|
Gorn Address
A Gorn address (Gorn, 1967) is a method of identifying and addressing any node within a tree data structure. This notation is often used for identifying nodes in a parse tree defined by phrase structure rules. The Gorn address is a sequence of zero or more integers conventionally separated by dots, e.g., ''0'' or ''1.0.1''. The root which Gorn calls * can be regarded as the empty sequence. And the j-th child of the i-th child has an address i.j, counting from 0. It is named after American computer scientist Saul Gorn Saul Gorn (10 November 1912 – 22 February 1992) was an American pioneer in computer and information science who was a member of the School of Engineering and Applied Science at the University of Pennsylvania for more than 30 years. Gorn was hir .... References *Gorn, S. (1967). Explicit definitions and linguistic dominoes. Systems and Computer Science, Eds. J. Hart & S. Takasu. 77-115. University of Toronto Press, Toronto Canada. {{DEFAULTSORT:Gorn Address ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertex (graph Theory)
In discrete mathematics, and more specifically in graph theory, a vertex (plural vertices) or node is the fundamental unit of which graphs are formed: an undirected graph consists of a set of vertices and a set of edges (unordered pairs of vertices), while a directed graph consists of a set of vertices and a set of arcs (ordered pairs of vertices). In a diagram of a graph, a vertex is usually represented by a circle with a label, and an edge is represented by a line or arrow extending from one vertex to another. From the point of view of graph theory, vertices are treated as featureless and indivisible objects, although they may have additional structure depending on the application from which the graph arises; for instance, a semantic network is a graph in which the vertices represent concepts or classes of objects. The two vertices forming an edge are said to be the endpoints of this edge, and the edge is said to be incident to the vertices. A vertex ''w'' is said to be ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tree (data Structure)
In computer science, a tree is a widely used abstract data type that represents a hierarchical tree structure with a set of connected nodes. Each node in the tree can be connected to many children (depending on the type of tree), but must be connected to exactly one parent, except for the ''root'' node, which has no parent. These constraints mean there are no cycles or "loops" (no node can be its own ancestor), and also that each child can be treated like the root node of its own subtree, making recursion a useful technique for tree traversal. In contrast to linear data structures, many trees cannot be represented by relationships between neighboring nodes in a single straight line. Binary trees are a commonly used type, which constrain the number of children for each parent to exactly two. When the order of the children is specified, this data structure corresponds to an ordered tree in graph theory. A value or pointer to other data may be associated with every node in the tre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
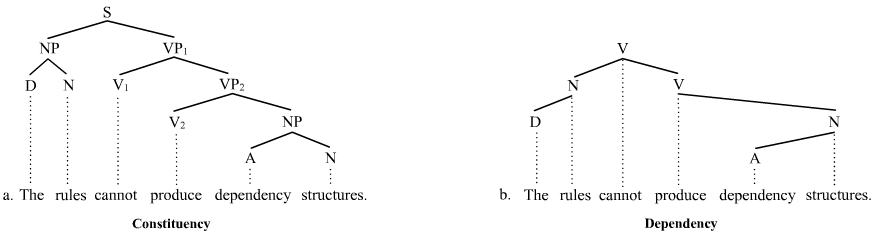
Parse Tree
A parse tree or parsing tree or derivation tree or concrete syntax tree is an ordered, rooted tree that represents the syntactic structure of a string according to some context-free grammar. The term ''parse tree'' itself is used primarily in computational linguistics; in theoretical syntax, the term ''syntax tree'' is more common. Concrete syntax trees reflect the syntax of the input language, making them distinct from the abstract syntax trees used in computer programming. Unlike Reed-Kellogg sentence diagrams used for teaching grammar, parse trees do not use distinct symbol shapes for different types of constituents. Parse trees are usually constructed based on either the constituency relation of constituency grammars (phrase structure grammars) or the dependency relation of dependency grammars. Parse trees may be generated for sentences in natural languages (see natural language processing), as well as during processing of computer languages, such as programming languages. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrase Structure Rules
Phrase structure rules are a type of rewrite rule used to describe a given language's syntax and are closely associated with the early stages of transformational grammar, proposed by Noam Chomsky in 1957. They are used to break down a natural language sentence into its constituent parts, also known as syntactic categories, including both lexical categories (parts of speech) and phrasal categories. A grammar that uses phrase structure rules is a type of phrase structure grammar. Phrase structure rules as they are commonly employed operate according to the constituency relation, and a grammar that employs phrase structure rules is therefore a ''constituency grammar''; as such, it stands in contrast to ''dependency grammars'', which are based on the dependency relation. Definition and examples Phrase structure rules are usually of the following form: :A \to B \quad C meaning that the constituent A is separated into the two subconstituents B and C. Some examples for English are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saul Gorn
Saul Gorn (10 November 1912 – 22 February 1992) was an American pioneer in computer and information science who was a member of the School of Engineering and Applied Science at the University of Pennsylvania for more than 30 years. Gorn was hired by the Moore School as an associate professor in 1955. He worked on the early ENIAC and EDVAC computers. The concept of a Gorn address comes from a paper by him, and the Association for Computing Machinery The Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) is a US-based international learned society for computing. It was founded in 1947 and is the world's largest scientific and educational computing society. The ACM is a non-profit professional member ... (ACM) presented him its Distinguished Service Award for 1974. The Saul Gorn Memorial Lecture series has been established at the University of Pennsylvania in his memory. References External links *Self-Annihilating Sentences: Saul Gorn's Compendium of Rarely Used Clichés, Unive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |