|
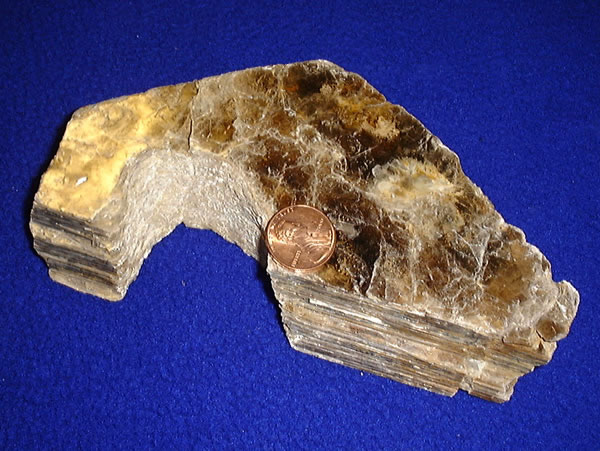
Granite Block
Granite () is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies underground. It is common in the continental crust of Earth, where it is found in igneous intrusions. These range in size from dikes only a few centimeters across to batholiths exposed over hundreds of square kilometers. Granite is typical of a larger family of ''granitic rocks'', or ''granitoids'', that are composed mostly of coarse-grained quartz and feldspars in varying proportions. These rocks are classified by the relative percentages of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase (the QAPF classification), with true granite representing granitic rocks rich in quartz and alkali feldspar. Most granitic rocks also contain mica or amphibole minerals, though a few (known as leucogranites) contain almost no dark minerals. Granite is nearly alway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Feldspar
Potassium feldspar refers to a number of minerals in the feldspar group, and containing potassium: *Orthoclase (endmember formula K Al Si3 O8), an important tectosilicate mineral that forms igneous rock *Microcline, chemically the same as orthoclase, but with a different crystalline structure *Sanidine, the high-temperature form of potassium feldspar *Adularia, a more ordered low-temperature variety of orthoclase or partially disordered microcline *Amazonite Amazonite, also known as Amazonstone, is a green tectosilicate mineral, a variety of the potassium feldspar called microcline. Its chemical formula is KAlSi3O8, which is polymorphic to orthoclase. Its name is taken from that of the Amazon Rive ... (sometimes called "Amazon stone"), a green variety of microcline {{SIA Feldspar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igneous Intrusion
In geology, an igneous intrusion (or intrusive body or simply intrusion) is a body of intrusive igneous rock that forms by crystallization of magma slowly cooling below the surface of the Earth. Intrusions have a wide variety of forms and compositions, illustrated by examples like the Palisades Sill of New York and New Jersey; the Henry Mountains of Utah; the Bushveld Igneous Complex of South Africa; Shiprock in New Mexico; the Ardnamurchan intrusion in Scotland; and the Sierra Nevada Batholith of California. Because the solid country rock into which magma intrudes is an excellent insulator, cooling of the magma is extremely slow, and intrusive igneous rock is coarse-grained (phaneritic). Intrusive igneous rocks are classified separately from extrusive igneous rocks, generally on the basis of their mineral content. The relative amounts of quartz, alkali feldspar, plagioclase, and feldspathoid is particularly important in classifying intrusive igneous rocks. Intrusions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): Minerals'; p. 1. In the series ''Geology: Landforms, Minerals, and Rocks''. Rosen Publishing Group. The geological definition of mineral normally excludes compounds that occur only in living organisms. However, some minerals are often biogenic (such as calcite) or are organic compounds in the sense of chemistry (such as mellite). Moreover, living organisms often synthesize inorganic minerals (such as hydroxylapatite) that also occur in rocks. The concept of mineral is distinct from rock, which is any bulk solid geologic material that is relatively homogeneous at a large enough scale. A rock may consist of one type of mineral, or may be an aggregate of two or more different types of minerals, spacially segregated into distinct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feldspar
Feldspars are a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the ''plagioclase'' (sodium-calcium) feldspars and the ''alkali'' (potassium-sodium) feldspars. Feldspars make up about 60% of the Earth's crust, and 41% of the Earth's continental crust by weight. Feldspars crystalize from magma as both intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks and are also present in many types of metamorphic rock. Rock formed almost entirely of calcic plagioclase feldspar is known as anorthosite. Feldspars are also found in many types of sedimentary rocks. Compositions The feldspar group of minerals consists of tectosilicates, silicate minerals in which silicon ions are linked by shared oxygen ions to form a three-dimensional network. Compositions of major elements in common feldspars can be expressed in terms of three endmembers: * potassium feldspar (K-spar) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holocrystalline
Crystallinity refers to the degree of structural order in a solid. In a crystal, the atoms or molecules are arranged in a regular, periodic manner. The degree of crystallinity has a big influence on hardness, density, transparency and diffusion. In an ideal gas, the relative positions of the atoms or molecules are completely random. Amorphous materials, such as liquids and glasses, represent an intermediate case, having order over short distances (a few atomic or molecular spacings) but not over longer distances. Many materials, such as glass-ceramics and some polymers, can be prepared in such a way as to produce a mixture of crystalline and amorphous regions. In such cases, crystallinity is usually specified as a percentage of the volume of the material that is crystalline. Even within materials that are completely crystalline, however, the degree of structural perfection can vary. For instance, most metallic alloys are crystalline, but they usually comprise many independent cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mineralogy Igneous Rocks EN
Mineralogy is a subject of geology specializing in the scientific study of the chemistry, crystal structure, and physical (including optical) properties of minerals and mineralized artifacts. Specific studies within mineralogy include the processes of mineral origin and formation, classification of minerals, their geographical distribution, as well as their utilization. History Early writing on mineralogy, especially on gemstones, comes from ancient Babylonia, the ancient Greco-Roman world, ancient and medieval China, and Sanskrit texts from ancient India and the ancient Islamic world. Books on the subject included the ''Naturalis Historia'' of Pliny the Elder, which not only described many different minerals but also explained many of their properties, and Kitab al Jawahir (Book of Precious Stones) by Persian scientist Al-Biruni. The German Renaissance specialist Georgius Agricola wrote works such as '' De re metallica'' (''On Metals'', 1556) and ''De Natura Fossilium'' (' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granite Qapf
Granite () is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies underground. It is common in the continental crust of Earth, where it is found in igneous intrusions. These range in size from dikes only a few centimeters across to batholiths exposed over hundreds of square kilometers. Granite is typical of a larger family of ''granitic rocks'', or ''granitoids'', that are composed mostly of coarse-grained quartz and feldspars in varying proportions. These rocks are classified by the relative percentages of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase (the QAPF classification), with true granite representing granitic rocks rich in quartz and alkali feldspar. Most granitic rocks also contain mica or amphibole minerals, though a few (known as leucogranites) contain almost no dark minerals. Granite is nearly alway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granito Nicol Incrociati
Granito (''Granite'') is a city in the state of Pernambuco, Brazil. The population in 2020, according with IBGE was 7,537 inhabitants and the total area is . Geography * State - Pernambuco * Region - Sertão Pernambucano * Boundaries - Exu and Moreilândia (N); Parnamirim (S); Serrita (E); Bodocó (W). * Area - 521.86 km² * Elevation - 447 m * Hydrography - Brigida River * Vegetation - Caatinga * Climate - semi arid - (Sertão) hot * Annual average temperature - 25.4 c * Distance to Recife - 592 km Economy The main economic activities in Granito are based in agribusiness, especially creation of cattle, sheep, goats, donkeys, chickens; and plantations of corn Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. Th .... Economic Indicators Economy by Sector ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leucogranite
Leucogranite is a light-colored, granitic, igneous rock containing almost no dark minerals. Alaskite is a synonym. Leucogranites have been reported from a variety of orogenies involving continental collisions. Examples include the ( of Proterozoic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mica
Micas ( ) are a group of silicate minerals whose outstanding physical characteristic is that individual mica crystals can easily be split into extremely thin elastic plates. This characteristic is described as perfect basal cleavage. Mica is common in igneous and metamorphic rock and is occasionally found as small flakes in sedimentary rock. It is particularly prominent in many granites, pegmatites, and schists, and "books" (large individual crystals) of mica several feet across have been found in some pegmatites. Micas are used in products such as drywalls, paints, fillers, especially in parts for automobiles, roofing and shingles, as well as in electronics. The mineral is used in cosmetics and food to add "shimmer" or "frost." Properties and structure The mica group is composed of 37 phyllosilicate minerals. All crystallize in the monoclinic system, with a tendency towards pseudohexagonal crystals, and are similar in structure but vary in chemical composition. Micas are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
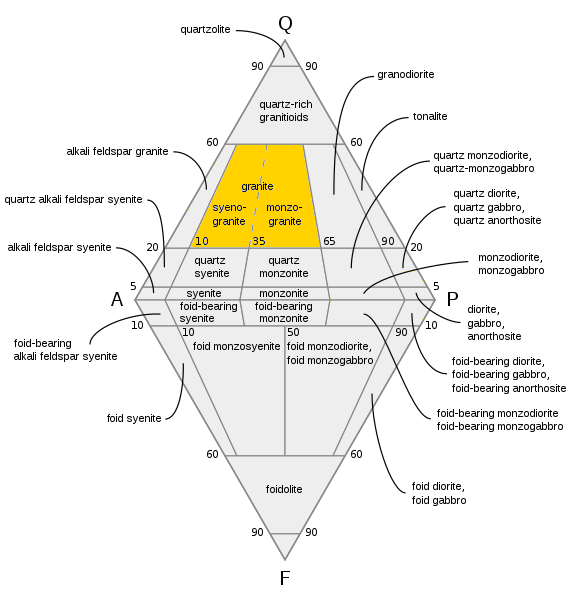
QAPF Diagram
A QAPF diagram is a double ternary diagram which is used to classify igneous rocks based on mineralogic composition. The acronym QAPF stands for "Quartz, Alkali feldspar, Plagioclase, Feldspathoid (Foid)". These are the mineral groups used for classification in QAPF diagram. Q, A, P and F percentages are normalized (recalculated so that their sum is 100%). Origin QAPF diagrams were created by the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS): ''Subcommission on the Systematics of Igneous Rocks'' fostered by Albert Streckeisen (whence their alternative name: Streckeisen diagrams). Geologists worldwide accept the diagrams as a classification of igneous, especially plutonic rocks. Usage QAPF diagrams are mostly used to classify plutonic rocks (phaneritic rocks), but are also used to classify volcanic rocks if modal mineralogical compositions have been determined. QAPF diagrams are not used to classify pyroclastic rocks or volcanic rocks if modal mineralogical composition is n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |