|
Grand Council Of Aargau
The Grand Council of Aargau (german: Grosser Rat) is the legislature of the Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Aargau, in Switzerland. Aargau has a unicameral legislature. The Grand Council has 140 seats, with members elected every four years. The most recent election was on October 18, 2020. Parties At the elections between 1997 and 2020 the parties won the following number of seats and votes: Members * List of members of the Grand Council of Aargau (2021–2024) References External links *Grand Council of Aargau official website {{DEFAULTSORT:Grand Council Of Aargau Cantonal legislatures of Switzerland, Aargau Politics of Aargau Unicameral legislatures, Aargau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unicameral Legislature
Unicameralism (from ''uni''- "one" + Latin ''camera'' "chamber") is a type of legislature, which consists of one house or assembly, that legislates and votes as one. Unicameral legislatures exist when there is no widely perceived need for multicameralism (two or more chambers). Many multicameral legislatures were created to give separate voices to different sectors of society. Multiple houses allowed, for example, for a guaranteed representation of different social classes (as in the Parliament of the United Kingdom or the French States-General). Sometimes, as in New Zealand and Denmark, unicameralism comes about through the abolition of one of two bicameral chambers, or, as in Sweden, through the merger of the two chambers into a single one, while in others a second chamber has never existed from the beginning. Rationale for unicameralism and criticism The principal advantage of a unicameral system is more efficient lawmaking, as the legislative process is simpler and there is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unicameral
Unicameralism (from ''uni''- "one" + Latin ''camera'' "chamber") is a type of legislature, which consists of one house or assembly, that legislates and votes as one. Unicameral legislatures exist when there is no widely perceived need for multicameralism (two or more chambers). Many multicameral legislatures were created to give separate voices to different sectors of society. Multiple houses allowed, for example, for a guaranteed representation of different social classes (as in the Parliament of the United Kingdom or the French States-General). Sometimes, as in New Zealand and Denmark, unicameralism comes about through the abolition of one of two bicameral chambers, or, as in Sweden, through the merger of the two chambers into a single one, while in others a second chamber has never existed from the beginning. Rationale for unicameralism and criticism The principal advantage of a unicameral system is more efficient lawmaking, as the legislative process is simpler and there is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
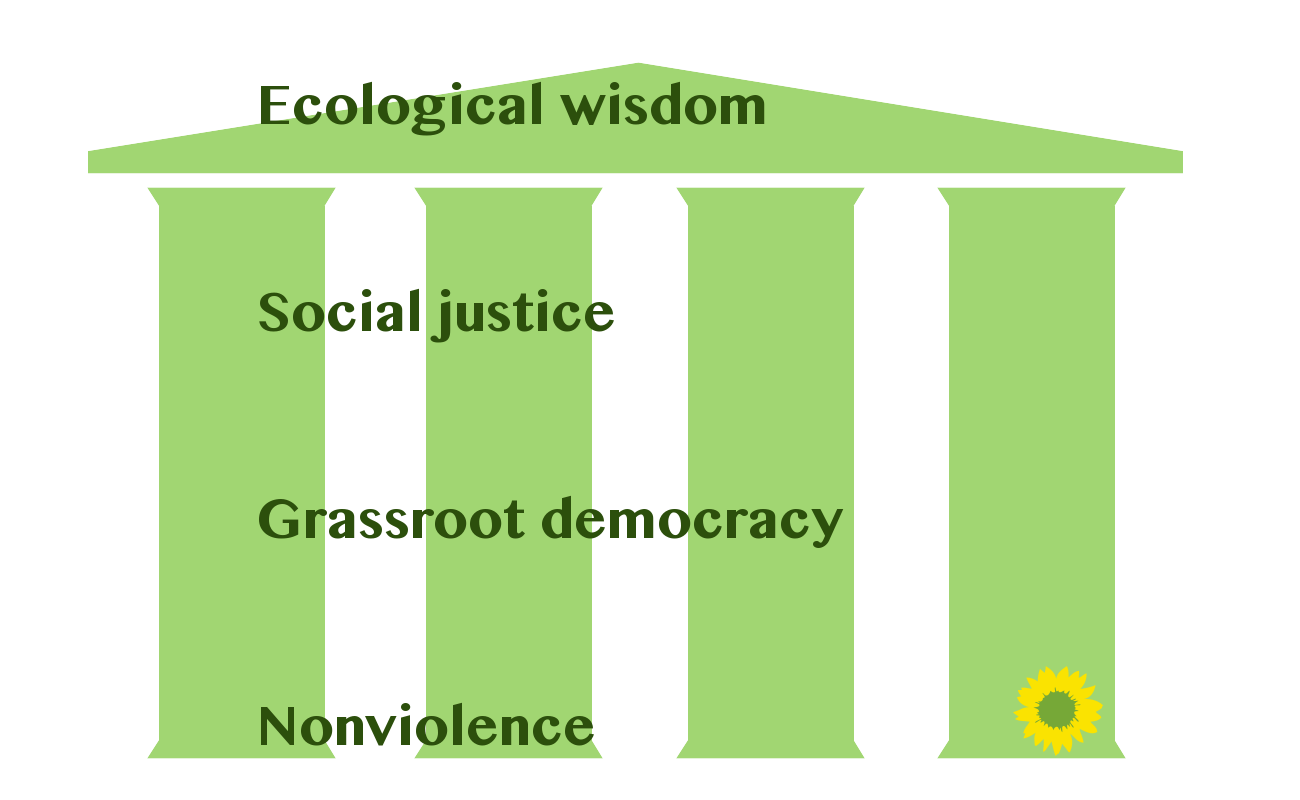
Green Politics
Green politics, or ecopolitics, is a political ideology that aims to foster an ecologically sustainable society often, but not always, rooted in environmentalism, nonviolence, social justice and grassroots democracy. Wall 2010. p. 12-13. It began taking shape in the western world in the 1970s; since then Green parties have developed and established themselves in many countries around the globe and have achieved some electoral success. The political term green was used initially in relation to ''die Grünen'' (German for "the Greens"), a green party formed in the late 1970s. The term political ecology is sometimes used in academic circles, but it has come to represent an interdisciplinary field of study as the academic discipline offers wide-ranging studies integrating ecological social sciences with political economy in topics such as degradation and marginalization, environmental conflict, conservation and control and environmental identities and social movements. Supporte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Liberalism
Classical liberalism is a political tradition Political culture describes how culture impacts politics. Every political system is embedded in a particular political culture. Definition Gabriel Almond defines it as "the particular pattern of orientations toward political actions in which ... and a History of liberalism, branch of liberalism that advocates free market and laissez-faire economics; civil liberties under the rule of law with especial emphasis on individual autonomy, limited government, economic freedom, political freedom and freedom of speech. It gained full flowering in the early 18th century, building on ideas stemming at least as far back as the 13th century within the Iberian, Anglo-Saxon, and central European contexts and was foundational to the American Revolution and "American Project" more broadly. Notable liberal individuals whose ideas contributed to classical liberalism include John Locke,Steven M. Dworetz (1994). ''The Unvarnished Doctrine: Lock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Democracy
Christian democracy (sometimes named Centrist democracy) is a political ideology that emerged in 19th-century Europe under the influence of Catholic social teaching and neo-Calvinism. It was conceived as a combination of modern democratic ideas and traditional Christian values, incorporating social justice and the social teachings espoused by the Catholic, Lutheran, Reformed, Pentecostal, and other denominational traditions of Christianity in various parts of the world. After World War II, Catholic and Protestant movements of neo-scholasticism and the Social Gospel shaped Christian democracy. On the traditional left-right political spectrum Christian Democracy has been difficult to pinpoint as Christian democrats rejected liberal economics and individualism and advocated state intervention, but simultaneously defended private property rights against excessive state intervention. This has meant that Christian Democracy has historically been considered centre left on eco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Democracy
Social democracy is a Political philosophy, political, Social philosophy, social, and economic philosophy within socialism that supports Democracy, political and economic democracy. As a policy regime, it is described by academics as advocating Economic interventionism, economic and social interventions to promote social justice within the framework of a liberal-democratic polity and a capitalist-oriented mixed economy. The protocols and norms used to accomplish this involve a commitment to Representative democracy, representative and participatory democracy, measures for income redistribution, regulation of the economy in the Common good, general interest, and social welfare provisions. Due to longstanding governance by social democratic parties during the post-war consensus and their influence on socioeconomic policy in Northern and Western Europe, social democracy became associated with Keynesianism, the Nordic model, the social-liberal paradigm, and welfare states within po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Conservatism
National conservatism is a nationalist variant of conservatism that concentrates on upholding national and cultural identity. National conservatives usually combine nationalism with conservative stances promoting traditional cultural values, family values and opposition to immigration. It shares characteristics with traditionalist conservatism and social conservatism since all three variations focus on preservation and tradition. As national conservatism seeks to preserve national interests, traditionalist conservatism emphasizes the preservation of social order. Additionally, social conservatism emphasizes traditional family values which regulate moral behavior to preserve one's traditional status in society. National conservative parties often have roots in environments with a rural, traditionalist or peripheral basis, contrasting with the more urban support base of liberal-conservative parties. In Europe, most embrace some form of Euroscepticism.Traynor, IanThe EU's wear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Council Of Aargau Election, 2009
Grand may refer to: People with the name * Grand (surname) * Grand L. Bush (born 1955), American actor * Grand Mixer DXT, American turntablist * Grand Puba (born 1966), American rapper Places * Grand, Oklahoma * Grand, Vosges, village and commune in France with Gallo-Roman amphitheatre * Grand Concourse (other), several places * Grand County (other), several places * Grand Geyser, Upper Geyser Basin of Yellowstone * Grand Rounds National Scenic Byway, a parkway system in Minneapolis, Minnesota, United States * Le Grand, California, census-designated place * Grand Staircase, a place in the US. Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Grand'' (Erin McKeown album), 2003 * ''Grand'' (Matt and Kim album), 2009 * ''Grand'' (magazine), a lifestyle magazine related to related to grandparents * ''Grand'' (TV series), American sitcom, 1990 * Grand piano, musical instrument * Grand Production, Serbian record label company * The Grand Tour, a new British automobile show Oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Council Of Aargau
The Grand Council of Aargau (german: Grosser Rat) is the legislature of the Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Aargau, in Switzerland. Aargau has a unicameral legislature. The Grand Council has 140 seats, with members elected every four years. The most recent election was on October 18, 2020. Parties At the elections between 1997 and 2020 the parties won the following number of seats and votes: Members * List of members of the Grand Council of Aargau (2021–2024) References External links *Grand Council of Aargau official website {{DEFAULTSORT:Grand Council Of Aargau Cantonal legislatures of Switzerland, Aargau Politics of Aargau Unicameral legislatures, Aargau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alliance Of Independents
The Alliance of Independents, Ring of Independents, or National Ring of Independents, (german: Landesring der Unabhängigen (LdU), french: Alliance des Indépendants (AdI), it, Anello degli Indipendenti) was a social liberal political party in Switzerland that existed between 1936 and 1999. History of the party Formation Gottlieb Duttweiler – the founder of Migros, a retail business and consumer cooperative – was dissatisfied with the state of Swiss politics in the 1930s and therefore founded the Alliance of Independents with a group of like-minded people as an association. According to its statutes, it was not meant to be a political party at first but to be an association to help to reconcile capitalists and workers. From the beginning, the LdU also served the interests of the Migros cooperative, successfully lobbying against legislation that impeded its business model by restricting networks of general stores or sales by trucks (one of Migros' marketing strategies). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freedom Party Of Switzerland
The Freedom Party of Switzerland (FPS) (german: Freiheits-Partei der Schweiz; french: Parti suisse de la liberté / PSL) is a minor right-wing populist political party in Switzerland. Its president and leading representative is Jürg Scherrer, formerly the head of the security department in the city government of Biel/Bienne until 2008. The party is against much government involvement in the economy, especially environmental regulations, but is for strict controls on immigration and strict punishments for selling drugs. The party opposes Swiss EU membership. History The FPS was founded 1984 in Zürich by Dr. Michael E. Dreher and other right-wing politicians as ''Autopartei'' (Automobile Party). It was intended to counter the then upsurging Green Party of Switzerland and the contemporary concerns about forest dieback due to acid rain. Focusing initially on personal mobility issues, one of its more well-known slogans was "Freie Fahrt für freie Bürger" (''A free road for fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss Democrats
The Swiss Democrats (german: Schweizer Demokraten; french: Démocrates Suisses; it, Democratici Svizzeri; rm, Democrats Svizers) are a nationalist political party in Switzerland. It was called the National Action against the Alienation of the People and the Home (german: Nationale Aktion gegen Überfremdung von Volk und Heimat; ''NA'') until 1977 and the National Action for People and Home (german: Nationale Aktion für Volk und Heimat) until 1990, when it was renamed to its current name. History The ''Nationale Aktion'' was originally a far-right xenophobic movement pursuing an anti-immigration agenda, founded in 1961. The party "emerged as a reaction to the influx of foreign workers," particularly Italians, during this time. The party submitted several popular initiatives that supported reduced immigration, most notably one in June 1970 that narrowly failed. Its first representative in the National Council was James Schwarzenbach, who was first elected in 1967. After a host ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |