|
Gorm The Old
Gorm the Old ( da, Gorm den Gamle; non, Gormr gamli; la, Gormus Senex), also called Gorm the Languid ( da, Gorm Løge, Gorm den Dvaske), was ruler of Denmark, reigning from to his death or a few years later.Lund, N. (2020), p. 147''Pilemedia'' (in Swedish), 25 October 2020 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
August Carl Vilhelm Thomsen
August is the eighth month of the year in the Julian and Gregorian calendars, and the fifth of seven months to have a length of 31 days. Its zodiac sign is Leo and was originally named '' Sextilis'' in Latin because it was the 6th month in the original ten-month Roman calendar under Romulus in 753 BC, with March being the first month of the year. About 700 BC, it became the eighth month when January and February were added to the year before March by King Numa Pompilius, who also gave it 29 days. Julius Caesar added two days when he created the Julian calendar in 46 BC (708 AUC), giving it its modern length of 31 days. In 8 BC, it was renamed in honor of Emperor Augustus. According to a Senatus consultum quoted by Macrobius, he chose this month because it was the time of several of his great triumphs, including the conquest of Egypt. Commonly repeated lore has it that August has 31 days because Augustus wanted his month to match the length of Julius Caesar's July, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adam Of Bremen
Adam of Bremen ( la, Adamus Bremensis; german: Adam von Bremen) (before 1050 – 12 October 1081/1085) was a German medieval chronicler. He lived and worked in the second half of the eleventh century. Adam is most famous for his chronicle '' Gesta Hammaburgensis ecclesiae pontificum'' (''Deeds of Bishops of the Hamburg Church''). He was "one of the foremost historians and early ethnographers of the medieval period". In his chronicle, he included a chapter mentioning the Norse outpost of Vinland, and was thus the first European to write about the New World. Life Little is known of his life other than hints from his own chronicles. He is believed to have come from Meissen, then its own margravate. The dates of his birth and death are uncertain, but he was probably born before 1050 and died on 12 October of an unknown year (possibly 1081, at the latest 1085). From his chronicles, it is apparent that he was familiar with a number of authors. The honorary name of ''Magister Adam'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treene (river)
The Treene ( da, Trenen) is a river, hydrologically and nominally long, in the north of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is a right-bank tributary of the River Eider. It starts in northern Angeln, southeast of Flensburg, and flows mainly south-south-west before joining the Eider near Friedrichstadt. The upper course is called Bondenau. Its source is situated in the ground of Mohrkirch. The name 'Treene' begins at the Tresssee lake near Großsolt in the district of Schleswig-Flensburg. After about it reaches the town of Friedrichstadt (in Nordfriesland district). There it is released through valves into the estuary of the Eider, above the Eider Barrage. It is the most important tributary of Eider river. Since the construction of Kiel Canal, it is even stronger than Eider river itself. Details The Bondenau, as the main headstream of the Treene, rises east of the Tressee on the peninsula of Angeln, bounded by the Flensburger Förde and the Schlei. So the Treene is an unusu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
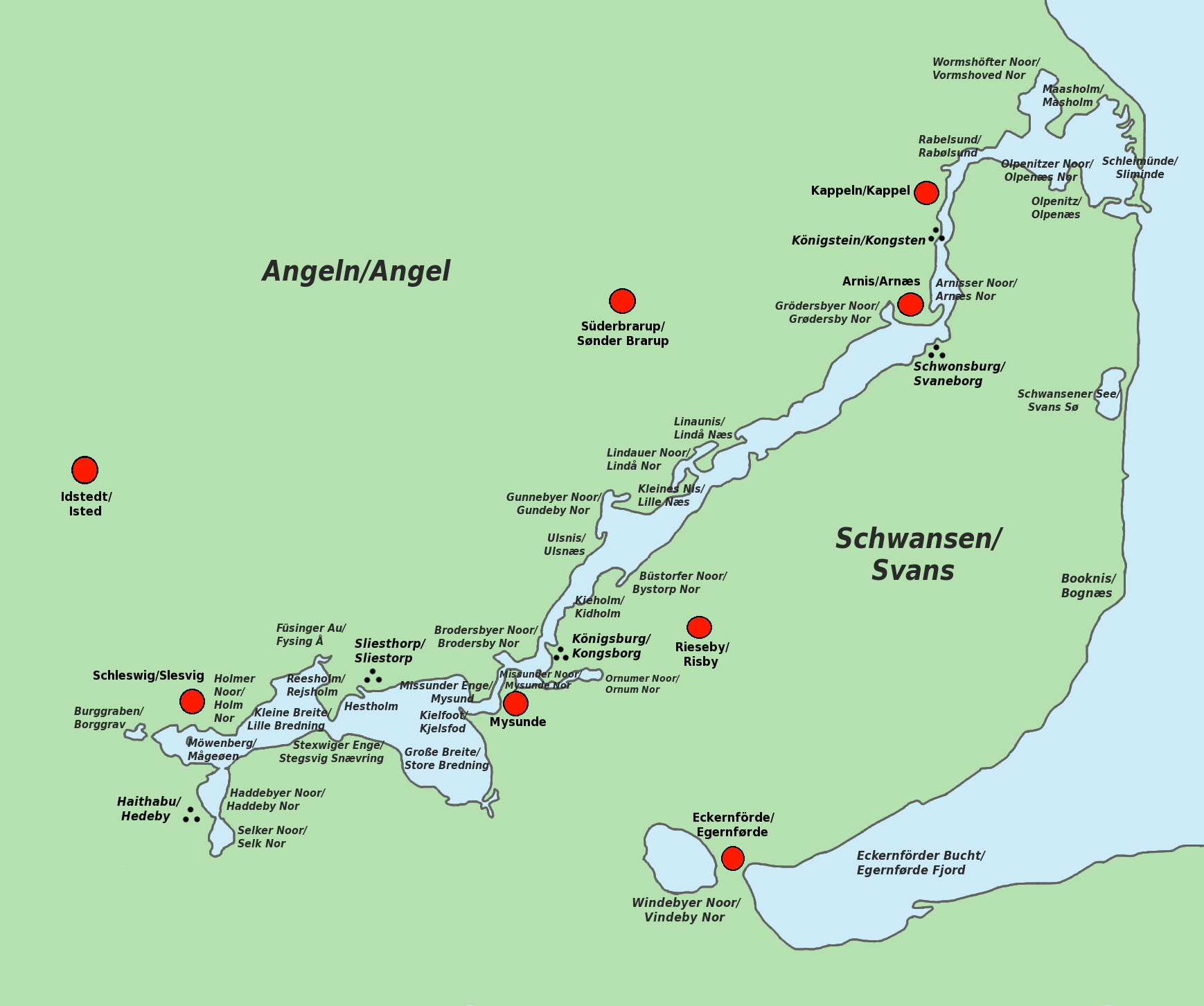
Schlei
The Schlei (; da, Slien, also ''Slesvig Fjord''e.g. in: Adolph Frederik Bergsøe: ''Den danske stats statistik'', Kjøbenhavn 1844, p. 156) (more often referred to in English as the Sly Firth) is a narrow inlet of the Baltic Sea in Schleswig-Holstein in northern Germany Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou .... It stretches for approximately 20 miles (32 kilometers) from the Baltic near Kappeln and Arnis to the city of Schleswig. Along the Schlei are many small bays and swamps. It separates the Angeln peninsula to the north from the Schwansen peninsula to the south. The important Viking settlement of Hedeby was located at the head of the firth ( fjord), but was later abandoned in favor of the city of Schleswig. A museum has been built on the site, telling the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxon
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic * * * * peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country ( Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the North Sea coast of northern Germania, in what is now Germany. In the late Roman Empire, the name was used to refer to Germanic coastal raiders, and as a name similar to the later " Viking". Their origins are believed to be in or near the German North Sea coast where they appear later, in Carolingian times. In Merovingian times, continental Saxons had been associated with the activity and settlements on the coast of what later became Normandy. Their precise origins are uncertain, and they are sometimes described as fighting inland, coming into conflict with the Franks and Thuringians. There is possibly a single classical reference to a smaller homeland of an early Saxon tribe, but its interpretation is disputed. According to this proposal, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danevirke
The Danevirke or Danework (modern Danish spelling: ''Dannevirke''; in Old Norse; ''Danavirki'', in German; ''Danewerk'', literally meaning '' earthwork of the Danes'') is a system of Danish fortifications in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. This historically important linear defensive earthwork across the neck of the Cimbrian peninsula was initiated by the Danes in the Nordic Iron Age about AD 650. It was later expanded multiple times during Denmark's Viking Age and High Middle Ages. The Danevirke was last used for military purposes in 1864 during the Second War of Schleswig. The Danevirke consists of several walls, trenches and the Schlei Barrier. The walls stretch for 30 km, from the former Viking trade centre of Hedeby near Schleswig on the Baltic Sea coast in the east to the extensive marshlands in the west of the peninsula. One of the walls (named ''Østervolden''), between the Schlei and Eckernförde inlets, defended the Schwansen peninsula. According to written sources, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burial Mound
Burial, also known as interment or inhumation, is a method of final disposition whereby a dead body is placed into the ground, sometimes with objects. This is usually accomplished by excavating a pit or trench, placing the deceased and objects in it, and covering it over. A funeral is a ceremony that accompanies the final disposition. Humans have been burying their dead since shortly after the origin of the species. Burial is often seen as indicating respect for the dead. It has been used to prevent the odor of decay, to give family members closure and prevent them from witnessing the decomposition of their loved ones, and in many cultures it has been seen as a necessary step for the deceased to enter the afterlife or to give back to the cycle of life. Methods of burial may be heavily ritualized and can include natural burial (sometimes called "green burial"); embalming or mummification; and the use of containers for the dead, such as shrouds, coffins, grave liners ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jutland
Jutland ( da, Jylland ; german: Jütland ; ang, Ēota land ), known anciently as the Cimbric or Cimbrian Peninsula ( la, Cimbricus Chersonesus; da, den Kimbriske Halvø, links=no or ; german: Kimbrische Halbinsel, links=no), is a peninsula of Northern Europe that forms the continental portion of Denmark and part of northern Germany. The names are derived from the Jutes and the Cimbri, respectively. As with the rest of Denmark, Jutland's terrain is flat, with a slightly elevated ridge down the central parts and relatively hilly terrains in the east. West Jutland is characterised by open lands, heaths, plains, and peat bogs, while East Jutland is more fertile with lakes and lush forests. Southwest Jutland is characterised by the Wadden Sea, a large unique international coastal region stretching through Denmark, Germany, and the Netherlands. Geography Jutland is a peninsula bounded by the North Sea to the west, the Skagerrak to the north, the Kattegat and Baltic Sea to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
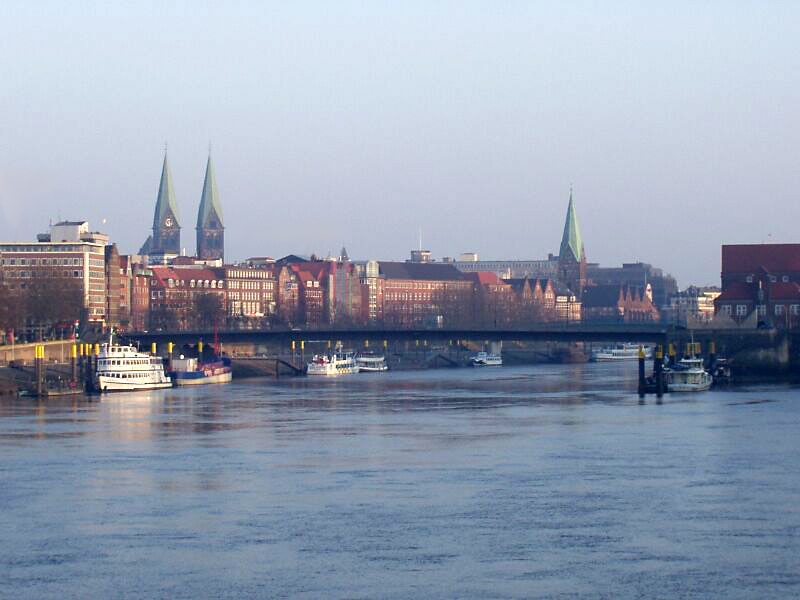
Bremen
Bremen (Low German also: ''Breem'' or ''Bräm''), officially the City Municipality of Bremen (german: Stadtgemeinde Bremen, ), is the capital of the Germany, German States of Germany, state Bremen (state), Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (''Freie Hansestadt Bremen''), a two-city-state consisting of the cities of Bremen and Bremerhaven. With about 570,000 inhabitants, the Hanseatic League, Hanseatic city is the List of cities in Germany by population, 11th largest city of Germany and the second largest city in Northern Germany after Hamburg. Bremen is the largest city on the River Weser, the longest river flowing entirely in Germany, lying some upstream from its River mouth, mouth into the North Sea, and is surrounded by the state of Lower Saxony. A commercial and industrial city, Bremen is, together with Oldenburg (city), Oldenburg and Bremerhaven, part of the Bremen/Oldenburg Metropolitan Region, with 2.5 million people. Bremen is contiguous with the Lower Saxon towns of Delmenhor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; nds, label=Hamburg German, Low Saxon, Hamborg ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg (german: Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg; nds, label=Low Saxon, Friee un Hansestadt Hamborg),. is the List of cities in Germany by population, second-largest city in Germany after Berlin, as well as the overall List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, 7th largest city and largest non-capital city in the European Union with a population of over 1.85 million. Hamburg's urban area has a population of around 2.5 million and is part of the Hamburg Metropolitan Region, which has a population of over 5.1 million people in total. The city lies on the River Elbe and two of its tributaries, the River Alster and the Bille (Elbe), River Bille. One of Germany's 16 States of Germany, federated states, Hamburg is surrounded by Schleswig-Holstein to the north and Lower Saxony to the south. The official name reflects History of Hamburg, Hamburg's history ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unni (archbishop)
Saint Unni was an archbishop of Hamburg-Bremen (916 – 17 September 936). He died as a missionary in Birka in Sweden, where he tried to continue Ansgar's work. According to Adam of Bremen, his body was buried in Birka, but his head was entombed in Bremen Cathedral. When the altar was taken down in 1840, a leaden plate was found with the inscription "VNNIS ARCHIEP(is)-C(opus)". After Ansgar and Rimbert of Turholt, epithet An epithet (, ), also byname, is a descriptive term (word or phrase) known for accompanying or occurring in place of a name and having entered common usage. It has various shades of meaning when applied to seemingly real or fictitious people, di ...ised ''Apostle of the North'' and ''second Apostle of the North'', Unni is revered as ''third Apostle of the North'' and as Saint. Literature * Notes 936 deaths 10th-century archbishops Archbishops of Hamburg-Bremen German Roman Catholic saints Year of birth unknown {{Germany-RC-bishop-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
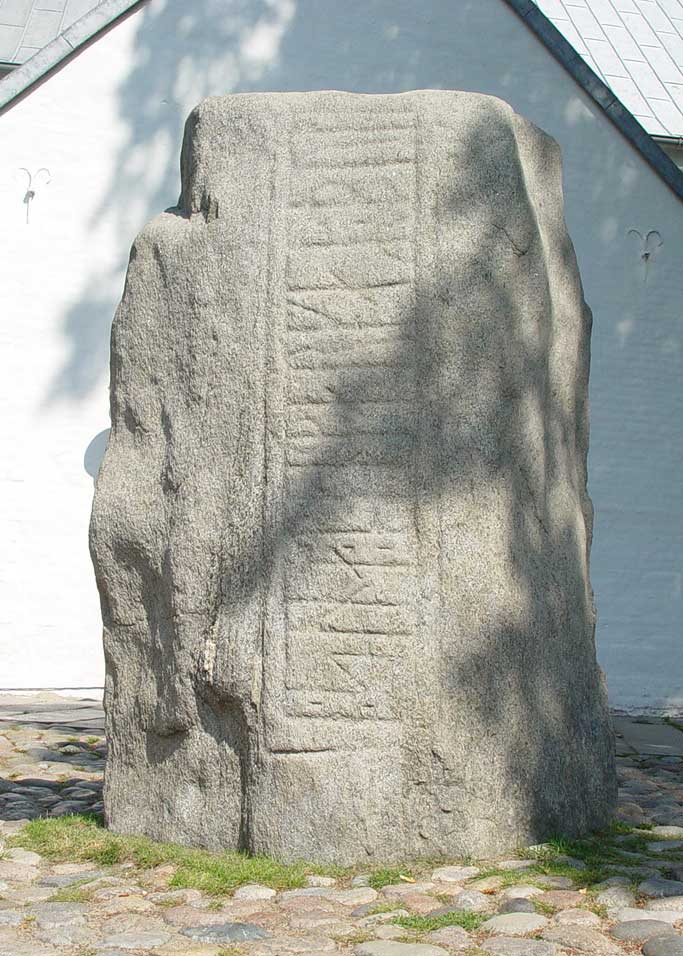
Gyrd And Gnupa
Gyrd and Gnupa were kings of Denmark in the 10th century according to Sweyn II of Denmark and Adam of Bremen. They were the sons of the Swedish chieftain Olof (or Olaf) the Brash who had conquered Denmark and they ruled together according to Swedish tradition. Gnupa is mentioned on the two Sigtrygg Runestones raised near Schleswig by his wife Asfrid for their son Sigtrygg. Likewise a Danish king ''Chnuba'' is named by Widukind of Corvey's Saxon chronicles The ''Deeds of the Saxons, or Three Books of Annals'' ( la, Res gestae Saxonicae sive annalium libri tres) is a three-volume chronicle of 10th century Germany written by Widukind of Corvey. Widukind, proud of his people and history, begins his chr ... as having been defeated and forced to accept baptism in 934, and Olav Tryggvasson's Saga tells of Gnupa's defeat by Gorm the Old. However, this chronology would contradict that of Adam of Bremen, who places the succession and subsequent defeat of Sigtrygg during the tenure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |