|
Graph Dynamical System
In mathematics, the concept of graph dynamical systems can be used to capture a wide range of processes taking place on graphs or networks. A major theme in the mathematical and computational analysis of GDSs is to relate their structural properties (e.g. the network connectivity) and the global dynamics that result. The work on GDSs considers finite graphs and finite state spaces. As such, the research typically involves techniques from, e.g., graph theory, combinatorics, algebra, and dynamical systems rather than differential geometry. In principle, one could define and study GDSs over an infinite graph (e.g. cellular automata or probabilistic cellular automata over \mathbb^k or interacting particle systems when some randomness is included), as well as GDSs with infinite state space (e.g. \mathbb as in coupled map lattices); see, for example, Wu. In the following, everything is implicitly assumed to be finite unless stated otherwise. Formal definition A graph dynamical system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boolean Network
A Boolean network consists of a discrete set of boolean variables each of which has a Boolean function (possibly different for each variable) assigned to it which takes inputs from a subset of those variables and output that determines the state of the variable it is assigned to. This set of functions in effect determines a topology (connectivity) on the set of variables, which then become nodes in a network. Usually, the dynamics of the system is taken as a discrete time series where the state of the entire network at time ''t''+1 is determined by evaluating each variable's function on the state of the network at time ''t''. This may be done synchronously or asynchronously. Boolean networks have been used in biology to model regulatory networks. Although Boolean networks are a crude simplification of genetic reality where genes are not simple binary switches, there are several cases where they correctly convey the correct pattern of expressed and suppressed genes. The se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algebra
Algebra () is one of the areas of mathematics, broad areas of mathematics. Roughly speaking, algebra is the study of mathematical symbols and the rules for manipulating these symbols in formulas; it is a unifying thread of almost all of mathematics. Elementary algebra deals with the manipulation of variable (mathematics), variables (commonly represented by Roman letters) as if they were numbers and is therefore essential in all applications of mathematics. Abstract algebra is the name given, mostly in mathematical education, education, to the study of algebraic structures such as group (mathematics), groups, ring (mathematics), rings, and field (mathematics), fields (the term is no more in common use outside educational context). Linear algebra, which deals with linear equations and linear mappings, is used for modern presentations of geometry, and has many practical applications (in weather forecasting, for example). There are many areas of mathematics that belong to algebra, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamical Systems
In mathematics, a dynamical system is a system in which a function describes the time dependence of a point in an ambient space. Examples include the mathematical models that describe the swinging of a clock pendulum, the flow of water in a pipe, the random motion of particles in the air, and the number of fish each springtime in a lake. The most general definition unifies several concepts in mathematics such as ordinary differential equations and ergodic theory by allowing different choices of the space and how time is measured. Time can be measured by integers, by real or complex numbers or can be a more general algebraic object, losing the memory of its physical origin, and the space may be a manifold or simply a set, without the need of a smooth space-time structure defined on it. At any given time, a dynamical system has a state representing a point in an appropriate state space. This state is often given by a tuple of real numbers or by a vector in a geometr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
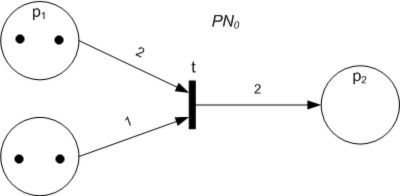
Petri Net
A Petri net, also known as a place/transition (PT) net, is one of several mathematical modeling languages for the description of distributed systems. It is a class of discrete event dynamic system. A Petri net is a directed bipartite graph that has two types of elements, places and transitions. Place elements are depicted as white circles and transition elements are depicted as rectangles. A place can contain any number of tokens, depicted as black circles. A transition is enabled if all places connected to it as inputs contain at least one token. Some sources state that Petri nets were invented in August 1939 by Carl Adam Petri—at the age of 13—for the purpose of describing chemical processes. Like industry standards such as UML activity diagrams, Business Process Model and Notation, and event-driven process chains, Petri nets offer a graphical notation for stepwise processes that include choice, iteration, and concurrent execution. Unlike these standards, Petri nets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kauffman Network
Kaufmann is a surname with many variants such as Kauffmann, Kaufman, and Kauffman. In German, the name means ''merchant''. It is the cognate of the English '' Chapman'' (which had a similar meaning in the Middle Ages, though it disappeared from modern English). ''Kaufmann'' may refer to: Kaufmann * Alexander Kaufmann (1817–1893), German poet and folklorist, brother of Leopold * Aloys P. Kaufmann (1902–1984), Mayor of St. Louis, Missouri * Andrea Kaufmann (born 1969), Austrian politician * Andreas Kaufmann (born 1973), German footballer * Andy Kaufmann (born 1967), American basketball player * Arthur Kaufmann (1872–1938), Austrian attorney, philosopher and chess master * Arthur Kaufmann (artist) (1888–1971, German avant-garde painter * Bob Kauffman (1946–2015), American basketball player * Carl Kaufmann (1936–2008), West German sprint runner * Christian Kaufmann (alpine guide) (1872-1939), Swiss mountain guide active in Canada * Christian Kaufmann (canoeist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hopfield Net
A Hopfield network (or Ising model of a neural network or Ising–Lenz–Little model) is a form of recurrent artificial neural network and a type of spin glass system popularised by John Hopfield in 1982 as described earlier by Little in 1974 based on Ernst Ising's work with Wilhelm Lenz on the Ising model. Hopfield networks serve as content-addressable ("associative") memory systems with binary threshold nodes, or with continuous variables. Hopfield networks also provide a model for understanding human memory. Origins The Ising model of a neural network as a memory model was first proposed by William A. Little in 1974, which was acknowledged by Hopfield in his 1982 paper. Networks with continuous dynamics were developed by Hopfield in his 1984 paper. A major advance in memory storage capacity was developed by Krotov and Hopfield in 2016 through a change in network dynamics and energy function. This idea was further extended by Demircigil and collaborators in 2017. The contin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finite State Machine
A finite-state machine (FSM) or finite-state automaton (FSA, plural: ''automata''), finite automaton, or simply a state machine, is a mathematical model of computation. It is an abstract machine that can be in exactly one of a finite number of '' states'' at any given time. The FSM can change from one state to another in response to some inputs; the change from one state to another is called a ''transition''. An FSM is defined by a list of its states, its initial state, and the inputs that trigger each transition. Finite-state machines are of two types— deterministic finite-state machines and non-deterministic finite-state machines. A deterministic finite-state machine can be constructed equivalent to any non-deterministic one. The behavior of state machines can be observed in many devices in modern society that perform a predetermined sequence of actions depending on a sequence of events with which they are presented. Simple examples are vending machines, which dispense ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Science
Social science is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among individuals within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the field of sociology, the original "science of society", established in the 19th century. In addition to sociology, it now encompasses a wide array of academic disciplines, including anthropology, archaeology, economics, human geography, linguistics, management science, communication science and political science. Positivist social scientists use methods resembling those of the natural sciences as tools for understanding society, and so define science in its stricter modern sense. Interpretivist social scientists, by contrast, may use social critique or symbolic interpretation rather than constructing empirically falsifiable theories, and thus treat science in its broader sense. In modern academic practice, researchers are often eclectic, using multiple methodologies (for instan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamic Network Analysis
Dynamic network analysis (DNA) is an emergent scientific field that brings together traditional social network analysis (SNA), link analysis (LA), social simulation and multi-agent systems (MAS) within network science and network theory. Dynamic networks are a function of time (modeled as a subset of the real numbers) to a set of graphs; for each time point there is a graph. This is akin to the definition of dynamical systems, in which the function is from time to an ambient space, where instead of ambient space time is translated to relationships between pairs of vertices. Overview There are two aspects of this field. The first is the statistical analysis of DNA data. The second is the utilization of simulation to address issues of network dynamics. DNA networks vary from traditional social networks in that they are larger, dynamic, multi-mode, multi-plex networks, and may contain varying levels of uncertainty Uncertainty refers to Epistemology, epistemic situations i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Reaction Network Theory
Chemical reaction network theory is an area of applied mathematics that attempts to model the behaviour of real-world chemical systems. Since its foundation in the 1960s, it has attracted a growing research community, mainly due to its applications in biochemistry and theoretical chemistry. It has also attracted interest from pure mathematicians due to the interesting problems that arise from the mathematical structures involved. History Dynamical properties of reaction networks were studied in chemistry and physics after the invention of the law of mass action. The essential steps in this study were introduction of detailed balance for the complex chemical reactions by Rudolf Wegscheider (1901), development of the quantitative theory of chemical chain reactions by Nikolay Semyonov (1934), development of kinetics of catalytic reactions by Cyril Norman Hinshelwood, and many other results. Three eras of chemical dynamics can be revealed in the flux of research and publications. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probabilistic Cellular Automata
Stochastic cellular automata or probabilistic cellular automata (PCA) or random cellular automata or locally interacting Markov chains are an important extension of cellular automaton. Cellular automata are a discrete-time dynamical system of interacting entities, whose state is discrete. The state of the collection of entities is updated at each discrete time according to some simple homogeneous rule. All entities' states are updated in parallel or synchronously. Stochastic Cellular Automata are CA whose updating rule is a stochastic one, which means the new entities' states are chosen according to some probability distributions. It is a discrete-time random dynamical system. From the spatial interaction between the entities, despite the simplicity of the updating rules, complex behaviour may emerge like self-organization. As mathematical object, it may be considered in the framework of stochastic processes as an interacting particle system in discrete-time. See for a more det ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |