|
GoLoco Motif
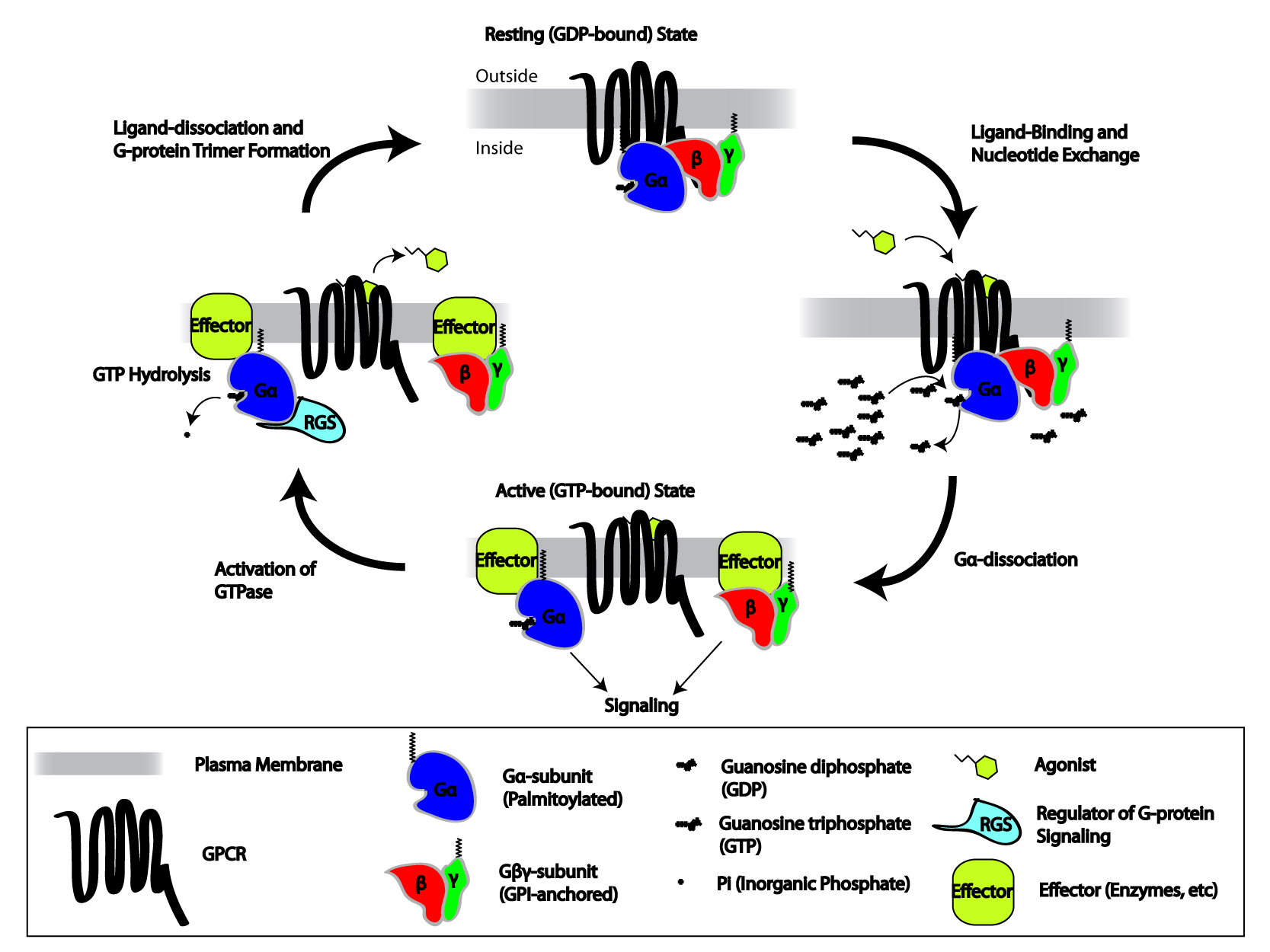
GoLoco motif is a protein structural motif. In heterotrimeric G protein, heterotrimeric G-protein signalling, cell surface receptors (G protein-coupled receptor, GPCRs) are coupled to membrane-associated heterotrimers comprising a GTP-hydrolyzing subunit G-alpha and a G-beta/G-gamma dimer. The inactive form contains the alpha subunit bound to GDP and complexes with the beta and gamma subunit. When the ligand is associated to the receptor, GDP is displaced from G-alpha and GTP is bound. The GTP/G-alpha complex dissociates from the trimer and associates to an effector until the intrinsic GTPase activity of G-alpha returns the protein to GDP bound form. Reassociation of GDP-bound G-alpha with G-beta/G-gamma dimer terminates the signal. Several mechanisms regulate the signal output at different stage of the G-protein cascade. Two classes of intracellular proteins act as inhibitors of G protein activation: GTPase activating proteins (GAPs), which enhance GTP hydrolysis (sePDOC501 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Motif
In a polymer, chain-like biological molecule, such as a protein or nucleic acid, a structural motif is a common Biomolecular structure#Tertiary structure, three-dimensional structure that appears in a variety of different, evolutionarily unrelated molecules. A structural motif does not have to be associated with a sequence motif; it can be represented by different and completely unrelated sequences in different proteins or RNA. In nucleic acids Depending upon the sequence and other conditions, nucleic acids can form a variety of structural motifs which is thought to have biological significance. ;Stem-loop: Stem-loop intramolecular base pairing is a pattern that can occur in single-stranded DNA or, more commonly, in RNA. The structure is also known as a hairpin or hairpin loop. It occurs when two regions of the same strand, usually complementary in nucleotide sequence when read in opposite directions, base-pair to form a double helix that ends in an unpaired loop. The re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterotrimeric G Protein
Heterotrimeric G protein, also sometimes referred to as the ''"large" G proteins'' (as opposed to the subclass of smaller, monomeric small GTPases) are membrane-associated G proteins that form a Heteromer, heterotrimeric complex. The biggest non-structural difference between heterotrimeric and monomeric G protein is that heterotrimeric proteins bind to their cell-surface receptors, called G protein-coupled receptors, directly. These G proteins are made up of ''alpha'' (α), ''beta'' (β) and ''gamma'' (γ) Protein subunit, subunits. The alpha subunit is attached to either a GTP or GDP, which serves as an on-off switch for the activation of G-protein. When ligands bind a GPCR, the GPCR acquires GEF (guanine nucleotide exchange factor) ability, which activates the G-protein by exchanging the GDP on the ''alpha'' subunit to GTP. The binding of GTP to the ''alpha'' subunit results in a structural change and its dissociation from the rest of the G-protein. Generally, the ''alpha'' su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G Protein-coupled Receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily-related proteins that are cell surface receptors that detect molecules outside the cell and activate cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times. Text was copied from this source, which is available under Attribution 2.5 Generic (CC BY 2.5) license. Ligands can bind either to extracellular N-terminus and loops (e.g. glutamate receptors) or to the binding site within transmembrane helices (Rhodopsin-like family). They are all activated by agonists although a spontaneous auto-activation of an empty receptor can also be observed. G protein-coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G-alpha
G alpha subunits are one of the three types of subunit of guanine nucleotide binding proteins, which are membrane-associated, heterotrimeric G proteins. Background G proteins and their receptors ( GPCRs) form one of the most prevalent signalling systems in mammalian cells, regulating systems as diverse as sensory perception, cell growth and hormonal regulation. At the cell surface, the binding of ligands such as hormones and neurotransmitters to a GPCR activates the receptor by causing a conformational change, which in turn activates the bound G protein on the intracellular-side of the membrane. The activated receptor promotes the exchange of bound GDP for GTP on the G protein alpha subunit. GTP binding changes the conformation of switch regions within the alpha subunit, which allows the bound trimeric G protein (inactive) to be released from the receptor, and to dissociate into active alpha subunit (GTP-bound) and beta/gamma dimer. The alpha subunit and the beta/gamma dimer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G-beta/G-gamma
The G beta-gamma complex (Gβγ) is a tightly bound dimeric protein complex, composed of one Gβ and one Gγ subunit, and is a component of heterotrimeric G proteins. Heterotrimeric G proteins, also called guanosine nucleotide-binding proteins, consist of three subunits, called alpha, beta, and gamma subunits, or Gα, Gβ, and Gγ. When a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) is activated, Gα dissociates from Gβγ, allowing both subunits to perform their respective downstream signaling effects. One of the major functions of Gβγ is the inhibition of the Gα subunit. History The individual subunits of the G protein complex were first identified in 1980 when the regulatory component of adenylate cyclase was successfully purified, yielding three polypeptides of different molecular weights. Initially, it was thought that Gα, the largest subunit, was the major effector regulatory subunit, and that Gβγ was largely responsible for inactivating the Gα subunit and enhancing membrane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arginine Finger
In molecular biology, an arginine finger is an amino acid residue of some enzymes. Arginine fingers are often found in the protein superfamily of AAA+ ATPases, GTPases, and dUTPases, where they assist in the catalysis of the gamma phosphate or gamma and beta phosphates from ATP or GTP, which creates a release of energy which can be used to perform cellular work. Thus, they are essential for many forms of life, and are highly conserved. Arginine fingers function through non-covalent interactions. They may also assist in dimerization, and while they are found in a wide variety of enzymes, they are not ubiquitous. Role in catalytic mechanisms Generally, the role of the arginine finger in catalysis is to function in transition state stabilization to allow water to perform a nucleophilic attack to cleave off a number of phosphate groups. However, there are exceptions, and arginine fingers can assist in other roles. Additionally, arginine fingers may be attached to different subuni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPSM1
G-protein-signaling modulator 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GPSM1'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba .... G proteins propagate intracellular signals initiated by G protein-coupled receptors. GPSM1, a receptor-independent activator of G protein signaling, is one of several factors that influence the basal activity of G protein signaling systems (Pizzinat et al., 2001). upplied by OMIMref name="entrez" /> References Further reading * * * * * * * * * {{protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPSM2
G-protein-signaling modulator 2, also called LGN for its 10 Leucine-Glycine-Asparagine repeats, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GPSM2'' gene. Function Heterotrimeric G proteins transduce extracellular signals received by cell surface receptors into integrated cellular responses. GPSM2 belongs to a group of proteins that modulate activation of G proteins (Blumer et al., 2002). upplied by OMIMref name="entrez"/> Interactions GPSM2 has been shown to interact with nuclear mitotic apparatus protein 1 and GNAI2 Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(i), alpha-2 subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GNAI2'' gene. Interactions GNAI2 has been shown to interact with: * EYA2, * GPSM2, * Interleukin 8 receptor, alpha, * MDFI, * RGS5, .... References Further reading * * * * * * * External links * * {{gene-1-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PCP2
PCP site 2 is a binding site that was identified as a high-affinity target for phencyclidine (PCP), an anesthetic and dissociative hallucinogen that acts primarily as an NMDA receptor antagonist. The site is distinct from the PCP binding site on the NMDA receptor (otherwise known as PCP site 1) and the common/main sites on the monoamine transporters (, , ). It is associated with monoamine reuptake inhibition, and it has been suggested that the site may be an allosteric/regulatory site of the monoamine transporters. RTI-4793-14 (HBMP), a ligand with high affinity for the PCP site 2 and high selectivity for this site over the PCP site 1, has been developed. Similarly to PCP, RTI-4793-1 inhibits monoamine reuptake with moderate potency Potency may refer to: * Potency (pharmacology), a measure of the activity of a drug in a biological system * Virility * Cell potency, a measure of the differentiation potential of stem cells * In homeopathic dilutions, potency is a measure of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAP1GAP
Rap1 GTPase-activating protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''RAP1GAP'' gene. Interactions RAP1GAP has been shown to interact with MLLT4 Afadin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''AFDN'' gene. Function Afadin is a Ras (see HRAS; MIM 190020) target that regulates cell–cell adhesions downstream of Ras activation. It is fused with MLL (MIM 159555) in leukemias caused .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-1-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RGS12
Regulator of G-protein signaling 12 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RGS12'' gene. This gene encodes a member of the 'regulator of G protein signaling' (RGS) gene family. The encoded protein may function as a guanosine triphosphatase (GTPase)-activating protein as well as a transcriptional repressor. This protein may play a role in tumorigenesis. Multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been identified for this gene. Other alternative splice variants have been described but their biological nature has not been determined. Interactions RGS12 has been shown to interact with GNAI1, GNAI3 Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(k) subunit alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GNAI3'' gene. Interactions GNAI3 has been shown to interact with: * RGS10 * RGS12, * RGS14, * RGS16, * RGS18, * RGS19, * RGS5, * RIC8A, ..., and the kappa opioid receptor. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{Gene-4-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |