|
Graham Creek (Sonoma County, California)
Graham Creek is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map , accessed March 10, 2011 perennial stream in Sonoma County, California, tributary to Sonoma Creek. Graham Creek rises in the northern Sonoma Mountains and flows generally northeasterly down the northeastern flank of Sonoma Mountain. Historically this watercourse was called Wild Water Creek, a name used in the time of author Jack London, some of whose work was inspired by the stream. Steelhead, ''Oncorhynchus mykiss'', have historically entered Graham Creek via Sonoma Creek for spawning. Stream surveys conducted from 1966 to 1986 indicated significant, but declining populations of anadromous fish. The spawning habitat of Graham Creek is considered medium to high value, with both winter and summer sheltering characteristics. Land uses in the watershed are primarily open space, agriculture and low density residential uses; waste disposal within the watershed cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguous states border Canada to the north and Mexico to the south, with the semi-exclave of Alaska in the northwest and the archipelago of Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean. The United States asserts sovereignty over five Territories of the United States, major island territories and United States Minor Outlying Islands, various uninhabited islands in Oceania and the Caribbean. It is a megadiverse country, with the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest land area and List of countries and dependencies by population, third-largest population, exceeding 340 million. Its three Metropolitan statistical areas by population, largest metropolitan areas are New York metropolitan area, New York, Greater Los Angeles, Los Angel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habitat
In ecology, habitat refers to the array of resources, biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species' habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ecological niche. Thus "habitat" is a species-specific term, fundamentally different from concepts such as Biophysical environment, environment or vegetation assemblages, for which the term "habitat-type" is more appropriate. The physical factors may include (for example): soil, moisture, range of temperature, and Luminous intensity, light intensity. Biotic index, Biotic factors include the availability of food and the presence or absence of Predation, predators. Every species has particular habitat requirements, habitat generalist species are able to thrive in a wide array of environmental conditions while habitat specialist species require a very limited set of factors to survive. The habitat of a species is not necessarily found in a ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archeological
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. The discipline involves surveying, excavation, and eventually analysis of data collected, to learn more about the past. In broad scope, archaeology relies on cross-disciplinary research. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological
Ecology () is the natural science of the relationships among living organisms and their environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere levels. Ecology overlaps with the closely related sciences of biogeography, evolutionary biology, genetics, ethology, and natural history. Ecology is a branch of biology, and is the study of abundance, biomass, and distribution of organisms in the context of the environment. It encompasses life processes, interactions, and adaptations; movement of materials and energy through living communities; successional development of ecosystems; cooperation, competition, and predation within and between species; and patterns of biodiversity and its effect on ecosystem processes. Ecology has practical applications in fields such as conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource management, and human ecology. The word ''ecology'' () was coined in 1866 by the German scientist Ern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grazing
In agriculture, grazing is a method of animal husbandry whereby domestic livestock are allowed outdoors to free range (roam around) and consume wild vegetations in order to feed conversion ratio, convert the otherwise indigestible (by human digestive system, human gut) cellulose within grass and other forages into meat, milk, wool and other animal products, often on land that is unsuitable for arable farming. Farmers may employ many different strategies of grazing for crop yield, optimum production: grazing may be continuous, seasonal, or rotational grazing, rotational within a grazing period. Longer rotations are found in ley farming, alternating arable and fodder crops; in rest rotation, deferred rotation, and mob grazing, giving grasses a longer time to recover or leaving land fallow. Patch-burn sets up a rotation of fresh grass after burning with two years of rest. Conservation grazing proposes to use grazing animals to improve the biodiversity of a site. Grazing has existed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fauna
Fauna (: faunae or faunas) is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding terms for plants and fungi are ''flora'' and '' funga'', respectively. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as '' biota''. Zoologists and paleontologists use ''fauna'' to refer to a typical collection of animals found in a specific time or place, e.g. the " Sonoran Desert fauna" or the " Burgess Shale fauna". Paleontologists sometimes refer to a sequence of faunal stages, which is a series of rocks all containing similar fossils. The study of animals of a particular region is called faunistics. Etymology ''Fauna'' comes from the name Fauna, a Roman goddess of earth and fertility, the Roman god Faunus, and the related forest spirits called Fauns. All three words are cognates of the name of the Greek god Pan, and ''panis'' is the Modern Greek equivalent of fauna (πανίς or rather πανίδα). ''Fauna'' is also the word fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora
Flora (: floras or florae) is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous (ecology), indigenous) native plant, native plants. The corresponding term for animals is ''fauna'', and for fungi, it is ''funga''. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora as in the terms ''gut flora'' or ''skin flora'' for purposes of specificity. Etymology The word "flora" comes from the Latin name of Flora (mythology), Flora, the goddess of plants, flowers, and fertility in Roman mythology. The technical term "flora" is then derived from a metonymy of this goddess at the end of the sixteenth century. It was first used in poetry to denote the natural vegetation of an area, but soon also assumed the meaning of a work cataloguing such vegetation. Moreover, "Flora" was used to refer to the flowers of an artificial garden in the seventeenth century. The distinction between vegetation (the general appearance of a community) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
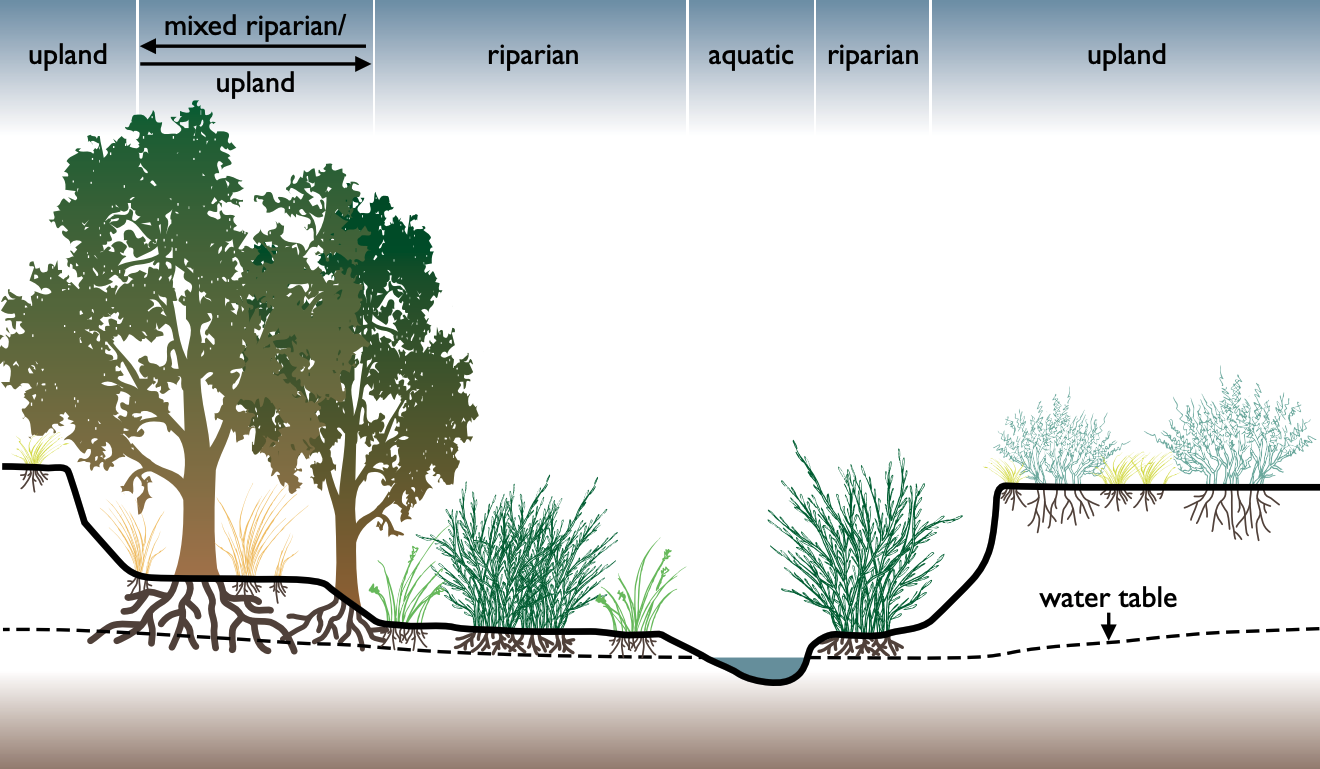
Riparian
A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or stream. In some regions, the terms riparian woodland, riparian forest, riparian buffer zone, riparian corridor, and riparian strip are used to characterize a riparian zone. The word ''riparian'' is derived from Latin '' ripa'', meaning " river bank". Riparian is also the proper nomenclature for one of the terrestrial biomes of the Earth. Plant habitats and communities along the river margins and banks are called riparian vegetation, characterized by hydrophilic plants. Riparian zones are important in ecology, environmental resource management, and civil engineering because of their role in soil conservation, their habitat biodiversity, and the influence they have on terrestrial and semiaquatic fauna as well as aquatic ecosystems, including grasslands, woodlands, wetlands, and even non-vegetative areas. Riparian zones may be natural or engineered for soil stabilization or restoration. These zon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habitat
In ecology, habitat refers to the array of resources, biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species' habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ecological niche. Thus "habitat" is a species-specific term, fundamentally different from concepts such as Biophysical environment, environment or vegetation assemblages, for which the term "habitat-type" is more appropriate. The physical factors may include (for example): soil, moisture, range of temperature, and Luminous intensity, light intensity. Biotic index, Biotic factors include the availability of food and the presence or absence of Predation, predators. Every species has particular habitat requirements, habitat generalist species are able to thrive in a wide array of environmental conditions while habitat specialist species require a very limited set of factors to survive. The habitat of a species is not necessarily found in a ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California Oak Woodland
California oak woodland is a plant community found throughout the California chaparral and woodlands ecoregion of California in the United States and northwestern Baja California in Mexico. Oak woodland is widespread at lower elevations in coastal California; in interior valleys of the Coast Ranges, Transverse Ranges and Peninsular Ranges; and in a ring around the California Central Valley grasslands. The dominant trees are oaks, interspersed with other broadleaf and coniferous trees, with an understory of grasses, herbs, geophytes, and California native plants. Oak savannas occur where the oaks are more widely spaced due a combination of lack of available moisture, and low-intensity frequent fires. The oak woodlands of Southern California and coastal Northern California are dominated by coast live oak ('' Quercus agrifolia''), but also include valley oak ( ''Q. lobata''), California black oak ( ''Q. kelloggii''), canyon live oak ( ''Q. chrysolepis''), and other Califor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lagoon
A lagoon is a shallow body of water separated from a larger body of water by a narrow landform, such as reefs, barrier islands, barrier peninsulas, or isthmuses. Lagoons are commonly divided into ''coastal lagoons'' (or ''barrier lagoons'') and ''atoll lagoons''. They have also been identified as occurring on mixed-sand and gravel coastlines. There is an overlap between bodies of water classified as coastal lagoons and bodies of water classified as Estuary, estuaries. Lagoons are common coastal features around many parts of the world. Definition and terminology Lagoons are shallow, often elongated bodies of water separated from a larger body of water by a shallow or exposed shoal, reef, coral reef, or similar feature. Some authorities include fresh water bodies in the definition of "lagoon", while others explicitly restrict "lagoon" to bodies of water with some degree of salinity. The distinction between "lagoon" and "estuary" also varies between authorities. Richard A. Davis J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septic Tank
A septic tank is an underground chamber made of concrete, fiberglass, or plastic through which domestic wastewater (sewage) flows for basic sewage treatment. Settling and anaerobic digestion processes reduce solids and organics, but the treatment efficiency is only moderate (referred to as "primary treatment"). Septic tank systems are a type of simple onsite sewage facility. They can be used in areas that are not connected to a sewerage system, such as rural areas. The treated liquid effluent is commonly disposed in a septic drain field, which provides further treatment. Nonetheless, groundwater pollution may occur and is a problem. The term "septic" refers to the Anaerobic digestion, anaerobic bacterial environment that develops in the tank that decomposes or mineralizes the waste discharged into the tank. Septic tanks can be coupled with other Onsite sewage facility, onsite wastewater treatment units such as biofilters or aerobic systems involving artificially forced aeration. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |