|
Gonia Frontosa
''Gonia frontosa'' is a species of fly in the family Tachinidae. Distribution United States, Canada Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot .... References Diptera of North America Tachinidae Taxa named by Thomas Say Insects described in 1829 {{tachinidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Say
Thomas Say (June 27, 1787 – October 10, 1834) was an American entomologist, conchologist, and Herpetology, herpetologist. His studies of insects and shells, numerous contributions to scientific journals, and scientific expeditions to Florida, Georgia, the Rocky Mountains, Mexico, and elsewhere made him an internationally known naturalist. Say has been called the father of American descriptive entomology and American conchology. He served as librarian for the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia, curator at the American Philosophical Society (elected in 1817), and professor of natural history at the University of Pennsylvania. Early life and education Born in Philadelphia into a prominent Religious Society of Friends, Quaker family, Thomas Say was the great-grandson of John Bartram, and the great-nephew of William Bartram. His father, Dr. Benjamin Say, was brother-in-law to another Bartram son, Moses Bartram. The Say family had a house, "The Cliffs" at Gray's Ferry Bridge, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
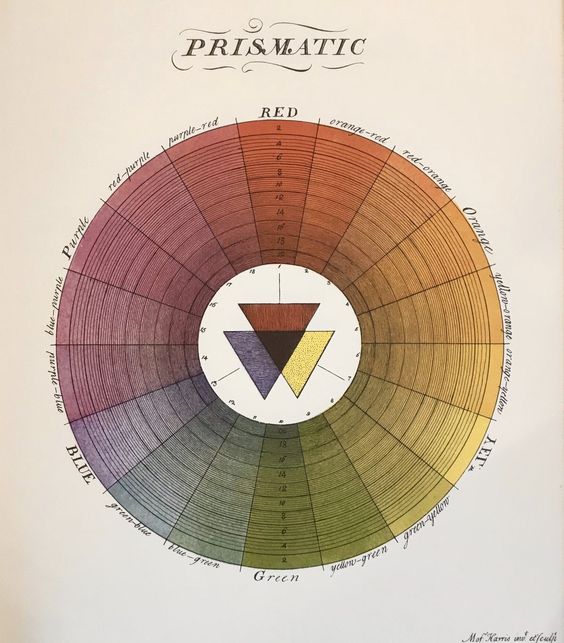
Moses Harris
Moses Harris (15 April 1730 – 1787) was an English entomologist and engraver. Life and work Harris was encouraged in entomology from a young age by his uncle, a member of the Society of the Aurelians. In 1762 he became secretary of a second Society of Aurelians. He was a skilled artist, displaying some of his insect drawings at the Royal Academy in 1785. He drew and engraved illustrations for books including Dru Drury's ''Illustrations of Natural History'' (3 volumes, 1770–1782) and John Coakley Lettsom's ''The Naturalist's and Traveller's Companion'' (1772). Colour theory In "The Natural System of Colours" published in 1766, Harris discussed the multitude of colours that can be created using three "grand or principle" colours: red, yellow and blue. As a naturalist and an engraver, Harris focussed on the relationships between colours and how they are coded and created. He explained how three colours can be íntermixed, tinted and shaded to create 660 colours "materially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre-Justin-Marie Macquart
Pierre-Justin-Marie Macquart (8 April 1778 – 25 November 1855) was a French entomologist specialising in the study of Diptera. He worked on world species as well as European and described many new species. Biography Early years Macquart was born in Hazebrouck, France, in 1778 and died in Lille in 1855. He was interested in natural history from an early age due to his older brother who was an ornithologist and a Fellow of the Société de Sciences de l’Agriculture et des Arts de la Ville de Lille and whose bird collection became the foundation of the societies museum, the Musée d'Histoire Naturelle de Lille. A second brother founded a botanic garden with a collection of over 3000 species of plants. Macquart, too became interested in natural history. In 1796 he joined the staff of General Armand Samuel then campaigning in the French Revolutionary Wars: Campaigns of 1796, Revolutionary Wars. He was a secretary and draftsman. The general staff was stationed in Schwetzingen, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Henry Tyler Townsend
Charles Henry Tyler Townsend (5 December 1863 – 17 March 1944) was an American entomologist specializing in the study of tachinids (Tachinidae), a large and diverse family of flies (Diptera) with larvae that are parasitoids of other insects. He was perhaps the most prolific publisher of new tachinids, naming and describing some 3000 species and genera. He made important contributions to the biological control of insect pests and he was the first to identify the insect vector of a debilitating disease in Peru. Townsend was also a controversial figure and criticism of his approach to insect taxonomy continues to this day. Biography Townsend was born in Oberlin, Ohio, in 1863. He attended high school in Constantine, Michigan and graduated in 1882. From 1887 to 1891 he studied medicine at Columbian University (now George Washington University) in Washington, D.C. At the same time he worked in the United States Department of Agriculture as an assistant entomologist for Charles V. Ril ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tachinidae
The Tachinidae are a large and variable family of true flies within the insect order Diptera, with more than 8,200 known species and many more to be discovered. Over 1,300 species have been described in North America alone. Insects in this family commonly are called tachinid flies or simply tachinids. As far as is known, they all are protelean parasitoids, or occasionally parasites, of arthropods, usually other insects. The family is known from many habitats in all zoogeographical regions and is especially diverse in South America. Life cycle Reproductive strategies vary greatly between Tachinid species, largely, but not always clearly, according to their respective life cycles. This means that they tend to be generalists rather than specialists. Comparatively few are restricted to a single host species, so there is little tendency towards the close co-evolution one finds in the adaptations of many specialist species to their hosts, such as are typical of protelean parasito ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diptera Of North America
Flies are insects of the order Diptera, the name being derived from the Greek δι- ''di-'' "two", and πτερόν ''pteron'' "wing". Insects of this order use only a single pair of wings to fly, the hindwings having evolved into advanced mechanosensory organs known as halteres, which act as high-speed sensors of rotational movement and allow dipterans to perform advanced aerobatics. Diptera is a large order containing an estimated 1,000,000 species including horse-flies, crane flies, hoverflies and others, although only about 125,000 species have been described. Flies have a mobile head, with a pair of large compound eyes, and mouthparts designed for piercing and sucking (mosquitoes, black flies and robber flies), or for lapping and sucking in the other groups. Their wing arrangement gives them great maneuverability in flight, and claws and pads on their feet enable them to cling to smooth surfaces. Flies undergo complete metamorphosis; the eggs are often laid on the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By Thomas Say
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_(10144905255).jpg)
