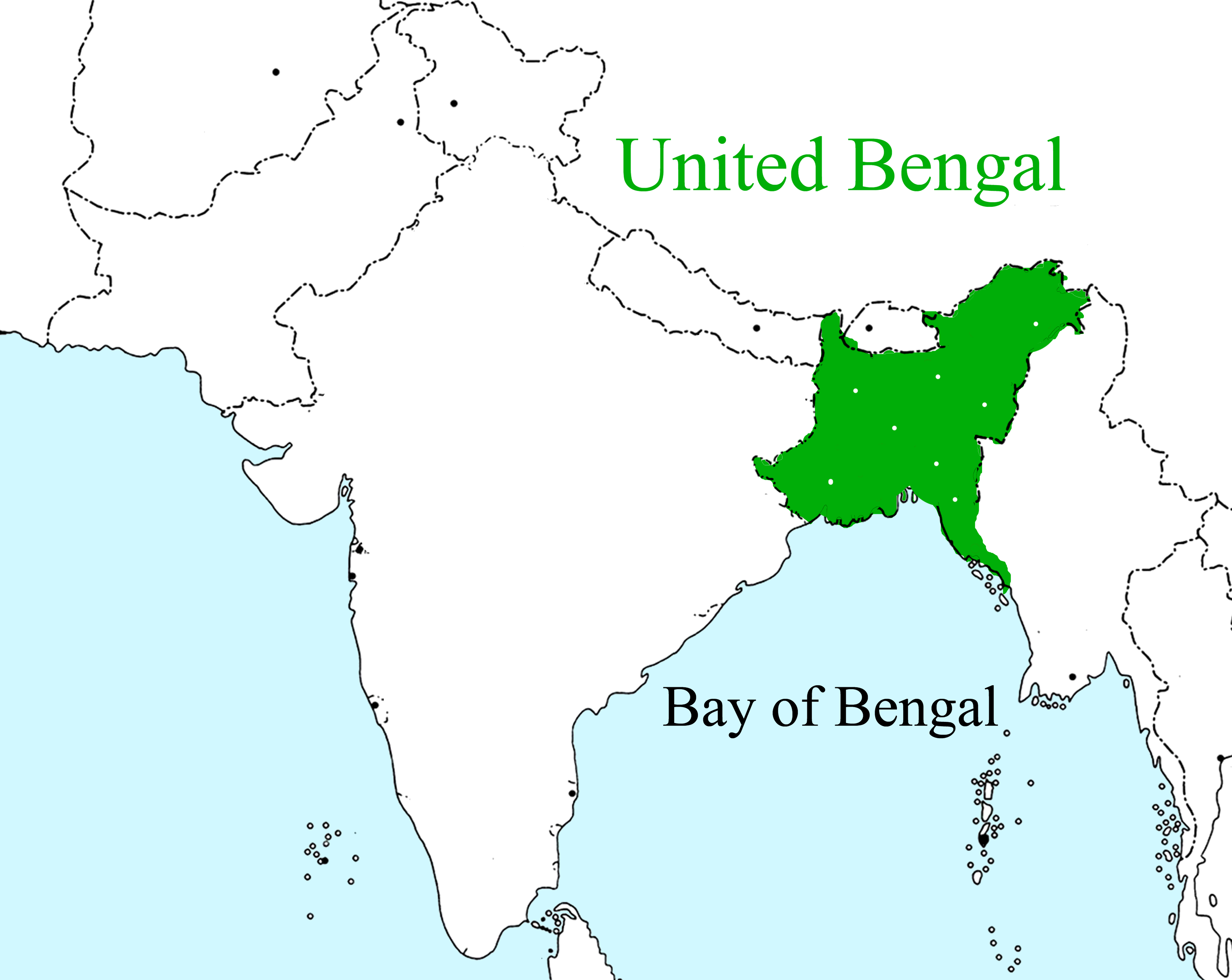
United Bengal
United Bengal was a proposal to transform Bengal Province into an undivided, sovereign state at the time of the Partition of India in 1947. It sought to prevent the division of Bengal on religious grounds. The proposed state was to be called the Free State of Bengal. A confessionalist political system was mooted. The proposal was not put up for a vote. The British government proceeded to partition Bengal in accordance with the Mountbatten Plan and Radcliffe Line. History On 27 April 1947, Huseyn Shaheed Suhrawardy, the Prime Minister of Bengal and a Muslim League leader, addressed a press conference in New Delhi outlining his opposition to the looming partition of Bengal under the British government's plans. At the press conference, Suhrawardy made an impassioned plea for setting aside religious differences in order to create an "independent, undivided, and sovereign Bengal". Suhrawardy, a lawyer from Midnapore, did not want to lose western Bengal to the opposing side ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengal Region
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predominantly covering present-day Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal. Geographically, it consists of the Ganges-Brahmaputra delta system, the largest river delta in the world and a section of the Himalayas up to Nepal and Bhutan. Dense woodlands, including hilly rainforests, cover Bengal's northern and eastern areas, while an elevated forested plateau covers its central area; the highest point is at Sandakphu. In the littoral southwest are the Sundarbans, the world's largest mangrove forest. The region has a monsoon climate, which the Bengali calendar divides into six seasons. Bengal, then known as Gangaridai, was a leading power in ancient South Asia, with extensive trade networks forming connections to as far away as Roman Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctive varieties of the Chinese language. The estimated 1.4 billion Han Chinese people, worldwide, are primarily concentrated in the People's Republic of China (including Mainland China, Hong Kong and Macau) where they make up about 92% of the total population. In the Republic of China (Taiwan), they make up about 97% of the population. People of Han Chinese descent also make up around 75% of the total population of Singapore. Originating from Northern China, the Han Chinese trace their cultural ancestry to the Huaxia, the confederation of agricultural tribes living along the Yellow River. This collective Neolithic confederation included agricultural tribes Hua and Xia, hence the name. They settled along the Central Plains around the middle and lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengalis
Bengalis (singular Bengali bn, বাঙ্গালী/বাঙালি ), also rendered as Bangalee or the Bengali people, are an Indo-Aryan peoples, Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the Bengal region of South Asia. The current population is divided between the independent country Bangladesh and the Indian states of West Bengal, Tripura and parts of Assam, Meghalaya and Manipur. Most of them speak Bengali language, Bengali, a language from the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language family. Bengalis are the List of contemporary ethnic groups, third-largest ethnic group in the world, after the Han Chinese and Arabs. Thus, they are the largest ethnic group within the Indo-Europeans and the largest ethnic group in South Asia. Apart from Bangladesh and the Indian states of West Bengal, Tripura, Manipur, and Assam's Barak Valley, Bengali-majority populations also reside in India's union territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population Density
Population density (in agriculture: standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geographical term.Matt RosenberPopulation Density Geography.about.com. March 2, 2011. Retrieved on December 10, 2011. In simple terms, population density refers to the number of people living in an area per square kilometre, or other unit of land area. Biological population densities Population density is population divided by total land area, sometimes including seas and oceans, as appropriate. Low densities may cause an extinction vortex and further reduce fertility. This is called the Allee effect after the scientist who identified it. Examples of the causes of reduced fertility in low population densities are * Increased problems with locating sexual mates * Increased inbreeding Human densities Population density is the number of people per unit of area, usuall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Bengal
ur, , common_name = East Bengal , status = Province of the Dominion of Pakistan , p1 = Bengal Presidency , flag_p1 = Flag of British Bengal.svg , s1 = East Pakistan , flag_s1 = Flag of Pakistan.svg , national_anthem = , image_map = Bangladesh on the globe (Bangladesh centered).svg , image_flag = , flag_caption = , image_coat = , capital = Dacca (currently known as Dhaka) , common_languages = Bengali, Urdu and English , religion = , government_type = Parliamentary constitutional monarchy , legislature = Legislative Assembly , date_start = 14 August , year_start = 1947 , event_start = Partition of Bengal , date_end = 14 October , year_end = 19551970 – 1971 , event_end = One ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animists
Animism (from Latin: ' meaning 'breath, spirit, life') is the belief that objects, places, and creatures all possess a distinct spiritual essence. Potentially, animism perceives all things—animals, plants, rocks, rivers, weather systems, human handiwork, and perhaps even words—as animated and alive. Animism is used in the anthropology of religion, as a term for the belief system of many Indigenous peoples, especially in contrast to the relatively more recent development of organized religions. Animism focuses on the metaphysical universe, with a specific focus on the concept of the immaterial soul. Although each culture has its own mythologies and rituals, animism is said to describe the most common, foundational thread of indigenous peoples' "spiritual" or "supernatural" perspectives. The animistic perspective is so widely held and inherent to most indigenous peoples, that they often do not even have a word in their languages that corresponds to "animism" (or even "religio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengali Christians
Bengali Christians ( bn, বাঙালি খ্রিস্টান) are adherents of Christianity among the Bengali people. Christianity took root in Bengal after the arrival of Portuguese voyagers in the 16th century. It witnessed further conversions among the Bengali upper-caste elite during the 19th century Bengali Renaissance. Bengali Christians have made significant contributions to Bengali culture, commerce and society. The region is home to venerable Christian missionary institutions, including the Missionaries of Charity founded by Mother Teresa. History Christianity was established in Bengal by the Portuguese missionaries in the 16th century. Basilica of the Holy Rosary, Bandel is the first church known to have been constructed in 1599 at Hugli-Chuchura in the Hooghly district of West Bengal, India. Another is known to have been established from the historical records was in Ishwaripore, Jessore (erstwhile Chandecan) in 1600 under patronage of Pratapaditya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengali Buddhists
