|
Phrase Structure Rules
Phrase structure rules are a type of rewrite rule used to describe a given language's syntax and are closely associated with the early stages of transformational grammar, proposed by Noam Chomsky in 1957. They are used to break down a natural language sentence into its constituent parts, also known as syntactic category, syntactic categories, including both lexical categories (part of speech, parts of speech) and phrase, phrasal categories. A grammar that uses phrase structure rules is a type of phrase structure grammar. Phrase structure rules as they are commonly employed operate according to the constituent (linguistics), constituency relation, and a grammar that employs phrase structure rules is therefore a phrase structure grammar, ''constituency grammar''; as such, it stands in contrast to dependency grammar, ''dependency grammars'', which are based on the government (linguistics), dependency relation. Definition and examples Phrase structure rules are usually of the following ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rewrite Rule
In mathematics, computer science, and logic, rewriting covers a wide range of methods of replacing subterms of a well-formed formula, formula with other terms. Such methods may be achieved by rewriting systems (also known as rewrite systems, rewrite engines, or reduction systems). In their most basic form, they consist of a set of objects, plus Relation (mathematics), relations on how to transform those objects. Rewriting can be non-deterministic algorithm, non-deterministic. One rule to rewrite a term could be applied in many different ways to that term, or more than one rule could be applicable. Rewriting systems then do not provide an algorithm for changing one term to another, but a set of possible rule applications. When combined with an appropriate algorithm, however, rewrite systems can be viewed as computer programs, and several automated theorem proving, theorem provers and declarative programming languages are based on term rewriting. Example cases Logic In logic, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verb Phrase
In linguistics, a verb phrase (VP) is a syntax, syntactic unit composed of a verb and its argument (linguistics), arguments except the subject (grammar), subject of an independent clause or coordinate clause. Thus, in the sentence ''A fat man quickly put the money into the box'', the words ''quickly put the money into the box'' constitute a verb phrase; it consists of the verb ''put'' and its arguments, but not the subject ''a fat man''. A verb phrase is similar to what is considered a ''predicate (grammar), predicate'' in traditional grammars. Verb phrases generally are divided among two types: finite, of which the Head (linguistics), head of the phrase is a finite verb; and nonfinite, where the head is a nonfinite verb, such as an infinitive, participle or gerund. Phrase structure grammars acknowledge both types, but dependency grammars treat the subject as just another verbal dependent, and they do not recognize the finite verbal phrase constituent (linguistics), constituent. Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimalist Program
In linguistics, the minimalist program is a major line of inquiry that has been developing inside generative grammar since the early 1990s, starting with a 1993 paper by Noam Chomsky. Following Imre Lakatos's distinction, Chomsky presents minimalism as a research program, program, understood as a mode of inquiry that provides a conceptual framework which guides the development of linguistic theory. As such, it is characterized by a broad and diverse range of research directions. For Chomsky, there are two basic Minimalist grammar, minimalist questions—What is language? and Why does it have the properties it has?—but the answers to these two questions can be framed in any theory.Boeckx, Cedric ''Linguistic Minimalism. Origins, Concepts, Methods and Aims'', pp. 84 and 115. Conceptual framework Goals and assumptions Minimalism is an approach developed with the goal of understanding the nature of language. It models a speaker's knowledge of language as a computational syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passivization
A passive voice construction is a grammatical voice construction that is found in many languages. In a clause with passive voice, the grammatical subject expresses the ''theme'' or ''patient'' of the main verb – that is, the person or thing that undergoes the action or has its state changed. This contrasts with active voice, in which the subject has the agent role. For example, in the passive sentence "The tree was pulled down", the subject (''the tree'') denotes the patient rather than the agent of the action. In contrast, the sentences "Someone pulled down the tree" and "The tree is down" are active sentences. Typically, in passive clauses, what is usually expressed by the object (or sometimes another argument) of the verb is now expressed by the subject, while what is usually expressed by the subject is either omitted or is indicated by some adjunct of the clause. Thus, turning an active sense of a verb into a passive sense is a valence-decreasing process ("detransitivi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negation (linguistics)
In linguistics and grammar, affirmation ( abbreviated ) and negation () are ways in which grammar encodes positive and negative polarity into verb phrases, clauses, or utterances. An affirmative (positive) form is used to express the validity or truth of a basic assertion, while a negative form expresses its falsity. For example, the affirmative sentence "Joe is here" asserts that it is true that Joe is currently located near the speaker. Conversely, the negative sentence "Joe is not here" asserts that it is not true that Joe is currently located near the speaker. The grammatical category associated with affirmatives and negatives is called polarity. This means that a clause, sentence, verb phrase, etc. may be said to have either affirmative or negative polarity (its polarity may be either affirmative or negative). Affirmative is typically the unmarked polarity, whereas a negative statement is marked in some way. Negative polarity can be indicated by negating words or particle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immediate Constituent Analysis
In linguistics, Immediate Constituent Analysis (ICA) is a syntactic theory which focuses on the hierarchical structure of sentences by isolating and identifying the Constituent (linguistics), constituents. While the idea of breaking down sentences into smaller components can be traced back to early psychological and linguistic theories, ICA as a formal method was developed in the early 20th century. It was influenced by Wilhelm Wundt's psychological theories of sentence structure but was later refined and formalized within the framework of structural linguistics by Leonard Bloomfield. The method gained traction in the distributionalist tradition through the work of Zellig Harris and Charles F. Hockett, who expanded and applied it to sentence analysis. Additionally, ICA was further explored within the context of glossematics by Knud Togeby. These contributions helped ICA become a central tool in syntactic analysis, focusing on the hierarchical relationships between sentence constituen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendrogram
A dendrogram is a diagram representing a Tree (graph theory), tree graph. This diagrammatic representation is frequently used in different contexts: * in hierarchical clustering, it illustrates the arrangement of the clusters produced by the corresponding analyses. * in computational biology, it shows the clustering of genes or samples, sometimes in the margins of heat map, heatmaps. * in phylogenetics, it displays the evolutionary relationships among various biological taxa. In this case, the dendrogram is also called a phylogenetic tree. The name ''dendrogram'' derives from the two ancient greek words (), meaning "tree", and (), meaning "drawing, mathematical figure". Clustering example For a clustering example, suppose that five taxa (a to e) have been clustered by UPGMA based on a matrix of genetic distances. The hierarchical clustering dendrogram would show a column of five nodes representing the initial data (here individual taxa), and the remaining nodes repre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
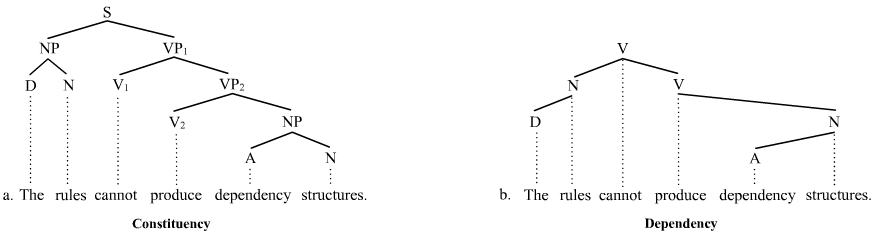
Parse Tree
A parse tree or parsing tree (also known as a derivation tree or concrete syntax tree) is an ordered, rooted tree that represents the syntactic structure of a string according to some context-free grammar. The term ''parse tree'' itself is used primarily in computational linguistics; in theoretical syntax, the term ''syntax tree'' is more common. Concrete syntax trees reflect the syntax of the input language, making them distinct from the abstract syntax trees used in computer programming. Unlike Reed-Kellogg sentence diagrams used for teaching grammar, parse trees do not use distinct symbol shapes for different types of constituents. Parse trees are usually constructed based on either the constituency relation of constituency grammars ( phrase structure grammars) or the dependency relation of dependency grammars. Parse trees may be generated for sentences in natural languages (see natural language processing), as well as during processing of computer languages, such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colorless Green Ideas Sleep Furiously
''Colorless green ideas sleep furiously'' was composed by Noam Chomsky in his 1957 book '' Syntactic Structures'' as an example of a sentence that is grammatically well-formed, but semantically nonsensical. The sentence was originally used in his 1955 thesis '' The Logical Structure of Linguistic Theory'' and in his 1956 paper "Three Models for the Description of Language". There is no obvious understandable meaning that can be derived from it, which demonstrates the distinction between syntax and semantics, and the idea that a syntactically well-formed sentence is not guaranteed to also be semantically well-formed. As an example of a category mistake, it was intended to show the inadequacy of certain probabilistic models of grammar, and the need for more structured models. Senseless but grammatical Chomsky wrote in his 1957 book '' Syntactic Structures'': It is fair to assume that neither sentence (1) nor (2) had ever previously occurred in an English discourse. Hence, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantics
Semantics is the study of linguistic Meaning (philosophy), meaning. It examines what meaning is, how words get their meaning, and how the meaning of a complex expression depends on its parts. Part of this process involves the distinction between sense and reference. Sense is given by the ideas and concepts associated with an expression while reference is the object to which an expression points. Semantics contrasts with syntax, which studies the rules that dictate how to create grammatically correct sentences, and pragmatics, which investigates how people use language in communication. Lexical semantics is the branch of semantics that studies word meaning. It examines whether words have one or several meanings and in what lexical relations they stand to one another. Phrasal semantics studies the meaning of sentences by exploring the phenomenon of compositionality or how new meanings can be created by arranging words. Formal semantics (natural language), Formal semantics relies o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammaticality
In linguistics, grammaticality is determined by the conformity to language usage as derived by the grammar of a particular speech variety. The notion of grammaticality rose alongside the theory of generative grammar, the goal of which is to formulate rules that define well-formed, grammatical sentences. These rules of grammaticality also provide explanations of ill-formed, ungrammatical sentences. In theoretical linguistics, a speaker's judgement on the well-formedness of a linguistic 'string'—called a grammaticality judgement—is based on whether the sentence is interpreted in accordance with the rules and constraints of the relevant grammar. If the rules and constraints of the particular lect are followed, then the sentence is judged to be grammatical. In contrast, an ungrammatical sentence is one that violates the rules of the given language variety. Linguists use grammaticality judgements to investigate the syntactic structure of sentences. Generative linguists are larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |