|
Glande
Glande (baptized as ''Richard'') was the leader of Sambians, one of the Prussian clans, during the Great Prussian Uprising (1260–1274) against the papal crusades undertaken by the Teutonic Knights. There is nothing known about his life or achievements, except that once the uprising started, Sambians elected him as their leader. The Prussian duke Glande was felled by a spear and his aid Swayno fell soon after. In the confusion and hopelessness, the Samlandians retreated to their villages. Hercus Monte Herkus Monte (also Hercus; Old Prussian: ''Erks Mānts''; lt, Herkus Mantas; la, Henricus Montemin) was the most famous leader of the Great Prussian Uprising against the Teutonic Knights and Northern Crusaders. The uprising began in September ... came to their aid, but was also heavily wounded by a spear. Samlandians were the first tribe to give up the fight and surrendered in 1265.Urban, William. ''The Prussian Crusade'', p. 306. References Old Prussian people People fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Prussian Uprising
The Prussian uprisings were two major and three smaller uprisings by the Old Prussians, one of the Balts, Baltic tribes, against the Teutonic Knights that took place in the 13th century during the Prussian Crusade. The crusading Military order (society), military order, supported by the Popes and Christian Europe, sought to conquer and convert the paganism, pagan Prussians. In the first ten years of the crusade, five of the seven major Prussian clans fell under the control of the less numerous Teutonic Knights. However, the Prussians rose against their conquerors on five occasions. The first uprising was supported by Duke Swietopelk II, Duke of Pomerania. The Prussians were successful at first, reducing the Knights to only five of their strongest castles. The duke then suffered a series of military defeats and was eventually forced to make peace with the Teutonic Knights. With Duke Swietopelk's support for the Prussians broken, a prelate of Pope Innocent IV negotiated a peace tre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
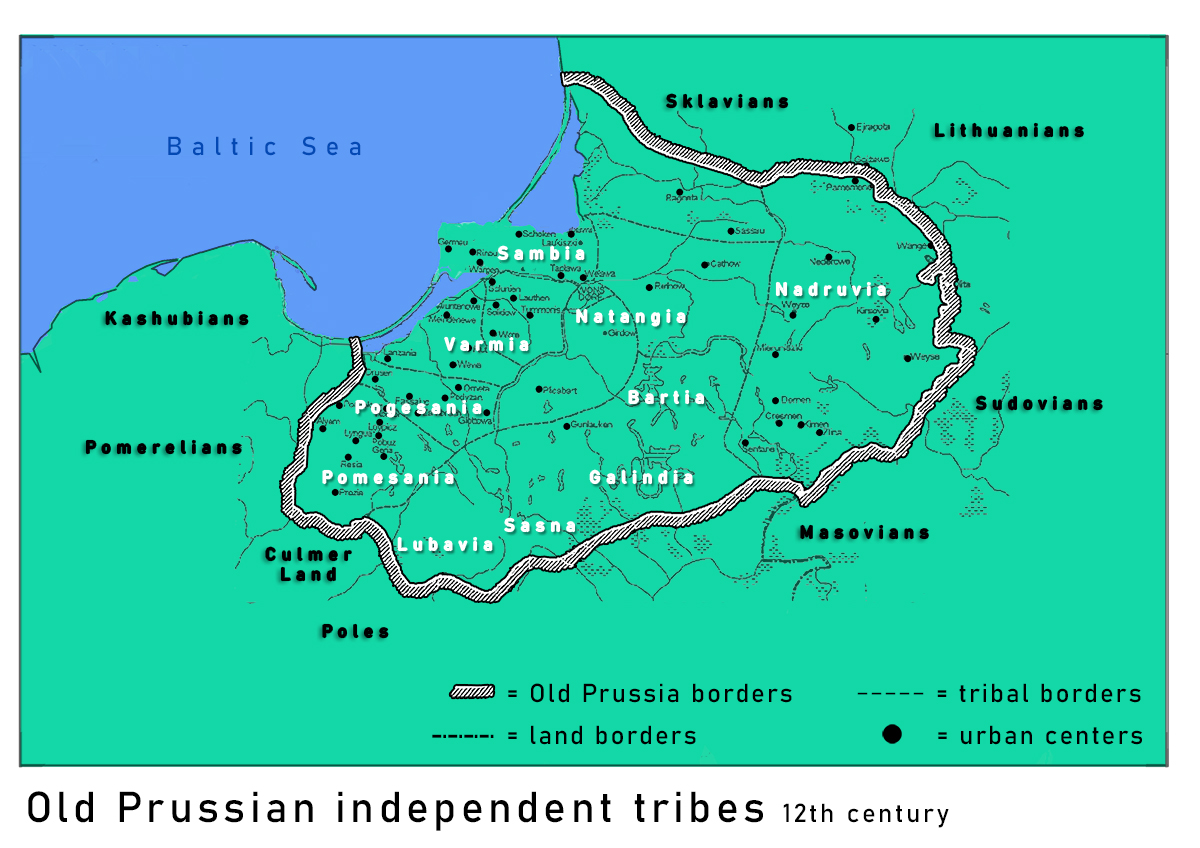
Sambians
The Sambians were a Old Prussians, Prussian tribe. They inhabited the Sambia Peninsula north of the city of Königsberg (now Kaliningrad). Sambians were located in a coastal territory rich in amber and engaged in trade early on (see Amber Road). Therefore, they established contacts with foreign nations before any other Prussians. However, as all other Prussians, they were conquered by the Teutonic Knights, and, exposed to cultural assimilation, assimilation and Germanisation of Prussia, Germanization, became extinct sometime in the 17th century. The Sambians bordered the Natangians in the south, and the Nadruvians in the east. History Engaged in the amber trade, Sambia was the richest and most densely populated region of Prussia (region), Prussia. It provides a wealth of artifacts from the Bronze Age, including imported goods from the Roman Empire. Sambians, unlike other Prussians, did not cremate their dead. They built earth barrows above graves and surrounded them with stone ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Prussians
Old Prussians, Baltic Prussians or simply Prussians (Old Prussian: ''prūsai''; german: Pruzzen or ''Prußen''; la, Pruteni; lv, prūši; lt, prūsai; pl, Prusowie; csb, Prësowié) were an indigenous tribe among the Baltic peoples that inhabited the region of Prussia, at the south-eastern shore of the Baltic Sea between the Vistula Lagoon to the west and the Curonian Lagoon to the east. The Old Prussians, who spoke an Indo-European language now known as Old Prussian and worshipped pre-Christian deities, lent their name, despite very few commonalities, to the later, predominantly Low German-speaking inhabitants of the region. The duchy of the Polans under Mieszko I, which was the predecessor of the Kingdom of Poland, first attempted to conquer and baptize the Baltic tribes during the 10th century, but repeatedly encountered strong resistance. Not until the 13th century were the Old Prussians subjugated and their lands conquered by the Teutonic Order. The remaining Old Prus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teutonic Knights
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem, commonly known as the Teutonic Order, is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. It was formed to aid Christians on their pilgrimages to the Holy Land and to establish hospitals. Its members have commonly been known as the Teutonic Knights, having a small voluntary and mercenary military membership, serving as a crusading military order for the protection of Christians in the Holy Land and the Baltics during the Middle Ages. Purely religious since 1810, the Teutonic Order still confers limited honorary knighthoods. The Bailiwick of Utrecht of the Teutonic Order, a Protestant chivalric order, is descended from the same medieval military order and also continues to award knighthoods and perform charitable work. Name The name of the Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem is in german: Orden der Brüder vom Deutschen Haus der He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hercus Monte
Herkus Monte (also Hercus; Old Prussian: ''Erks Mānts''; lt, Herkus Mantas; la, Henricus Montemin) was the most famous leader of the Great Prussian Uprising against the Teutonic Knights and Northern Crusaders. The uprising began in September 1260, following the Knights' defeat at the Battle of Durbe, and lasted for the next fourteen years. History The ''Chronicon terrae Prussiae'' stated that Herkus was originally from Natangia, one of the lands of the Old Prussians. The Prussians were the first of the Baltic tribes to be conquered by the Teutonic Knights, who first arrived in Chełmno in 1226 at the request of Konrad I of Masovia, whose own struggle with the Prussians had proved unsuccessful. As part of the Northern Crusades, the Knights proceeded to attack the Prussians with the purported aim of converting them to Christianity. As a young boy, Herkus was taken hostage by the Teutonic Knights and brought to Magdeburg, Germany. Having lived there for about ten years, and hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Prussian People
Old Prussians, Baltic Prussians or simply Prussians (Old Prussian: ''prūsai''; german: Pruzzen or ''Prußen''; la, Pruteni; lv, prūši; lt, prūsai; pl, Prusowie; csb, Prësowié) were an indigenous tribe among the Baltic peoples that inhabited the region of Prussia, at the south-eastern shore of the Baltic Sea between the Vistula Lagoon to the west and the Curonian Lagoon to the east. The Old Prussians, who spoke an Indo-European language now known as Old Prussian and worshipped pre-Christian deities, lent their name, despite very few commonalities, to the later, predominantly Low German-speaking inhabitants of the region. The duchy of the Polans under Mieszko I, which was the predecessor of the Kingdom of Poland, first attempted to conquer and baptize the Baltic tribes during the 10th century, but repeatedly encountered strong resistance. Not until the 13th century were the Old Prussians subjugated and their lands conquered by the Teutonic Order. The remaining Old Prus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Prussia Proper
A person (plural, : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal obligation, legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pagans Of The Prussian Crusade
Pagans may refer to: * Paganism, a group of pre-Christian religions practiced in the Roman Empire * Modern Paganism, a group of contemporary religious practices * Order of the Vine, a druidic faction in the ''Thief'' video game series * Pagan's Motorcycle Club, a motorcycle club * The Pagans The Pagans were an American punk rock band from Cleveland, Ohio, United States, that was originally active from 1977 to 1979. They reformed several times, from 1982-1983, from 1986-1989 and again in 2014-2017. Along with fellow Cleveland band ..., a 1970s American punk band * ''The Pagans'' (film), a 1953 Italian film See also * Pagan (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_statute_book_of_1340%2C_a_copy_from_the_16th_century.jpg)
_1938.jpg)