|
Globe Effect
The globe effect, sometimes called the rolling ball effect or the spinning globe effect, is an optical phenomenon—perhaps partially an optical illusion—that occurs with visual optical instruments, in particular binoculars and telescopes, that are designed to be free of distortion. When these instruments are panned, the moving image appears to roll over a curved, convex surface. In 1949, Horst Koehler at Zeiss (Jena) suggested adding some pincushion distortion to the optical design to eliminate the globe effect.H. Koehler, "Grundsaetzliches zum Fernrohrsehen", ''Deutsche Optische Wochenschrift'' 35, Vol. 6, p. 41 (1949). August Sonnefeld conducted experiments with volunteers, which supported the claim that a supplementary distortion could improve the imaging of visual optical instruments. Since that time, most binocular manufacturers have followed Zeiss's example and added pincushion distortion to their optical design. The origin of the globe effect initially remained unclear a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globe Effect
The globe effect, sometimes called the rolling ball effect or the spinning globe effect, is an optical phenomenon—perhaps partially an optical illusion—that occurs with visual optical instruments, in particular binoculars and telescopes, that are designed to be free of distortion. When these instruments are panned, the moving image appears to roll over a curved, convex surface. In 1949, Horst Koehler at Zeiss (Jena) suggested adding some pincushion distortion to the optical design to eliminate the globe effect.H. Koehler, "Grundsaetzliches zum Fernrohrsehen", ''Deutsche Optische Wochenschrift'' 35, Vol. 6, p. 41 (1949). August Sonnefeld conducted experiments with volunteers, which supported the claim that a supplementary distortion could improve the imaging of visual optical instruments. Since that time, most binocular manufacturers have followed Zeiss's example and added pincushion distortion to their optical design. The origin of the globe effect initially remained unclear a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Because light is an electromagnetic wave, other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties. Most optical phenomena can be accounted for by using the classical electromagnetic description of light. Complete electromagnetic descriptions of light are, however, often difficult to apply in practice. Practical optics is usually done using simplified models. The most common of these, geometric optics, treats light as a collection of rays that travel in straight lines and bend when they pass through or reflect from surfaces. Physical optics is a more comprehensive model of light, which includes wave effects such as diffraction and interference that cannot be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Illusion
Within visual perception, an optical illusion (also called a visual illusion) is an illusion caused by the visual system and characterized by a visual perception, percept that arguably appears to differ from reality. Illusions come in a wide variety; their categorization is difficult because the underlying cause is often not clear but a classification proposed by Richard Gregory is useful as an orientation. According to that, there are three main classes: physical, physiological, and cognitive illusions, and in each class there are four kinds: Ambiguities, distortions, paradoxes, and fictions. A classical example for a physical distortion would be the apparent bending of a stick half immerged in water; an example for a physiological paradox is the motion aftereffect (where, despite movement, position remains unchanged). An example for a physiological fiction is an afterimage. Three typical cognitive distortions are the Ponzo illusion, Ponzo, Poggendorff illusion, Poggendorff, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Instrument
An optical instrument (or "optic" for short) is a device that processes light waves (or photons), either to enhance an image for viewing or to analyze and determine their characteristic properties. Common examples include periscopes, microscopes, telescopes, and cameras. Image enhancement The first optical instruments were telescopes used for magnification of distant images, and microscopes used for magnifying very tiny images. Since the days of Galileo and Van Leeuwenhoek, these instruments have been greatly improved and extended into other portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. The binocular device is a generally compact instrument for both eyes designed for mobile use. A camera could be considered a type of optical instrument, with the pinhole camera and camera obscura being very simple examples of such devices. Analysis Another class of optical instrument is used to analyze the properties of light or optical materials. They include: *Interferometer for measuring the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binoculars
Binoculars or field glasses are two refracting telescopes mounted side-by-side and aligned to point in the same direction, allowing the viewer to use both eyes (binocular vision) when viewing distant objects. Most binoculars are sized to be held using both hands, although sizes vary widely from opera glasses to large pedestal-mounted military models. Unlike a (monocular) telescope, binoculars give users a three-dimensional image: each eyepiece presents a slightly different image to each of the viewer's eyes and the parallax allows the visual cortex to generate an impression of depth. Optical designs Galilean Almost from the invention of the telescope in the 17th century the advantages of mounting two of them side by side for binocular vision seems to have been explored. Most early binoculars used Galilean optics; that is, they used a convex objective and a concave eyepiece lens. The Galilean design has the advantage of presenting an erect image but has a narrow field of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Telescope
An optical telescope is a telescope that gathers and focuses light mainly from the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum, to create a magnified image for direct visual inspection, to make a photograph, or to collect data through electronic image sensors. There are three primary types of optical telescope: * Refracting telescopes, which use lenses and less commonly also prisms (dioptrics) * Reflecting telescopes, which use mirrors (catoptrics) * Catadioptric telescopes, which combine lenses and mirrors An optical telescope's ability to resolve small details is directly related to the diameter (or aperture) of its objective (the primary lens or mirror that collects and focuses the light), and its light-gathering power is related to the area of the objective. The larger the objective, the more light the telescope collects and the finer detail it resolves. People use optical telescopes (including monoculars and binoculars) for outdoor activities such as observational as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distortion (optics)
In geometric optics, distortion is a deviation from rectilinear projection; a projection in which straight lines in a scene remain straight in an image. It is a form of aberration in optical systems, optical aberration. Radial distortion Although distortion can be irregular or follow many patterns, the most commonly encountered distortions are radially symmetric, or approximately so, arising from the symmetry of a photographic lens. These ''radial distortions'' can usually be classified as either ''barrel'' distortions or ''pincushion'' distortions. Mathematically, barrel and pincushion distortion are quadratic function, quadratic, meaning they increase as the ''square'' of distance from the center. In mustache distortion the quartic function, quartic (degree 4) term is significant: in the center, the degree 2 barrel distortion is dominant, while at the edge the degree 4 distortion in the pincushion direction dominates. Other distortions are in principle possible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Zeiss AG
Carl Zeiss AG (), branded as ZEISS, is a German manufacturer of optical systems and optoelectronics, founded in Jena, Germany in 1846 by optician Carl Zeiss. Together with Ernst Abbe (joined 1866) and Otto Schott (joined 1884) he laid the foundation for today's multi-national company. The current company emerged from a reunification of Carl Zeiss companies in East and West Germany with a consolidation phase in the 1990s. ZEISS is active in four business segments with approximately equal revenue (Industrial Quality and Research, Medical Technology, Consumer Markets and Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology) in almost 50 countries, has 30 production sites and around 25 development sites worldwide. Carl Zeiss AG is the holding of all subsidiaries within Zeiss Group, of which Carl Zeiss Meditec AG is the only one that is traded at the stock market. Carl Zeiss AG is owned by the foundation Carl-Zeiss-Stiftung. The Zeiss Group has its headquarters in southern Germany, in the smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pincushion Distortion
In geometric optics, distortion is a deviation from rectilinear projection; a projection in which straight lines in a scene remain straight in an image. It is a form of optical aberration. Radial distortion Although distortion can be irregular or follow many patterns, the most commonly encountered distortions are radially symmetric, or approximately so, arising from the symmetry of a photographic lens. These ''radial distortions'' can usually be classified as either ''barrel'' distortions or ''pincushion'' distortions. Mathematically, barrel and pincushion distortion are quadratic, meaning they increase as the ''square'' of distance from the center. In mustache distortion the quartic (degree 4) term is significant: in the center, the degree 2 barrel distortion is dominant, while at the edge the degree 4 distortion in the pincushion direction dominates. Other distortions are in principle possible – pincushion in center and barrel at the edge, or higher order d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Design
Optical lens design is the process of designing a lens to meet a set of performance requirements and constraints, including cost and manufacturing limitations. Parameters include surface profile types (spherical, aspheric, holographic, diffractive, etc.), as well as radius of curvature, distance to the next surface, material type and optionally tilt and decenter. The process is computationally intensive, using ray tracing or other techniques to model how the lens affects light that passes through it. Design requirements Performance requirements can include: #Optical performance (image quality): This is quantified by various metrics, including encircled energy, modulation transfer function, Strehl ratio, ghost reflection control, and pupil performance (size, location and aberration control); the choice of the image quality metric is application specific. #Physical requirements such as weight, static volume, dynamic volume, center of gravity and overall configuration requirements. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
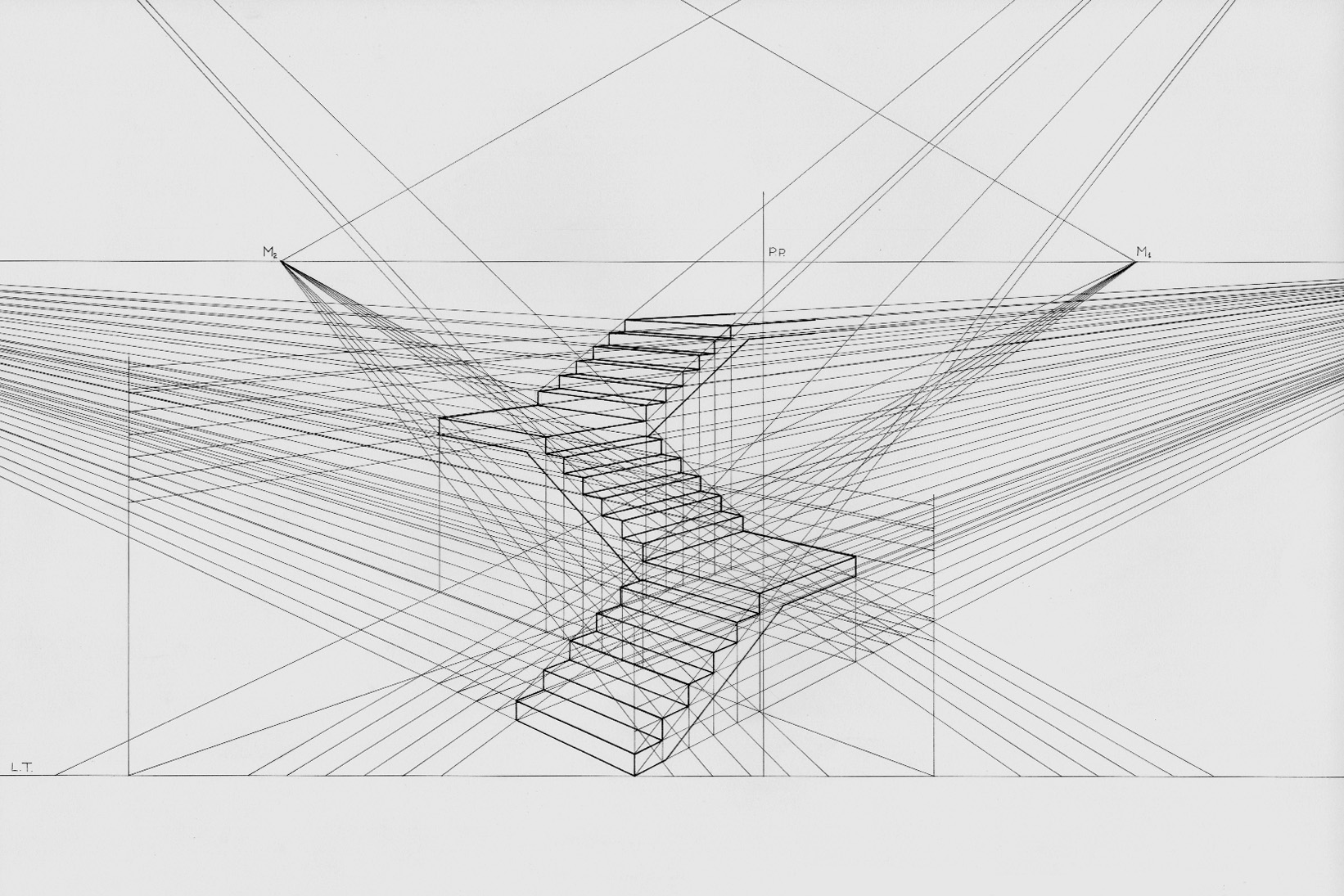
Perspective (visual)
Linear or point-projection perspective (from la, perspicere 'to see through') is one of two types of graphical projection perspective in the graphic arts; the other is parallel projection. Linear perspective is an approximate representation, generally on a flat surface, of an image as it is seen by the eye. Perspective drawing is useful for representing a three-dimensional scene in a two-dimensional medium, like paper. The most characteristic features of linear perspective are that objects appear smaller as their distance from the observer increases, and that they are subject to ''foreshortening'', meaning that an object's dimensions along the line of sight appear shorter than its dimensions across the line of sight. All objects will recede to points in the distance, usually along the horizon line, but also above and below the horizon line depending on the view used. Italian Renaissance painters and architects including Masaccio, Paolo Uccello, Piero della Francesca and Luca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Perception
Visual perception is the ability to interpret the surrounding environment through photopic vision (daytime vision), color vision, scotopic vision (night vision), and mesopic vision (twilight vision), using light in the visible spectrum reflected by objects in the environment. This is different from visual acuity, which refers to how clearly a person sees (for example "20/20 vision"). A person can have problems with visual perceptual processing even if they have 20/20 vision. The resulting perception is also known as vision, sight, or eyesight (adjectives ''visual'', ''optical'', and ''ocular'', respectively). The various physiological components involved in vision are referred to collectively as the visual system, and are the focus of much research in linguistics, psychology, cognitive science, neuroscience, and molecular biology, collectively referred to as vision science. Visual system In humans and a number of other mammals, light enters the eye through the cornea and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)