|
Gratitude Journal
A gratitude journal is a diary of things for which someone is grateful. Keeping a gratitude journal is a popular practice in the field of positive psychology. It is also referred to as “counting one's blessings” or “three good things”. Major empirical findings One of the early research studies on gratitude journals by Emmons & McCullough found that "counting one's blessings" in a journal led to improved psychological and physical functioning. Participants who recorded weekly journals, each consisting of five things they were grateful for, were more optimistic towards the upcoming week and life as a whole, spent more time exercising, and had fewer symptoms of physical illness. Participants who kept daily gratitude journals reported increased overall gratitude, positive affect, enthusiasm, determination, and alertness. They were also more likely to help others and make progress towards their personal goals, compared to those who did not keep gratitude journals. For a sam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gratitude Journal
A gratitude journal is a diary of things for which someone is grateful. Keeping a gratitude journal is a popular practice in the field of positive psychology. It is also referred to as “counting one's blessings” or “three good things”. Major empirical findings One of the early research studies on gratitude journals by Emmons & McCullough found that "counting one's blessings" in a journal led to improved psychological and physical functioning. Participants who recorded weekly journals, each consisting of five things they were grateful for, were more optimistic towards the upcoming week and life as a whole, spent more time exercising, and had fewer symptoms of physical illness. Participants who kept daily gratitude journals reported increased overall gratitude, positive affect, enthusiasm, determination, and alertness. They were also more likely to help others and make progress towards their personal goals, compared to those who did not keep gratitude journals. For a sam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diary
A diary is a written or audiovisual record with discrete entries arranged by date reporting on what has happened over the course of a day or other period. Diaries have traditionally been handwritten but are now also often digital. A personal diary may include a person's experiences, thoughts, and/or feelings, excluding comments on current events outside the writer's direct experience. Someone who keeps a diary is known as a diarist. Diaries undertaken for institutional purposes play a role in many aspects of human civilization, including government records (e.g. ''Hansard''), business ledgers, and military records. In British English, the word may also denote a preprinted journal format. Today the term is generally employed for personal diaries, normally intended to remain private or to have a limited circulation amongst friends or relatives. The word "journal" may be sometimes used for "diary," but generally a diary has (or intends to have) daily entries (from the Latin wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gratitude
Gratitude, thankfulness, or gratefulness is from the Latin word ''gratus,'' which means "pleasing" or "thankful." Is regarded as a feeling of appreciation (or similar positive response) by a recipient of another's kindness. This can be gifts, help, favors, or another form of generosity to another person. The absence of gratitude where gratitude is expected is called ingratitude or ungratefulness. Historically, gratitude has been a part of several world religions. It also has been a topic of interest to ancient, medieval, and modern philosophers. The systematic study of gratitude within the field of psychology began in 1998 when Martin Seligman introduced a new branch of psychology that he termed positive psychology. This new branch adds a new focus on the reinforcement of positive traits. The study of gratitude in psychology has included an attempt to understand the short term experience of the gratitude response (state gratitude), individual differences in how frequently grati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive Psychology
Positive psychology is the scientific study of what makes life most worth living, focusing on both individual and societal well-being. It studies "positive subjective experience, positive individual traits, and positive institutions...it aims to improve quality of life." It is a field of study that has been growing steadily throughout the years as individuals and researchers look for common ground on better well-being. Positive psychology began as a new domain of psychology in 1998 when Martin Seligman chose it as the theme for his term as president of the American Psychological Association. It is a reaction against past practices, which have tended to focus on mental illness and emphasized maladaptive behavior and negative thinking. It builds on the humanistic movement by Abraham Maslow, Rollo May, James Bugental, and Carl Rogers, which encourages an emphasis on happiness, well-being, and positivity, thus creating the foundation for what is now known as positive psychology. P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert A
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin. It is also in use as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe it entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including English, German, Dutch, Norwegian, Swedish, Scots, Danish, and Icelandic. It can be use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affect (psychology)
Affect, in psychology, refers to the underlying experience of feeling, emotion or mood. History The modern conception of affect developed in the 19th century with Wilhelm Wundt. The word comes from the German ''Gefühl'', meaning "feeling." A number of experiments have been conducted in the study of social and psychological affective preferences (i.e., what people like or dislike). Specific research has been done on preferences, attitudes, impression formation, and decision-making. This research contrasts findings with recognition memory (old-new judgments), allowing researchers to demonstrate reliable distinctions between the two. Affect-based judgments and cognitive processes have been examined with noted differences indicated, and some argue affect and cognition are under the control of separate and partially independent systems that can influence each other in a variety of ways (Zajonc, 1980). Both affect and cognition may constitute independent sources of effects within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optimism
Optimism is an attitude reflecting a belief or hope that the outcome of some specific endeavor, or outcomes in general, will be positive, favorable, and desirable. A common idiom used to illustrate optimism versus pessimism is a glass filled with water to the halfway point: an optimist is said to see the glass as half full, while a pessimist sees the glass as half empty. The term derives from the Latin ''optimum'', meaning "best". Being optimistic, in the typical sense of the word, is defined as expecting the best possible outcome from any given situation. This is usually referred to in psychology as dispositional optimism. It thus reflects a belief that future conditions will work out for the best. For this reason, it is seen as a trait that fosters resilience in the face of stress. Theories of optimism include dispositional models and models of explanatory style. Methods to measure optimism have been developed within both of these theoretical approaches, such as various form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
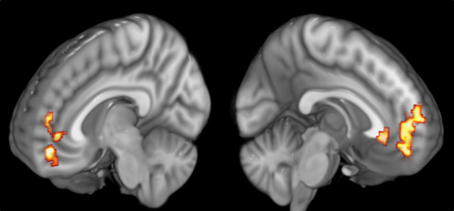
Neural Correlates Of Gratitude
In biology, the nervous system is the highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its actions and sensory information by transmitting signals to and from different parts of its body. The nervous system detects environmental changes that impact the body, then works in tandem with the endocrine system to respond to such events. Nervous tissue first arose in wormlike organisms about 550 to 600 million years ago. In vertebrates it consists of two main parts, the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord. The PNS consists mainly of nerves, which are enclosed bundles of the long fibers or axons, that connect the CNS to every other part of the body. Nerves that transmit signals from the brain are called motor nerves or '' efferent'' nerves, while those nerves that transmit information from the body to the CNS are called sensory nerves or '' afferent''. Spinal nerves are mixed nerves that serve both fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediated
''Mediated: How the Media Shapes Your World and the Way You Live in It'' is a non-fiction book by anthropologist Thomas de Zengotita published in 2005 by Bloomsbury about the effect of the media in the Western world. Summary ''Mediated'' aims at creating awareness rather than offering ready-made solutions to remedy the intrusion of too much media in our industrial societies. Rather than writing yet another pamphlet against the media, the author chooses to focus on the mechanisms and the processes of our ''mediated'' society. The basis of his analysis is that the opposite of reality is not phony or superficial, it is optional. We choose between options to determine who we are, to make statements to the world about who we are. People, he argues, have always done so, but the difference with today's situation is that we have a lot more options. In terms of options, comparing the modern world with the post-modern world is like comparing a breeze with a hurricane. The media force ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Happiness
Happiness, in the context of Mental health, mental or emotional states, is positive or Pleasure, pleasant emotions ranging from contentment to intense joy. Other forms include life satisfaction, well-being, subjective well-being, flourishing and eudaimonia. Since the 1960s, happiness research has been conducted in a wide variety of scientific disciplines, including gerontology, social psychology and positive psychology, Clinical research, clinical and medical research and happiness economics. Definitions "Happiness" is subject to debate on usage and meaning, and on possible differences in understanding by culture. The word is mostly used in relation to two factors: * the current experience of the feeling of an affect (psychology), emotion (affect) such as pleasure or joy, or of a more general sense of 'emotional condition as a whole'. For instance Daniel Kahneman has defined happiness as "''what I experience here and now''". This usage is prevalent in dictionary definiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kindness
Kindness is a type of behavior marked by acts of generosity, consideration, rendering assistant or concern for others, without expecting praise or reward in return. Kindness is a topic of interest in philosophy, religion, and psychology. Kindness was one of the main topics in the Bible. In Book II of "Rhetoric", Aristotle defines kindness as "helpfulness towards someone in need, not in return for anything, nor for the advantage of the helper himself, but for that of the person helped". Nietzsche considered kindness and love to be the "most curative herbs and agents in human intercourse". Kindness is considered to be one of the Knightly Virtues. In Meher Baba's teachings, God is synonymous with kindness: "God is so kind that it is impossible to imagine His unbounded kindness!" History In English, the word ''kindness'' is from approximately 1300, though the word's sense evolved to its current meanings in the late 1300s. Over time, it has acted in part of a personality trait as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonja Lyubomirsky
Sonja Lyubomirsky (russian: Соня Любомирская, born December 14, 1966) is a Russian-born American professor in the Department of Psychology at the University of California, Riverside and author of the ''The How of Happiness: A Scientific Approach to Getting the Life You Want''. Education Lyubomirsky received her B.A. from Harvard University and her Ph.D. in Social/Personality Psychology from Stanford University. Awards Lyubomirsky has received a John Templeton Foundation grant, a Science of Generosity grant, a Templeton Positive Psychology Prize, and a million-dollar grant (with Ken Sheldon) from the National Institute of Mental Health. In 2021, she received an honorary doctorate from the University of Basel. ''The How of Happiness'' ''The How of Happiness'' was published in 2008 by Penguin Press. The book has been translated into 22 languages. The premise of ''The How of Happiness'' is that 50 percent of a given human's long-term happiness level is gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


cropped.jpg)


.jpg)
