|
Gliese 436
Gliese 436 is a red dwarf approximately away in the zodiac constellation of Leo. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 10.67, which is much too faint to be seen with the naked eye. However, it can be viewed with even a modest telescope of aperture. In 2004, the existence of an extrasolar planet, Gliese 436b, was verified as orbiting the star. This planet was later discovered to transit its host star. Properties Gliese 436 is a M2.5V star, which means it is a red dwarf. Stellar models give both an estimated mass and size of about 43% that of the Sun. The same model predicts that the outer atmosphere has an effective temperature of 3,480 K, giving it the orange-red hue of an M-type star. Small stars such as this generate energy at a low rate, giving it only 2.5% of the Sun's luminosity. Gliese 436 is older than the Sun by several billion years and it has an abundance of heavy elements (with masses greater than helium-4) less than half% that of the Sun. The project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leo (constellation)
Leo is one of the constellations of the zodiac, between Cancer (constellation), Cancer the crab to the west and Virgo (constellation), Virgo the maiden to the east. It is located in the Northern celestial hemisphere. Its name is Latin for lion, and to the ancient Greeks represented the Nemean Lion killed by the mythical Greek hero Heracles meaning 'Glory of Hera' (known to the ancient Romans as Hercules) as one of his Twelve Labours, twelve labors. Its old astronomical symbol is (♌︎). One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, Leo remains one of the 88 modern constellations today, and one of the most easily recognizable due to its many bright stars and a distinctive shape that is reminiscent of the crouching lion it depicts. The lion's mane and shoulders also form an asterism (astronomy), asterism known as "The Sickle," which to modern observers may resemble a backwards "question mark." Features Stars Leo contains many bright stars, many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Effective Temperature
The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total amount of electromagnetic radiation. Effective temperature is often used as an estimate of a body's surface temperature when the body's emissivity curve (as a function of wavelength) is not known. When the star's or planet's net emissivity in the relevant wavelength band is less than unity (less than that of a black body), the actual temperature of the body will be higher than the effective temperature. The net emissivity may be low due to surface or atmospheric properties, including greenhouse effect. Star The effective temperature of a star is the temperature of a black body with the same luminosity per ''surface area'' () as the star and is defined according to the Stefan–Boltzmann law . Notice that the total (bolometric) luminosity of a star is then , where is the stellar radius. The definition of the stellar radius is obviously not straightf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sine
In mathematics, sine and cosine are trigonometric functions of an angle. The sine and cosine of an acute angle are defined in the context of a right triangle: for the specified angle, its sine is the ratio of the length of the side that is opposite that angle to the length of the longest side of the triangle (the hypotenuse), and the cosine is the ratio of the length of the adjacent leg to that of the hypotenuse. For an angle \theta, the sine and cosine functions are denoted simply as \sin \theta and \cos \theta. More generally, the definitions of sine and cosine can be extended to any real value in terms of the lengths of certain line segments in a unit circle. More modern definitions express the sine and cosine as infinite series, or as the solutions of certain differential equations, allowing their extension to arbitrary positive and negative values and even to complex numbers. The sine and cosine functions are commonly used to model periodic phenomena such as sound and lig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 times the mass of Earth, and slightly more massive than its near-twin Uranus. Neptune is denser and physically smaller than Uranus because its greater mass causes more gravitational compression of its atmosphere. It is referred to as one of the solar system's two ice giant planets (the other one being Uranus). Being composed primarily of gases and liquids, it has no well-defined "solid surface". The planet orbits the Sun once every 164.8 julian year (astronomy), years at an average distance of . It is named after the Neptune (mythology), Roman god of the sea and has the astronomical symbol , representing Neptune's trident. Neptune is not visible to the unaided eye and is the only planet in the Solar System found by mathematical prediction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. Its name is a reference to the Greek god of the sky, Uranus (mythology), Uranus (Caelus), who, according to Greek mythology, was the great-grandfather of Ares (Mars (mythology), Mars), grandfather of Zeus (Jupiter (mythology), Jupiter) and father of Cronus (Saturn (mythology), Saturn). It has the third-largest planetary radius and fourth-largest planetary mass in the Solar System. Uranus is similar in composition to Neptune, and both have bulk chemical compositions which differ from that of the larger gas giants Jupiter and Saturn. For this reason, scientists often classify Uranus and Neptune as "ice giants" to distinguish them from the other giant planets. As with gas giants, ice giants also lack a well defined "solid surface." Uranus's Atmosphere#Others, atmosphere is similar to Jupiter's and Saturn's in its primary composition of hydrogen and helium, but it contains more "volatiles, ices" such as water, ammonia, and methane, al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Giant
A gas giant is a giant planet composed mainly of hydrogen and helium. Gas giants are also called failed stars because they contain the same basic elements as a star. Jupiter and Saturn are the gas giants of the Solar System. The term "gas giant" was originally synonymous with "giant planet". However, in the 1990s, it became known that Uranus and Neptune are really a distinct class of giant planets, being composed mainly of heavier volatile substances (which are referred to as "ices"). For this reason, Uranus and Neptune are now often classified in the separate category of ice giants. Jupiter and Saturn consist mostly of hydrogen and helium, with heavier elements making up between 3 and 13 percent of their mass.The Interior of Jupiter, Guillot et al., in ''Jupiter: The Planet, Satellites and Magnetosphere'', Bagenal et al., editors, Cambridge University Press, 2004 They are thought to consist of an outer layer of compressed molecular hydrogen surrounding a layer of liquid metallic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Mass
An Earth mass (denoted as M_\mathrm or M_\oplus, where ⊕ is the standard astronomical symbol for Earth), is a unit of mass equal to the mass of the planet Earth. The current best estimate for the mass of Earth is , with a relative uncertainty of 10−4.The cited value is the recommended value published by the International Astronomical Union in 2009 (se2016 "Selected Astronomical Constants"in ). It is equivalent to an average density of . Using the nearest metric prefix, the Earth mass is approximately six ronnagrams, or 6.0 Rg. The Earth mass is a standard unit of mass in astronomy that is used to indicate the masses of other planets, including rocky terrestrial planets and exoplanets. One Solar mass is close to Earth masses. The Earth mass excludes the mass of the Moon. The mass of the Moon is about 1.2% of that of the Earth, so that the mass of the Earth+Moon system is close to . Most of the mass is accounted for by iron and oxygen (c. 32% each), magnesium and sil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methods Of Detecting Extrasolar Planets
Any planet is an extremely faint light source compared to its parent star. For example, a star like the Sun is about a billion times as bright as the reflected light from any of the planets orbiting it. In addition to the intrinsic difficulty of detecting such a faint light source, the light from the parent star causes a glare that washes it out. For those reasons, very few of the exoplanets reported have been observed directly, with even fewer being resolved from their host star. Instead, astronomers have generally had to resort to indirect methods to detect extrasolar planets. As of 2016, several different indirect methods have yielded success. Established detection methods The following methods have at least once proved successful for discovering a new planet or detecting an already discovered planet: Radial velocity A star with a planet will move in its own small orbit in response to the planet's gravity. This leads to variations in the speed with which the star move ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gliese 436 B
Gliese 436 b (sometimes called GJ 436 b) is a Neptune-sized exoplanet orbiting the red dwarf Gliese 436. It was the first hot Neptune discovered with certainty (in 2007) and was among the smallest-known transiting planets in mass and radius, until the much smaller Kepler exoplanet discoveries began circa 2010. In December 2013, NASA reported that clouds may have been detected in the atmosphere of GJ 436 b. In August 2022, this planet and its host star were included among 20 systems to be named by the third NameExoWorlds project. Discovery Gliese 436 b was discovered in August 2004 by R. Paul Butler and Geoffrey Marcy of the Carnegie Institute of Washington and University of California, Berkeley, respectively, using the radial velocity method. Together with 55 Cancri e, it was the first of a new class of planets with a minimum mass (M sin''i'') different to Neptune. The planet was recorded to transit its star by an automatic process at NMSU on January 11 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactic Coordinate System
The galactic coordinate system is a celestial coordinate system in spherical coordinates, with the Sun as its center, the primary direction aligned with the approximate center of the Milky Way Galaxy, and the fundamental plane parallel to an approximation of the galactic plane but offset to its north. It uses the right-handed convention, meaning that coordinates are positive toward the north and toward the east in the fundamental plane. Spherical coordinates Galactic longitude Longitude (symbol ) measures the angular distance of an object eastward along the galactic equator from the Galactic Center. Analogous to terrestrial longitude, galactic longitude is usually measured in degrees (°). Galactic latitude Latitude (symbol ) measures the angle of an object northward of the galactic equator (or midplane) as viewed from Earth. Analogous to terrestrial latitude, galactic latitude is usually measured in degrees (°). Definition The first galactic coordinate system was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old-disk Star
The thick disk is one of the structural components of about 2/3 of all disk galaxies, including the Milky Way. It was discovered first in external edge-on galaxies. Soon after, it was proposed as a unique galactic structure in the Milky Way, different from the thin disk and the halo in the 1983 article by Gilmore & Reid. It is supposed to dominate the stellar number density between above the galactic plane and, in the solar neighborhood, is composed almost exclusively of older stars. Its stellar chemistry and stellar kinematics (composition and motion of it stars) are also said to set it apart from the thin disk. Compared to the thin disk, thick disk stars typically have significantly lower levels of metals—that is, the abundance of elements other than hydrogen and helium. The thick disk is a source of early kinematic and chemical evidence for a galaxy's composition and thus is regarded as a very significant component for understanding galaxy formation. With the availabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
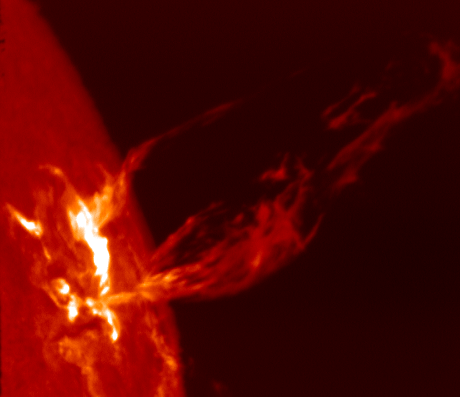
Stellar Magnetic Field
A stellar magnetic field is a magnetic field generated by the motion of conductive plasma inside a star. This motion is created through convection, which is a form of energy transport involving the physical movement of material. A localized magnetic field exerts a force on the plasma, effectively increasing the pressure without a comparable gain in density. As a result, the magnetized region rises relative to the remainder of the plasma, until it reaches the star's photosphere. This creates starspots on the surface, and the related phenomenon of coronal loops. Measurement The magnetic field of a star can be measured by means of the Zeeman effect. Normally the atoms in a star's atmosphere will absorb certain frequencies of energy in the electromagnetic spectrum, producing characteristic dark absorption lines in the spectrum. When the atoms are within a magnetic field, however, these lines become split into multiple, closely spaced lines. The energy also becomes polarized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)