|
Gravimetry
Gravimetry is the measurement of the strength of a gravitational field. Gravimetry may be used when either the magnitude of a gravitational field or the properties of matter responsible for its creation are of interest. Units of measurement Gravity is usually measured in units of acceleration. In the SI system of units, the standard unit of acceleration is 1 metre per second squared (abbreviated as m/s2). Other units include the cgs units, cgs Galileo (unit), gal (sometimes known as a ''galileo'', in either case with symbol Gal), which equals 1 centimetre per second squared, and the ''g-force, g'' (''g''n), equal to 9.80665 m/s2. The value of the ''g''n is defined approximately equal to the standard gravity, acceleration due to gravity at the Earth's surface (although the value of ''g'' varies by location). Gravimeters An instrument used to measure gravity is known as a gravimeter. For a small body, general relativity predicts gravitational effects indistinguishable from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth's Gravity
The gravity of Earth, denoted by , is the net acceleration that is imparted to objects due to the combined effect of gravitation (from mass distribution within Earth) and the centrifugal force (from the Earth's rotation). It is a vector quantity, whose direction coincides with a plumb bob and strength or magnitude is given by the norm g=\, \mathit\, . In SI units this acceleration is expressed in metres per second squared (in symbols, m/ s2 or m·s−2) or equivalently in newtons per kilogram (N/kg or N·kg−1). Near Earth's surface, the gravity acceleration is approximately , which means that, ignoring the effects of air resistance, the speed of an object falling freely will increase by about per second every second. This quantity is sometimes referred to informally as ''little '' (in contrast, the gravitational constant is referred to as ''big ''). The precise strength of Earth's gravity varies depending on location. The nominal "average" value at Earth's surface, known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accelerometer
An accelerometer is a tool that measures proper acceleration. Proper acceleration is the acceleration (the rate of change of velocity) of a body in its own instantaneous rest frame; this is different from coordinate acceleration, which is acceleration in a fixed coordinate system. For example, an accelerometer at rest on the surface of the Earth will measure an acceleration due to Earth's gravity, straight upwards (by definition) of g ≈ 9.81 m/s2. By contrast, accelerometers in free fall (falling toward the center of the Earth at a rate of about 9.81 m/s2) will measure zero. Accelerometers have many uses in industry and science. Highly sensitive accelerometers are used in inertial navigation systems for aircraft and missiles. Vibration in rotating machines is monitored by accelerometers. They are used in tablet computers and digital cameras so that images on screens are always displayed upright. In unmanned aerial vehicles, accelerometers help to stabilise flight. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Gravity
The standard acceleration due to gravity (or standard acceleration of free fall), sometimes abbreviated as standard gravity, usually denoted by or , is the nominal gravitational acceleration of an object in a vacuum near the surface of the Earth. It is defined by standard as . This value was established by the 3rd CGPM (1901, CR 70) and used to define the standard weight of an object as the product of its mass and this nominal acceleration. The acceleration of a body near the surface of the Earth is due to the combined effects of gravity and centrifugal acceleration from the rotation of the Earth (but the latter is small enough to be negligible for most purposes); the total (the apparent gravity) is about 0.5% greater at the poles than at the Equator. Although the symbol is sometimes used for standard gravity, (without a suffix) can also mean the local acceleration due to local gravity and centrifugal acceleration, which varies depending on one's position on Earth (see Earth's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gal (unit)
The gal (symbol: Gal), sometimes called galileo after Galileo Galilei, is a unit of acceleration sometimes used in gravimetry. BIPM ''SI brochure'', 8th ed. 2006Table 9: Non-SI units associated with the CGS and the CGS-Gaussian system of units. The gal is defined as 1 centimeter per second squared (1 cm/s2). The milligal (mGal) and microgal (µGal) are respectively one thousandth and one millionth of a gal. The gal is not part of the International System of Units (known by its French-language initials "SI"). In 1978 the CIPM decided that it was permissible to use the gal "with the SI until the CIPM considers that tsuse is no longer necessary". However, use of the gal is deprecated by ISO 80000-3:2006. The gal is a derived unit, defined in terms of the centimeter–gram–second (CGS) base unit of length, the centimeter, and the second, which is the base unit of time in both the CGS and the modern SI system. In SI base units, 1 Gal is equal to 0.01 m/s2. The a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravity Anomaly
The gravity anomaly at a location on the Earth's surface is the difference between the observed value of gravity and the value predicted by a theoretical model. If the Earth were an ideal oblate spheroid of uniform density, then the gravity measured at every point on its surface would be given precisely by a simple algebraic expression. However, the Earth has a rugged surface and non-uniform composition, which distorts its gravitational field. The theoretical value of gravity can be corrected for altitude and the effects of nearby terrain, but it usually still differs slightly from the measured value. This gravity anomaly can reveal the presence of subsurface structures of unusual density. For example, a mass of dense ore below the surface will give a positive anomaly due to the increased gravitational attraction of the ore. Different theoretical models will predict different values of gravity, and so a gravity anomaly is always specified with reference to a particular model. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galileo (unit)
The gal (symbol: Gal), sometimes called galileo after Galileo Galilei, is a unit of acceleration sometimes used in gravimetry.BIPM ''SI brochure'', 8th ed. 2006Table 9: Non-SI units associated with the CGS and the CGS-Gaussian system of units. The gal is defined as 1 centimeter per second squared (1 cm/s2). The milligal (mGal) and microgal (µGal) are respectively one thousandth and one millionth of a gal. The gal is not part of the International System of Units (known by its French-language initials "SI"). In 1978 the CIPM decided that it was permissible to use the gal "with the SI until the CIPM considers that tsuse is no longer necessary". However, use of the gal is deprecated by ISO 80000-3:2006. The gal is a derived unit, defined in terms of the centimeter–gram–second (CGS) base unit of length, the centimeter, and the second, which is the base unit of time in both the CGS and the modern SI system. In SI base units, 1 Gal is equal to 0.01 m/s2. The acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noise
Noise is unwanted sound considered unpleasant, loud or disruptive to hearing. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibrations through a medium, such as air or water. The difference arises when the brain receives and perceives a sound. Acoustic noise is any sound in the acoustic domain, either deliberate (e.g., music or speech) or unintended. In contrast, Noise (electronics), noise in electronics may not be audible to the human ear and may require instruments for detection. In audio engineering, noise can refer to the unwanted residual electronic noise signal that gives rise to acoustic noise heard as a Hiss (electromagnetic), hiss. This signal noise is commonly measured using A-weighting or ITU-R 468 noise weighting, ITU-R 468 weighting. In experimental sciences, noise can refer to any random fluctuations of data that hinders perception of a signal. Measurement Sound is measured based on the amplitude and frequency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oscillation
Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum and alternating current. Oscillations can be used in physics to approximate complex interactions, such as those between atoms. Oscillations occur not only in mechanical systems but also in dynamic systems in virtually every area of science: for example the beating of the human heart (for circulation), business cycles in economics, predator–prey population cycles in ecology, geothermal geysers in geology, vibration of strings in guitar and other string instruments, periodic firing of nerve cells in the brain, and the periodic swelling of Cepheid variable stars in astronomy. The term ''vibration'' is precisely used to describe a mechanical oscillation. Oscillation, especially rapid oscillation, may be an undesirable phenomenon in proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parts Per Billion
