|
Gray Isometry
The reflected binary code (RBC), also known as reflected binary (RB) or Gray code after Frank Gray, is an ordering of the binary numeral system such that two successive values differ in only one bit (binary digit). For example, the representation of the decimal value "1" in binary would normally be "" and "2" would be "". In Gray code, these values are represented as "" and "". That way, incrementing a value from 1 to 2 requires only one bit to change, instead of two. Gray codes are widely used to prevent spurious output from electromechanical switches and to facilitate error correction in digital communications such as digital terrestrial television and some cable TV systems. Motivation and name Many devices indicate position by closing and opening switches. If that device uses natural binary codes, positions 3 and 4 are next to each other but all three bits of the binary representation differ: : The problem with natural binary codes is that physical switches are not ideal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
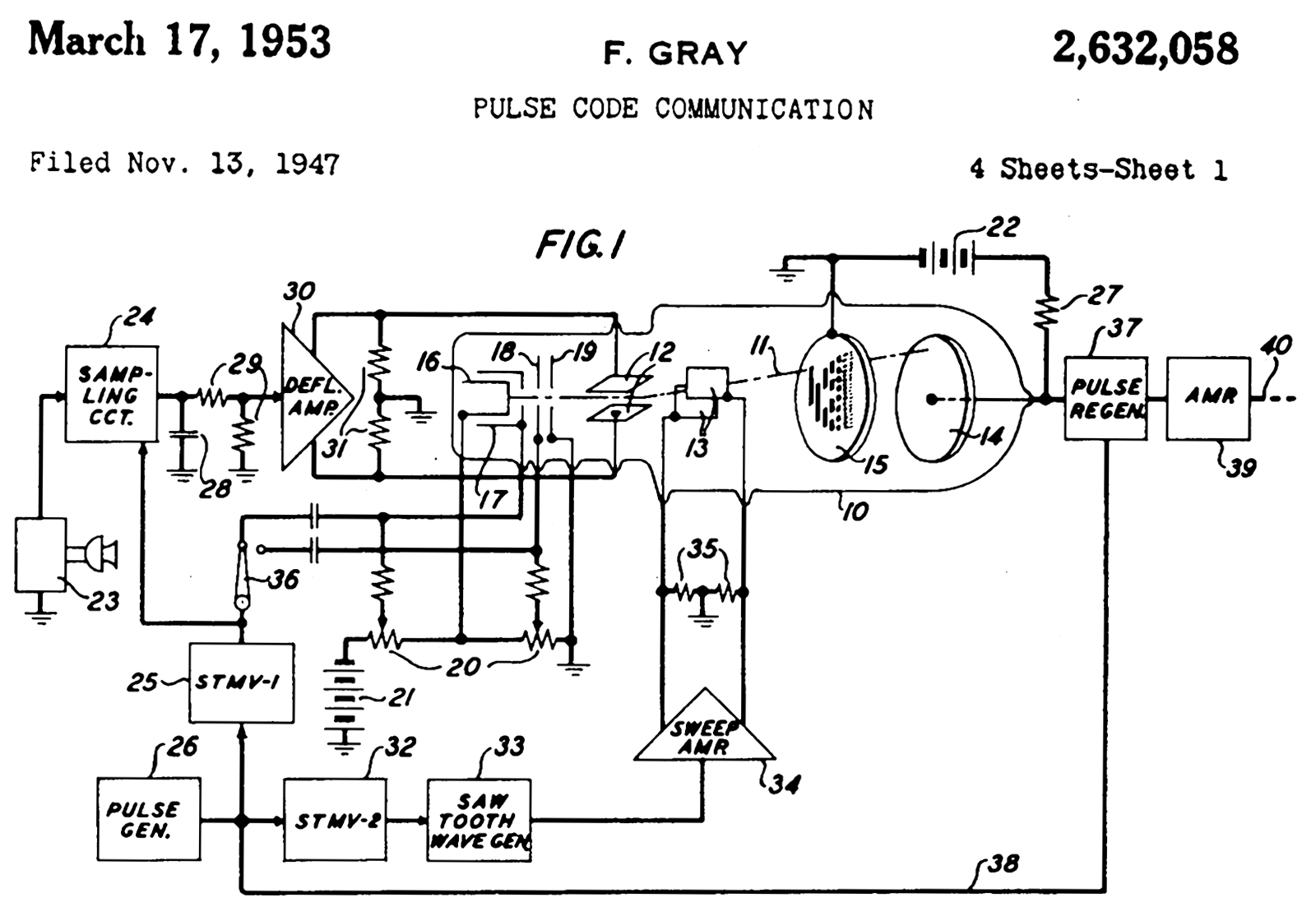
Frank Gray (researcher)
Frank Gray (13 September 1887 – 23 May 1969) was a physicist and researcher at Bell Labs who made numerous innovations in television, both mechanical and electronic, and is remembered for the Gray code. The Gray code, or reflected binary code (RBC), appearing in Gray's 1953 patent, is a binary numeral system often used in electronics, but with many applications in mathematics. Gray conducted pioneering research on the development of television; he proposed an early form of " flying spot scanner" for early TV systems in 1927, and helped develop a two-way mechanically scanned TV system in 1930. With Pierre Mertz, Gray wrote the classic paper on the mathematics of raster scan systems in 1934. He later participated in the early days of the digital revolution, with Raymond W. Sears, William M. Goodall, John Robinson Pierce, and others at Bell Labs, by providing the binary code used by Sears in his PCM tube, a beam deflection tube of the type that Sears and Pierce collaborated o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gray Code Number Line Arcs
Grey (more common in British English) or gray (more common in American English) is an intermediate color between black and white. It is a neutral or achromatic color, meaning literally that it is "without color", because it can be composed of black and white. It is the color of a cloud-covered sky, of ash and of lead. The first recorded use of ''grey'' as a color name in the English language was in 700 CE.Maerz and Paul ''A Dictionary of Color'' New York:1930 McGraw-Hill Page 196 ''Grey'' is the dominant spelling in European and Commonwealth English, while ''gray'' has been the preferred spelling in American English; both spellings are valid in both varieties of English. In Europe and North America, surveys show that grey is the color most commonly associated with neutrality, conformity, boredom, uncertainty, old age, indifference, and modesty. Only one percent of respondents chose it as their favorite color. Etymology ''Grey'' comes from the Middle English or , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin Gardner
Martin Gardner (October 21, 1914May 22, 2010) was an American popular mathematics and popular science writer with interests also encompassing scientific skepticism, micromagic, philosophy, religion, and literatureespecially the writings of Lewis Carroll, L. Frank Baum, and G. K. Chesterton.Martin (2010) He was also a leading authority on Lewis Carroll. '' The Annotated Alice'', which incorporated the text of Carroll's two Alice books, was his most successful work and sold over a million copies. He had a lifelong interest in magic and illusion and in 1999, MAGIC magazine named him as one of the "100 Most Influential Magicians of the Twentieth Century". He was considered the doyen of American puzzlers. He was a prolific and versatile author, publishing more than 100 books. Gardner was best known for creating and sustaining interest in recreational mathematicsand by extension, mathematics in generalthroughout the latter half of the 20th century, principally through his " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-ary
{{disambiguation ...
-ary may refer to: * The arity of a function, operation, or relation ** -ary associativity, a specific rule attached to -ary functions *** -ary group, a generalization of group * The radix of a numerical representation system * The number of letters in an alphabet (formal languages) ** An -ary code *** An -ary Gray code *** An -ary Huffman code * An -ary tree See also * n- (other)#Mathematics, science and technology * Unary (other) * Binary (other) * Ternary (other) Ternary (from Latin ''ternarius'') or trinary is an adjective meaning "composed of three items". It can refer to: Mathematics and logic * Ternary numeral system, a base-3 counting system ** Balanced ternary, a positional numeral system, useful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Édouard Lucas
__NOTOC__ François Édouard Anatole Lucas (; 4 April 1842 – 3 October 1891) was a French mathematician. Lucas is known for his study of the Fibonacci sequence. The related Lucas sequences and Lucas numbers are named after him. Biography Lucas was born in Amiens and educated at the École Normale Supérieure. He worked in the Paris Observatory and later became a professor of mathematics at the Lycée Saint Louis and the Lycée Charlemagne in Paris. Lucas served as an artillery officer in the French Army during the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–1871. In 1875, Lucas posed a challenge to prove that the only solution of the Diophantine equation: :\sum_^ n^2 = M^2\; with ''N'' > 1 is when ''N'' = 24 and ''M'' = 70. This is known as the cannonball problem, since it can be visualized as the problem of taking a square arrangement of cannonballs on the ground and building a square pyramid out of them. It was not until 1918 that a proof (using elliptic functions) was found f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Towers Of Hanoi
The Tower of Hanoi (also called The problem of Benares Temple or Tower of Brahma or Lucas' Tower and sometimes pluralized as Towers, or simply pyramid puzzle) is a mathematical game or puzzle consisting of three rods and a number of disks of various diameters, which can slide onto any rod. The puzzle begins with the disks stacked on one rod in order of decreasing size, the smallest at the top, thus approximating a conical shape. The objective of the puzzle is to move the entire stack to the last rod, obeying the following rules: # Only one disk may be moved at a time. # Each move consists of taking the upper disk from one of the stacks and placing it on top of another stack or on an empty rod. # No disk may be placed on top of a disk that is smaller than it. With 3 disks, the puzzle can be solved in 7 moves. The minimal number of moves required to solve a Tower of Hanoi puzzle is 2''n'' − 1, where ''n'' is the number of disks. Origins The puzzle was introduced to the West ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Rings Puzzle
Baguenaudier (; French for "time-waster"), also known as the Chinese rings, Cardan's suspension, Cardano's rings, Devil's needle or five pillars puzzle, is a disentanglement puzzle featuring a loop which must be disentangled from a sequence of rings on interlinked pillars. The loop can be either string or a rigid structure. It is thought to have been invented originally in China. The origins are obscure. The American ethnographer Stewart Culin related a tradition attributing the puzzle's invention to the 2nd/3rd century Chinese general Zhuge Liang. It was used by French peasants as a locking mechanism. Variations of this include the ''Devil's staircase'', ''Devil's Halo'' and the ''impossible staircase''. Another similar puzzle is the ''Giant's causeway'' which uses a separate pillar with an embedded ring. Mathematical solution The 19th-century French mathematician Édouard Lucas, the inventor of the Tower of Hanoi puzzle, was known to have come up with an elegant solution w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elisha Gray
Elisha Gray (August 2, 1835 – January 21, 1901) was an American electrical engineer who co-founded the Western Electric Manufacturing Company. Gray is best known for his development of a telephone prototype in 1876 in Highland Park, Illinois. Some recent authors have argued that Gray should be considered the true inventor of the telephone because Alexander Graham Bell allegedly stole the idea of the liquid transmitter from him. Although Gray had been using liquid transmitters in his telephone experiments for more than two years previously, Bell's telephone patent was upheld in numerous court decisions. Gray is also considered to be the father of the modern music synthesizer, and was granted over 70 patents for his inventions. He was one of the founders of Graybar, purchasing a controlling interest in the company shortly after its inception. Biography and early inventions Gray was born in Barnesville, Ohio, the son of Christiana (Edgerton) and David Gray. His family w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noise
Noise is unwanted sound considered unpleasant, loud or disruptive to hearing. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibrations through a medium, such as air or water. The difference arises when the brain receives and perceives a sound. Acoustic noise is any sound in the acoustic domain, either deliberate (e.g., music or speech) or unintended. In contrast, noise in electronics may not be audible to the human ear and may require instruments for detection. In audio engineering, noise can refer to the unwanted residual electronic noise signal that gives rise to acoustic noise heard as a hiss. This signal noise is commonly measured using A-weighting or ITU-R 468 weighting. In experimental sciences, noise can refer to any random fluctuations of data that hinders perception of a signal. Measurement Sound is measured based on the amplitude and frequency of a sound wave. Amplitude measures how forceful the wave is. The e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
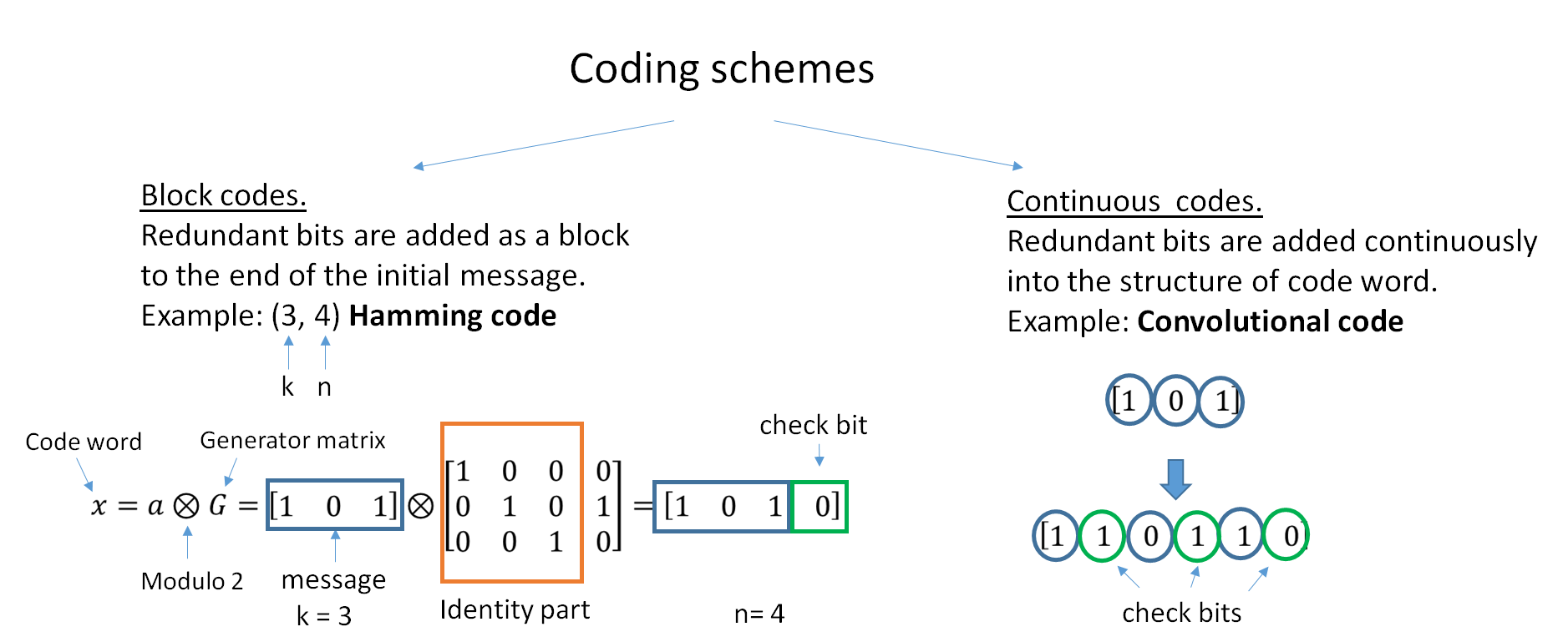
Forward Error Correction
In computing, telecommunication, information theory, and coding theory, an error correction code, sometimes error correcting code, (ECC) is used for controlling errors in data over unreliable or noisy communication channels. The central idea is the sender encodes the message with redundant information in the form of an ECC. The redundancy allows the receiver to detect a limited number of errors that may occur anywhere in the message, and often to correct these errors without retransmission. The American mathematician Richard Hamming pioneered this field in the 1940s and invented the first error-correcting code in 1950: the Hamming (7,4) code. ECC contrasts with error detection in that errors that are encountered can be corrected, not simply detected. The advantage is that a system using ECC does not require a reverse channel to request retransmission of data when an error occurs. The downside is that there is a fixed overhead that is added to the message, thereby requiring a hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constellation Diagram
A constellation diagram is a representation of a signal modulated by a digital modulation scheme such as quadrature amplitude modulation or phase-shift keying. It displays the signal as a two-dimensional ''xy''-plane scatter diagram in the complex plane at symbol sampling instants. In a manner similar to that of a phasor diagram, the angle of a point, measured counterclockwise from the horizontal axis, represents the phase shift of the carrier wave from a reference phase; the distance of a point from the origin represents a measure of the amplitude or power of the signal. In a digital modulation system, information is transmitted as a series of samples, each occupying a uniform time slot. During each sample, the carrier wave has a constant amplitude and phase, which is restricted to one of a finite number of values. So each sample encodes one of a finite number of "symbols", which in turn represent one or more binary digits (bits) of information. Each symbol is encoded as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symbol Rate
In a digitally modulated signal or a line code, symbol rate, modulation rate or baud rate is the number of symbol changes, waveform changes, or signaling events across the transmission medium per unit of time. The symbol rate is measured in '' baud'' (Bd) or ''symbols per second''. In the case of a line code, the symbol rate is the pulse rate in pulses per second. Each symbol can represent or convey one or several bits of data. The symbol rate is related to the '' gross bit rate'', expressed in '' bits per second''. Symbols A symbol may be described as either a pulse in digital baseband transmission or a tone in passband transmission using modems. A symbol is a waveform, a state or a significant condition of the communication channel that ''persists'', for a fixed period of time. A sending device places symbols on the channel at a fixed and known symbol rate, and the receiving device has the job of detecting the sequence of symbols in order to reconstruct the transmitted data ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |