|
Glory Wood And Devil's Den
Glory Wood and Devil's Den is a nature reserve south-east of Dorking in Surrey. It is owned by Mole Valley District Council, and was managed by the Surrey Wildlife Trust until 1 April 2019. There is a bowl barrow dating to the Late Neolithic or Bronze Age in Glory Wood. The highest points of this wooded site have views over the North Downs, North and South Downs. The main trees are Quercus robur, oak and sweet chestnut and mammals include bats, roe deer, Meles meles, badgers and Vulpes vulpes, foxes. There is access from Deepdene Avenue. On 1 April 2019, Surrey Wildlife Trust notices were removed from the reserve's notice board and replaced with a notice stating that Mole Valley District Council was taking over management. References {{Surrey Wildlife Trust Surrey Wildlife Trust Late Neolithic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorking
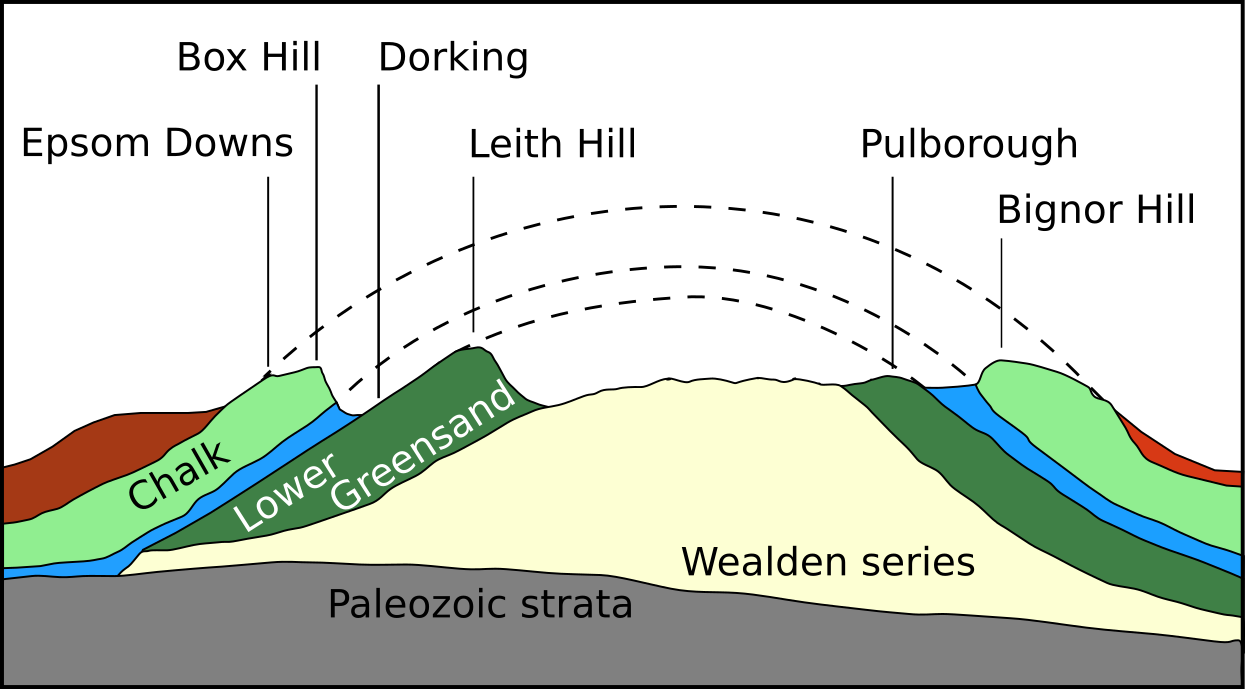
Dorking () is a market town in Surrey in South East England, about south of London. It is in Mole Valley District and the council headquarters are to the east of the centre. The High Street runs roughly east–west, parallel to the Pipp Brook and along the northern face of an outcrop of Lower Greensand. The town is surrounded on three sides by the Surrey Hills Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty and is close to Box Hill and Leith Hill. The earliest archaeological evidence of human activity is from the Mesolithic and Neolithic periods, and there are several Bronze Age bowl barrows in the local area. The town may have been the site of a staging post on Stane Street during Roman times, however the name 'Dorking' suggests an Anglo-Saxon origin for the modern settlement. A market is thought to have been held at least weekly since early medieval times and was highly regarded for the poultry traded there. The Dorking breed of domestic chicken is named after the town. The loca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surrey
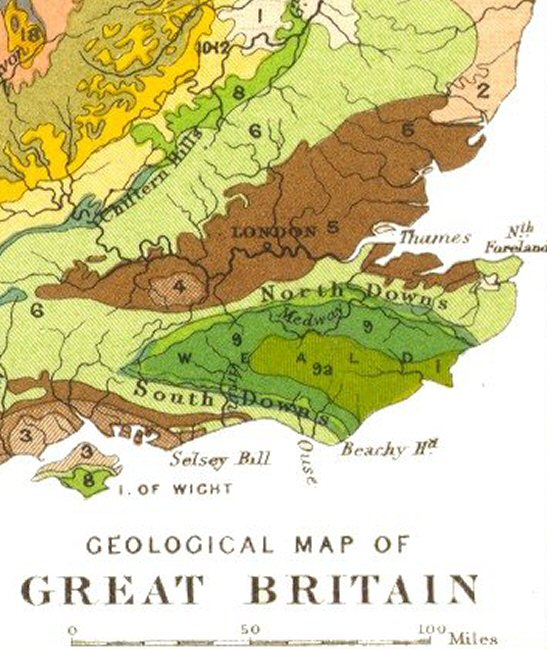
Surrey () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South East England, bordering Greater London to the south west. Surrey has a large rural area, and several significant urban areas which form part of the Greater London Built-up Area. With a population of approximately 1.2 million people, Surrey is the 12th-most populous county in England. The most populated town in Surrey is Woking, followed by Guildford. The county is divided into eleven districts with borough status. Between 1893 and 2020, Surrey County Council was headquartered at County Hall, Kingston-upon-Thames (now part of Greater London) but is now based at Woodhatch Place, Reigate. In the 20th century several alterations were made to Surrey's borders, with territory ceded to Greater London upon its creation and some gained from the abolition of Middlesex. Surrey is bordered by Greater London to the north east, Kent to the east, Berkshire to the north west, West Sussex to the south, East Sussex to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mole Valley District Council
Mole Valley is a local government district in Surrey, England. Its council is based in Dorking. The other town in the district is Leatherhead. The largest villages are Ashtead, Fetcham and Great Bookham, in the northern third of the district. Most of the district is on the escarpments of or adjoins the Surrey Hills AONB (the North Downs and Greensand Ridge including locally Leith Hill, Polesden Lacey, Box Hill and Denbies Wine Estate, the largest vineyard in the country and several golf courses) The North Downs are followed or parallelled by the Pilgrims' Way. There are stations on the London–Worthing and Reading–Gatwick Airport railways, and in the northern third, a commuter stopping-service pattern line, London–Guildford (via Epsom) line. The A24 road and the M25 motorway are the main thoroughfares and relative to London the incidence of car ownership is high. The area hosts hill-focussed sub-laps of the London–Surrey Classic cycling tour each year. Towns * Dor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surrey Wildlife Trust
Surrey Wildlife Trust (SWT) was founded in 1959 as Surrey Naturalists' Trust and it is one of forty-six wildlife trusts covering Great Britain, Northern Ireland, Isle of Man and Alderney. SWT carries out conservation activities on a considerable area of Surrey County Council's largcountryside estateand also manages land on behalf of thMinistry of Defence estate As of 2022 the SWT manages more than of land for wildlife and employs more than 100 staff. It had an income of £5.1 million and expenditure of £5.7 million. As of April 2022 the SWT manages sixty-eight nature reserves. Thirty-one are Sites of Special Scientific Interest, nine are Special Protection Areas, eight are Special Areas of Conservation, one is a national nature reserve, twelve are local nature reserves, four are Nature Conservation Review sites, two are Geological Conservation Reviews, five include scheduled monuments and two are listed on the Register of Historic Parks and Gardens of Special Historic Intere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bowl Barrow
A bowl barrow is a type of burial mound or tumulus. A barrow is a mound of earth used to cover a tomb. The bowl barrow gets its name from its resemblance to an upturned bowl. Related terms include ''cairn circle'', ''cairn ring'', ''howe'', ''kerb cairn'', ''tump'' and ''rotunda grave''. Description Bowl barrows were created from the Neolithic through to the Bronze Age in Great Britain. A bowl barrow is an approximately hemispherical mound covering one or more Inhumations or cremations. Where the mound is composed entirely of stone, rather than earth, the term cairn replaces the word barrow. The mound may be simply a mass of earth or stone, or it may be structured by concentric rings of posts, low stone walls, or upright stone slabs. In addition, the mound may have a kerb of stones or wooden posts. Barrows were usually built in isolation in various situations on plains, valleys and hill slopes, although the most popular sites were those on hilltops. Bowl barrows were first ide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Neolithic
In the archaeology of Southwest Asia, the Late Neolithic, also known as the Ceramic Neolithic or Pottery Neolithic, is the final part of the Neolithic period, following on from the Pre-Pottery Neolithic and preceding the Chalcolithic. It is sometimes further divided into Pottery Neolithic A (PNA) and Pottery Neolithic B (PNB) phases. The Late Neolithic began with the first experiments with pottery, around 7000 BCE, and lasted until the discovery of copper metallurgy and the start of the Chalcolithic around 4500 BCE. Southern Levant The Neolithic of the Southern Levant is divided into Pre-Pottery and Pottery or Late Neolithic phases, initially based on the sequence established by Kathleen Kenyon at Jericho. In the Mediterranean zone, the Pottery Neolithic is further subdivided into two subphases and several regional cultures, although the extent to which these represent real cultural phenomena is debated: * Pottery Neolithic A (PNA) or Late Neolithic 1 (LN1) ** Yar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second principal period of the three-age system proposed in 1836 by Christian Jürgensen Thomsen for classifying and studying ancient societies and history. An ancient civilization is deemed to be part of the Bronze Age because it either produced bronze by smelting its own copper and alloying it with tin, arsenic, or other metals, or traded other items for bronze from production areas elsewhere. Bronze is harder and more durable than the other metals available at the time, allowing Bronze Age civilizations to gain a technological advantage. While terrestrial iron is naturally abundant, the higher temperature required for smelting, , in addition to the greater difficulty of working with the metal, placed it out of reach of common use until the end o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Downs
The North Downs are a ridge of chalk hills in south east England that stretch from Farnham in Surrey to the White Cliffs of Dover in Kent. Much of the North Downs comprises two Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONBs): the Surrey Hills and the Kent Downs. The North Downs Way National Trail runs along the North Downs from Farnham to Dover. The highest point in the North Downs is Botley Hill, Surrey ( above sea level). The ''County Top'' of Kent is Betsom's Hill ( above sea level), which is less than 1 km from Westerham Heights, Bromley, the highest point in Greater London at an elevation of . Etymology 'Downs' is from Old English ''dun'', meaning, amongst other things, "hill". The word acquired the sense of "elevated rolling grassland" around the 14th century. The name contains "North" to distinguish them from a similar range of hills – the South Downs – which runs roughly parallel to them but some to the south. Geography The narrow spine of the Hog's Back between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Downs