In science and engineering, the parts-per notation is a set of pseudo-units to describe small values of miscellaneous dimensionless quantities, e.g. mole fraction or mass fraction. Since these fractions are quantity-per-quantity measures, they are pure numbers with no associated units of measurement. Commonly used are parts-per-million (ppm, ), parts-per-billion (ppb, ), parts-per-trillion (ppt, ) and parts-per-quadrillion (ppq, ). This notation is not part of the International System of Units (SI) system and its meaning is ambiguous. Overview Parts-per notation is often used describing dilute solutions in chemistry, for instance, the relative abundance of dissolved minerals or pollutants in water. The quantity "1 ppm" can be used for a mass fraction if a water-borne pollutant is present at one-millionth of a gram per gram of sample solution. When working with aqueous solutions, it is common to assume that the density of water is 1.00 g/mL. Therefore, it is common to equate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stable
A stable is a building in which livestock, especially horses, are kept. It most commonly means a building that is divided into separate stalls for individual animals and livestock. There are many different types of stables in use today; the American-style barn, for instance, is a large barn with a door at each end and individual stalls inside or free-standing stables with top and bottom-opening doors. The term "stable" is also used to describe a group of animals kept by one owner, regardless of housing or location. The exterior design of a stable can vary widely, based on climate, building materials, historical period and cultural styles of architecture. A wide range of building materials can be used, including masonry (bricks or stone), wood and steel. Stables also range widely in size, from a small building housing one or two animals to facilities at agricultural shows or race tracks that can house hundreds of animals. History The stable is typically historically the se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
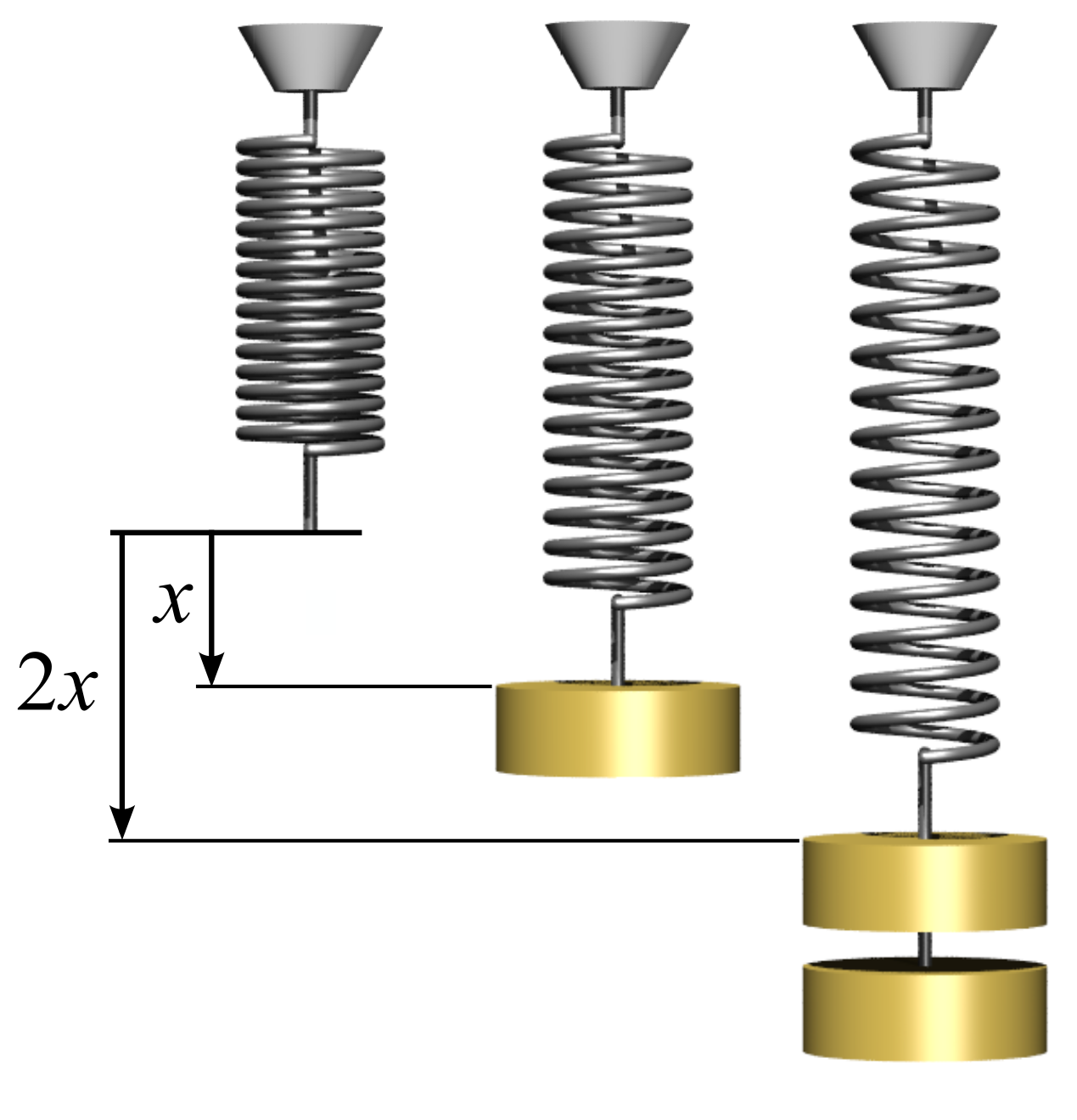
Hooke's Law
In physics, Hooke's law is an empirical law which states that the force () needed to extend or compress a spring (device), spring by some distance () Proportionality (mathematics)#Direct_proportionality, scales linearly with respect to that distance—that is, where is a constant factor characteristic of the spring (i.e., its stiffness), and is small compared to the total possible deformation of the spring. The law is named after 17th-century British physicist Robert Hooke. He first stated the law in 1676 as a Latin anagram. He published the solution of his anagram in 1678 as: ("as the extension, so the force" or "the extension is proportional to the force"). Hooke states in the 1678 work that he was aware of the law since 1660. Hooke's equation holds (to some extent) in many other situations where an elasticity (physics), elastic body is Deformation (physics), deformed, such as wind blowing on a tall building, and a musician plucking a string (music), string of a guitar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Clock
An atomic clock is a clock that measures time by monitoring the resonant frequency of atoms. It is based on atoms having different energy levels. Electron states in an atom are associated with different energy levels, and in transitions between such states they interact with a very specific frequency of electromagnetic radiation. This phenomenon serves as the basis for the International System of Units' (SI) definition of a second:The second, symbol s, is the SI unit of time. It is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the caesium frequency, \Delta \nu_\mathsf, the unperturbed ground-state hyperfine transition frequency of the caesium 133 atom, to be when expressed in the unit Hz, which is equal to s−1. This definition is the basis for the system of International Atomic Time (TAI), which is maintained by an ensemble of atomic clocks around the world. The system of Coordinated Universal Time, Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) that is the basis of civil time implements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)