Bengali Buddhists ( bn, বাঙালি বৌদ্ধ) are a religious subgroup of the Bengalis who adhere to or practice the religion of Buddhism. Bengali Buddhist people mainly live in Bangladesh and Indian states West Bengal and Tripura. Buddhism has a rich ancient heritage in the Bengal. The region was a bastion of the ancient Buddhist Mauryan and Palan empires, when the Mahayana and Vajrayana schools flourished. South-Eastern Bengal was ruled by the medieval Buddhist Kingdom of Mrauk U during the 16th and 17th centuries. The British Raj influenced the emergence of modern community. Today, Bengali Buddhists are followers of Theravāda Buddhism. History Ancient Bengal was a center of Buddhist learning and art. Buddhist artifacts have been excavated throughout the region, particularly in Wari-Bateshwar, Chandraketugarh, Paharpur, Mahasthangarh and Mainamati. The Mauryan Empire led by Ashoka extended its suzerainty to the region in the 2nd century BCE. Ashoka played a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengali Hindus
Bengali Hindus ( bn, বাঙ্গালী হিন্দু/বাঙালি হিন্দু, translit=Bāṅgālī Hindu/Bāṅāli Hindu) are an ethnoreligious population who make up the majority in the Indian states of West Bengal, Tripura, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Jharkhand, and Assam's Barak Valley region. In Bangladesh, they form the largest minority. They are adherents of Hinduism and are native to the Bengal region in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent. Comprising about one-thirds of the global Bengali population, they are the second-largest ethnic group among Hindus after Hindustani Hindus. Bengali Hindus speak Bengali, which belongs to the Indo-Aryan language family and adhere to Shaktism (majority, the Kalikula tradition) or Vaishnavism (minority, Gaudiya Vaishnavism and Vaishnava-Sahajiya) of their native religion Hinduism with some regional deities. There are significant numbers of Bengali-speaking Hindus in different Indian states. Aro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengali Muslims
Bengali Muslims ( bn, বাঙালি মুসলমান; ) are adherents of Islam who ethnically, linguistically and genealogically identify as Bengalis. Comprising about two-thirds of the global Bengali population, they are the second-largest ethnic group among Muslims after Arabs. Bengali Muslims make up the majority of Bangladesh's citizens, and are the largest minority in the Indian states of West Bengal, Tripura and Assam. They speak or identify the Bengali language as their mother tongue. The majority of Bengali Muslims are Sunnis who follow the Hanafi school of jurisprudence. The Bengal region was a leading power of the medieval Islamic East. European traders identified the Bengal Sultanate as "the richest country to trade with". During Emperor Aurangazeb's rule, the Bengal Subah and its citizens in eastern Bengal, chiefly Muslims, had the highest standard of living and real wages in the world. Bengal viceroy Muhammad Azam Shah assumed the imperial throne. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)