|
Gordon, Alaska
Gordon (or, in Inupiaq, ''Pattaktuq'', meaning “he/she/it is spanking”, alluding to the pounding of the waves on the shore, as though it is being spanked by someone; also ''Demarcation'') was a former fur trading post in North Slope Borough, Alaska, United States on the shore of Demarcation Bay, near the Canadian border in the east. It is located approximately 200 miles (325 km) north of the Arctic Circle, 2.5 miles (4 km) east of Demarcation Point and 65 miles (105 km) east of Kaktovik. It was one of the many trading outposts established along the north coast of Alaska in the early 20th century. History The place was named after Thomas Gordon, a Scottish whaler and trader who was sent by Charles Brower to Demarcation Point in 1917 to establish the post for the fur trading company H.B. Liebes Company of San Francisco. He founded the settlement with the help of Andrew Akootchook, his brother-in-law, and moved there with his wife and their families. After G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unincorporated Area
An unincorporated area is a region that is not governed by a local municipal corporation. Widespread unincorporated communities and areas are a distinguishing feature of the United States and Canada. Most other countries of the world either have no unincorporated areas at all or these are very rare: typically remote, outlying, sparsely populated or List of uninhabited regions, uninhabited areas. By country Argentina In Argentina, the provinces of Chubut Province, Chubut, Córdoba Province (Argentina), Córdoba, Entre Ríos Province, Entre Ríos, Formosa Province, Formosa, Neuquén Province, Neuquén, Río Negro Province, Río Negro, San Luis Province, San Luis, Santa Cruz Province, Argentina, Santa Cruz, Santiago del Estero Province, Santiago del Estero, Tierra del Fuego Province, Argentina, Tierra del Fuego, and Tucumán Province, Tucumán have areas that are outside any municipality or commune. Australia Unlike many other countries, Australia has only local government in Aus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trading Post
A trading post, trading station, or trading house, also known as a factory, is an establishment or settlement where goods and services could be traded. Typically the location of the trading post would allow people from one geographic area to trade in goods produced in another area. In some examples, local inhabitants could use a trading post to exchange local products for goods they wished to acquire. Examples Major towns in the Hanseatic League were known as '' kontors'', a form of trading posts. Charax Spasinu was a trading post between the Roman and Parthian Empires. Manhattan and Singapore were both established as trading posts, by Dutchman Peter Minuit and Englishman Stamford Raffles respectively, and later developed into major settlements. Other uses * In the context of scouting, trading post usually refers to a camp store in which snacks, craft materials, and general merchandise are sold. "Trading posts" also refers to a cub scout actitivty in which cub teams (or in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unincorporated Communities In North Slope Borough, Alaska
Unincorporated may refer to: * Unincorporated area, land not governed by a local municipality * Unincorporated entity, a type of organization * Unincorporated territories of the United States, territories under U.S. jurisdiction, to which Congress has determined that only select parts of the U.S. Constitution apply * Unincorporated association Unincorporated associations are one vehicle for people to cooperate towards a common goal. The range of possible unincorporated associations is nearly limitless, but typical examples are: :* An amateur football team who agree to hire a pitch onc ..., also known as voluntary association, groups organized to accomplish a purpose * ''Unincorporated'' (album), a 2001 album by Earl Harvin Trio {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaskan Athabaskans
The Alaskan Athabascans, Alaskan Athabascans, Alaskan AthapascansWilliam Simeone, ''A History of Alaskan Athapaskans'', 1982, Alaska Historical Commission or Dena (russian: атабаски Аляски, атапаски Аляски) are Alaska Native peoples of the Athabaskan-speaking ethnolinguistic group. They are the original inhabitants of the interior of Alaska. In Alaska, where they are the oldest, there are eleven groups identified by the languages they speak. These are the Dena’ina or Tanaina (''Ht’ana''), Ahtna or Copper River Athabascan (''Hwt’aene''), Deg Hit’an or Ingalik (''Hitʼan''), Holikachuk (''Hitʼan''), Koyukon (''Hut’aane''), Upper Kuskokwim or Kolchan (''Hwt’ana''), Tanana or Lower Tanana (''Kokht’ana''), Tanacross or Tanana Crossing (''Koxt’een''), Upper Tanana (''Kohtʼiin''), Gwich'in or Kutchin (''Gwich’in''), and Hän (''Hwëch’in''). The Alaskan Athabascan culture is an inland creek and river fishing (also coastal fishi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coastal Erosion
Coastal erosion is the loss or displacement of land, or the long-term removal of sediment and rocks along the coastline due to the action of waves, currents, tides, wind-driven water, waterborne ice, or other impacts of storms. The landward retreat of the shoreline can be measured and described over a temporal scale of tides, seasons, and other short-term cyclic processes. Coastal erosion may be caused by hydraulic action, abrasion, impact and corrosion by wind and water, and other forces, natural or unnatural. On non-rocky coasts, coastal erosion results in rock formations in areas where the coastline contains rock layers or fracture zones with varying resistance to erosion. Softer areas become eroded much faster than harder ones, which typically result in landforms such as tunnels, bridges, columns, and pillars. Over time the coast generally evens out. The softer areas fill up with sediment eroded from hard areas, and rock formations are eroded away. Also erosion co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
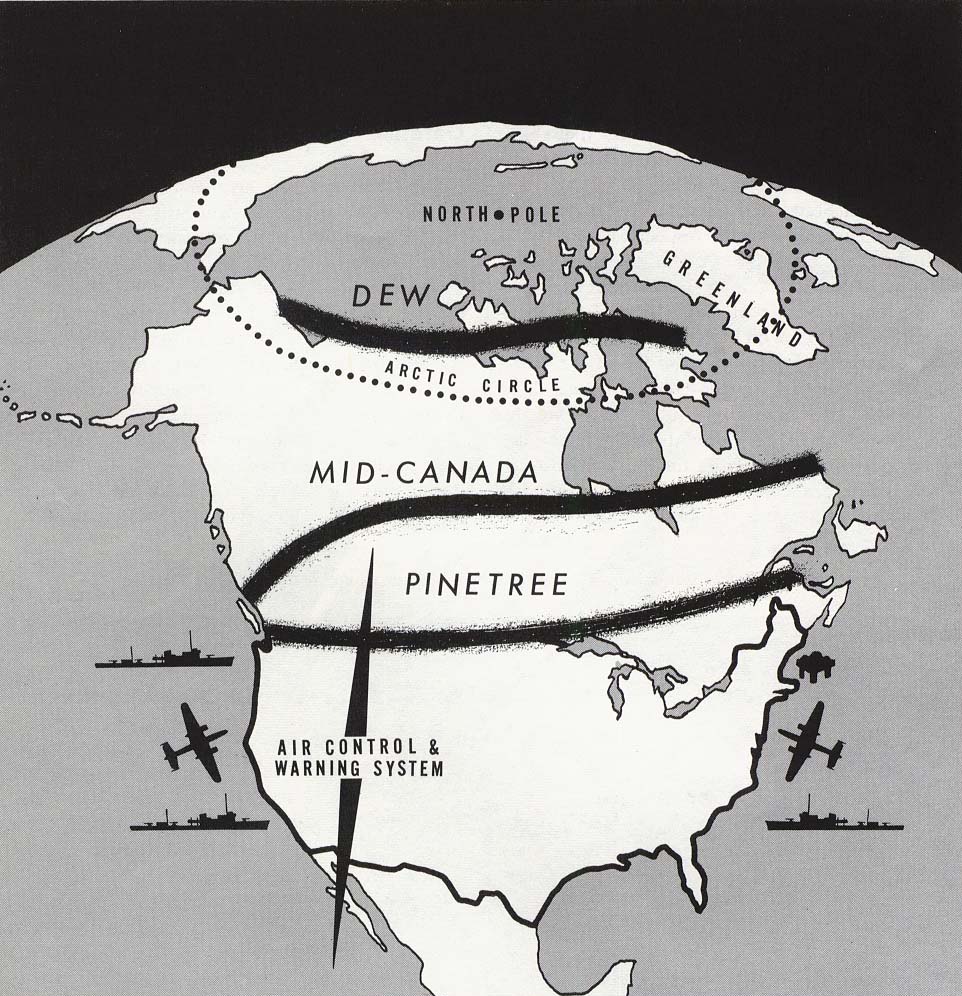
DEW Line
The Distant Early Warning Line, also known as the DEW Line or Early Warning Line, was a system of radar stations in the northern Arctic region of Canada, with additional stations along the north coast and Aleutian Islands of Alaska (see Project Stretchout and Project Bluegrass), in addition to the Faroe Islands, Greenland, and Iceland. It was set up to detect incoming bombers of the Soviet Union during the Cold War, and provide early warning of any sea-and-land invasion. The DEW Line was the northernmost and most capable of three radar lines in Canada and Alaska. The first of these was the joint Canadian-United States Pinetree Line, which ran from Newfoundland to Vancouver Island just north of the Canada–United States border, but even while it was being built there were concerns that it would not provide enough warning time to launch an effective counterattack. The Mid-Canada Line (MCL) was proposed as an inexpensive solution using bistatic radar. This provided a "trip w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barter Island
Barter Island is an island located on the Arctic coast of the U.S. state of Alaska, east of Arey Island in the Beaufort Sea. It is about four miles (6 km) long and about two miles (3 km) wide at its widest point. Until the late 19th century, Barter Island was a major trade center for the Inupiat people and was especially important as a bartering place for Inupiat from Alaska and Inuit from Canada, hence its name. At one time before about 1900, there had been a large whaling village on Barter Island. Tradition has it that the Alaska Inupiat drove the villagers, Canadian Inupiat, from the island in about 1900. In about 1919, trader Tom Gordon and his wife, Mary Agiaq Gordon, moved from Barrow to Barter Island with their family, some relatives, friends, and their families. Mary's younger brother, Andrew Akootchook, helped to choose the location for the trading post, because of its good harbor and convenient and accessible location for hunting on land and sea. Tom Gord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Gordon (Scottish Trader)
Thomas Gordon may refer to: * Thomas Gordon (lawyer) (1652–1722), American lawyer and politician of the colonial period * Thomas Gordon (Royal Scots Navy officer) (c. 1658–1741), Commodore in the Royal Scots Navy and then Admiral and Commander-in-Chief at Kronstadt of the Imperial Russian navy * Thomas Gordon (writer) (c. 1691–1750), British writer * Thomas Gordon (philosopher) (1714–1797), Scottish philosopher and antiquarian * Thomas Gordon (British Army officer) (1788–1841), British army officer and historian * Thomas Boston Gordon (1816–1891), civil war captain, lawyer and judge from Kentucky * Thomas Edward Gordon (1832–1914), British traveller, author of a book about 19th-century Kashgaria * Thomas Gisborne Gordon (1851–1935), Ireland rugby player * Thomas Gordon (Australian politician) (1882–1949), Australian politician and businessman * Thomas S. Gordon (1893–1959), U.S. Representative from Illinois * Thomas C. Gordon (1915–2003), Virginia state supre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaktovik
Kaktovik (; ik, Qaaktuġvik, ) is a city in North Slope Borough, Alaska, United States. The population was 283 at the 2020 census. History Until the late nineteenth century, Barter Island was a major trade center for the Inupiat and was especially important as a bartering place for Inupiat from Alaska and Inuit from Canada. Kaktovik was a traditional fishing place—''Kaktovik'' means "Seining Place"—that has a large pond of good fresh water on high ground. It had no permanent settlers until people from other parts of Barter Island and northern Alaska moved to the area around the construction of a runway and Distant Early Warning Line station in the 1950s. The area was incorporated as the City of Kaktovik in 1971. Due to Kaktovik's isolation, the village has maintained its Inupiat Eskimo traditions. Subsistence is highly dependent upon the hunting of caribou and whale. In the early twenty-first century Kaktovik became a tourist destination to view polar bears. This is i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demarcation Point
In telephony, the demarcation point is the point at which the public switched telephone network ends and connects with the customer's on-premises wiring. It is the dividing line which determines who is responsible for installation and maintenance of wiring and equipment—customer/subscriber, or telephone company/provider. The demarcation point varies between countries and has changed over time. ''Demarcation point'' is sometimes abbreviated as demarc, DMARC, or similar. The term MPOE (minimum or main point of entry) is synonymous, with the added implication that it occurs as soon as possible upon entering the customer premises. A network interface device often serves as the demarcation point. History Prior to Federal Communications Commission (FCC) regulations separating the ownership of customer premises telecommunication equipment from the telephone network, there was no need for a public standard governing the interconnection of customer premises equipment (CPE) to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctic Circle
The Arctic Circle is one of the two polar circles, and the most northerly of the five major circles of latitude A circle of latitude or line of latitude on Earth is an abstract east–west small circle connecting all locations around Earth (ignoring elevation) at a given latitude coordinate line. Circles of latitude are often called parallels because ... as shown on maps of Earth. Its southern equivalent is the Antarctic Circle. The Arctic Circle marks the southernmost latitude at which, on the December solstice, the shortest day of the year in the northern hemisphere, the sun will not rise all day, and on the June solstice, the longest day of the year in the northern hemisphere, the sun will not set. These phenomena are referred to as polar night and midnight sun respectively, and the further north one progresses, the more pronounced these effects become. For example, in the Russian port city of Murmansk, three degrees above the Arctic Circle, the sun does not rise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_1900.jpg)