The South Downs are a range of chalk hills that extends for about across the south-eastern coastal counties of England from the Itchen valley of Hampshire in the west to Beachy Head, in the Eastbourne Downland Estate, East Sussex, in the east. The Downs are bounded on the northern side by a steep escarpment, from whose crest there are extensive views northwards across the Weald. The South Downs National Park forms a much larger area than the chalk range of the South Downs and includes large parts of the Weald. The South Downs are characterised by rolling chalk downland with close-cropped turf and dry valleys, and are recognised as one of the most important chalk landscapes in England. The range is one of the four main areas of chalk downland in southern England. The South Downs are relatively less populated compared to South East England as a whole, although there has been large-scale urban encroachment onto the chalk downland by major seaside resorts, including most notably ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quercus Robur
''Quercus robur'', commonly known as common oak, pedunculate oak, European oak or English oak, is a species of flowering plant in the beech and oak family, Fagaceae. It is a large tree, native plant, native to most of Europe west of the Caucasus. It is widely cultivated in temperate regions elsewhere and has escaped into the wild in scattered parts of China and North America. Description ''Quercus robur'' is a large deciduous tree, with circumference of grand oaks from to an exceptional . The Majesty Oak with a circumference of is the thickest tree in Great Britain. The Brureika (Bridal Oak) in Norway with a circumference of (2018) and the Kaive Oak in Latvia with a circumference of are among the thickest trees in Northern Europe. The largest historical oak was known as the Imperial Oak from Bosnia and Herzegovina. This specimen was recorded at 17.5 m in circumference at breast height and estimated at over 150 m³ in total volume. It collapsed in 1998. The species has l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sweet Chestnut
''Castanea sativa'', the sweet chestnut, Spanish chestnut or just chestnut, is a species of tree in the family Fagaceae, native to Southern Europe and Asia Minor, and widely cultivated throughout the temperate world. A substantial, long-lived deciduous tree, it produces an edible seed, the chestnut, which has been used in cooking since ancient times. Description ''C. sativa'' attains a height of with a trunk often in diameter. Around 20 trees are recorded with diameters over including one in diameter at breast height. A famous ancient tree known as the Hundred Horse Chestnut in Sicily was historically recorded at in diameter (although it has split into multiple trunks above ground). The bark often has a net-shaped (retiform) pattern with deep furrows or fissures running spirally in both directions up the trunk. The trunk is mostly straight with branching starting at low heights. The oblong-lanceolate, boldly toothed leaves are long and broad. The flowers of both sexe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roe Deer
The roe deer (''Capreolus capreolus''), also known as the roe, western roe deer, or European roe, is a species of deer. The male of the species is sometimes referred to as a roebuck. The roe is a small deer, reddish and grey-brown, and well-adapted to cold environments. The species is widespread in Europe, from the Mediterranean to Scandinavia, from Scotland to the Caucasus, and east to northern Iran and Iraq. Etymology English ''roe'' is from Old English ''rā'' or ''rāha'', from Proto-Germanic ''*raihô'', cognate with Old Norse ''rá'', Old Saxon ''rēho'', Middle Dutch and Dutch ''ree'', Old High German ''rēh'', ''rēho'', ''rēia'', German ''Reh''. It is perhaps ultimately derived from a PIE root ''*rei-'', meaning "streaked, spotted or striped". The word is attested on the 5th-century Caistor-by-Norwich astragalus -a roe deer talus bone, written in Elder Futhark as , transliterated as ''raïhan''. In the English language, this deer was originally simply called a 'roe', b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)