|
Gjin Muzaka
Gjin is an Albanian male given name, clan, surname and onomastic element. As a name, it is usually held by Albanian Christians, as it is derived from the name of a saint, although the identity of this saint is unclear, as both theologists and linguists disagree on the relation of Saint Gjin to Saint Gjon (the latter of which is considered to be Saint John).Riska, Albert (2013)"The Christian Saints in the (Micro)toponymy of Albania" ''Anglisticum Journal (IJLLIS)'' vol 2 issue 3. Pages 167-176. Page 174 Origin The origin of the name "Gjin" is unclear, except for the fact that he is considered a Christian saint by Albanians. The Catholic clergy consider Shën Gjin (Saint Gjin) to be the same saint as Shën Gjon (Saint John) but the Christians of the Central Albanian Shpati region (who are Orthodox)) revere the two as separate saintsRiska, Albert (2013)"The Christian Saints in the (Micro)toponymy of Albania" ''Anglisticum Journal (IJLLIS)'' vol 2 issue 3. Pages 167-176. with two diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albanian Language
Albanian ( endonym: or ) is an Indo-European language and an independent branch of that family of languages. It is spoken by the Albanians in the Balkans and by the Albanian diaspora, which is generally concentrated in the Americas, Europe and Oceania. With about 7.5 million speakers, it comprises an independent branch within the Indo-European languages and is not closely related to any other modern Indo-European language. Albanian was first attested in the 15th century and it is a descendant of one of the Paleo-Balkan languages of antiquity. For historical and geographical reasons,: "It is often thought (for obvious geographic reasons) that Albanian descends from ancient Illyrian (see above), but this cannot be ascertained as we know next to nothing about Illyrian itself." the prevailing opinion among modern historians and linguists is that the Albanian language is a descendant of a southern Illyrian dialect spoken in much the same region in classical times. Alternativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Anne
According to Christian apocryphal and Islamic tradition, Saint Anne was the mother of Mary and the maternal grandmother of Jesus. Mary's mother is not named in the canonical gospels. In writing, Anne's name and that of her husband Joachim come only from New Testament apocrypha, of which the Gospel of James (written perhaps around 150) seems to be the earliest that mentions them. The mother of Mary is mentioned but not named in the Quran. Christian tradition The story is similar to that of Samuel, whose mother Hannah ( he, ''Ḥannāh'' "favour, grace"; etymologically the same name as Anne) had also been childless. The Immaculate Conception was eventually made dogma by the Catholic Church following an increased devotion to Anne in the 12th century. Dedications to Anne in Eastern Christianity occur as early as the 6th century. In the Eastern Orthodox tradition, Anne and Joachim are ascribed the title ''Ancestors of God'', and both the Nativity of Mary and the Presentation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gjonaj
Gjonaj is an Albanian surname. Notable people with the surname include: *Adriana Gjonaj, Albanian politician *Algert Gjonaj (born 1987), Albanian basketball player *Etilda Gjonaj (born 1981), Albanian politician *Kujtim Gjonaj (born 1946), Albanian screenwriter *Mark Gjonaj, American politician *Salvador Gjonaj (born 1992), Albanian footballer It is also a geological name: *Gjonaj, Prizren, village in Kosovo See also *Gjoni Gjon (definite form: ''Gjoni'') is an Albanian male given name, clan, surname and onomastic element. As given name Etymology and history ''Gjon'' as a given name is a form of the English name John. It is the name of the apostle Saint John in ... {{surname Albanian-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gjini Family
Gjini family (Croat: Ginni) (Italian: Gini, Ghini) was an Albanian medieval family who lived in Venetian Albania in the 16th and 17th century who played a major role in social and military history in the eastern Adriatic coast. The noble Mark Gjini belonged to the family. Name According to Krahe and Lambertz the noun ''Gjin'' may be an ancient Albanian name, a form of the anthroponym ''Gentius''.Riska, Albert (2013)"The Christian Saints in the (Micro)toponymy of Albania" ''Anglisticum Journal (IJLLIS)'' vol 2 issue 3. Pages 167-176. Page 174 The name ''Gjin'' is generally associated by Albanian Christians to the figure of a saint. Origin The Gjini family is mentioned for the first time in 1216 in a letter sent from Pope Innocent III to Demetrius Gjini, the Prince of Albania. Background The Ginni family, amongst families like the Bruti, Bruni, Krutaj, Skuraj, fled to Venetian Albania due to Ottoman pressure in the 16th century, although migrations had already begun in 1479, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gjin Zenebishi
John Zenevisi or Gjon Zenebishi ( sq, Gjon Zenebishi or ''Gjin Zenebishi''; died 1418) was an Albanian magnate that held the estates in Epirus, such as Argyrokastro (Gjirokastër) and Vagenetia. Name Zenevisi can be found with different spellings in historical documents. His name in modern English is usually ''John Zenevisi'' Elsie 2003, p. 53: "Lord John Sarbissa (Zenevisi) was lord of the town of Gjirokastra and the region of Vagenetia and Paracalo (Parakalamo)." or ''John Sarbissa''. In Italian, his name was spelled as ''Giovanni Sarbissa''. In Albanian, his name is mostly spelled as ''Gjin Zenebishi'' (less commonly as ''Zenebishti''), his given name scarcely spelled ''Gjon'', as well. In Serbian his name is spelled like ''Jovan Zenović''. Life The Zenevisi family was from the Zagoria region, between Përmet and Argyrokastro (Gjirokastër). In 1381 and 1384, the Catholic lords of Arta asked the Ottoman troops for protection against the invading Albanian clan of the Zenev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gjin Progoni
Gjin Progoni ( la, Ginius) was an ''archon'' (or lord) of Kruja, located in present-day Albania, from c. 1198 until his death in 1208.: "Even if it is hard to identify the outlook of Prince Gjin, the son of Progon, who died in 1208, it is clear that his successor, Dhimitër, saw Venice as the main enemy..." He succeeded his father, Progon of Kruja, becoming the second ruler of the House of Progon. Gjin was succeeded by his younger brother Dhimitër Progoni. See also *History of Albania *Monarchs of Albania References Citations Sources * {{DEFAULTSORT:Progoni, Gjin 12th-century births 1208 deaths Progon family, Gjin Albanian monarchs, Gjin Albanian princes, Gjin Medieval Albanian nobility 12th-century Albanian people 13th-century Albanian people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
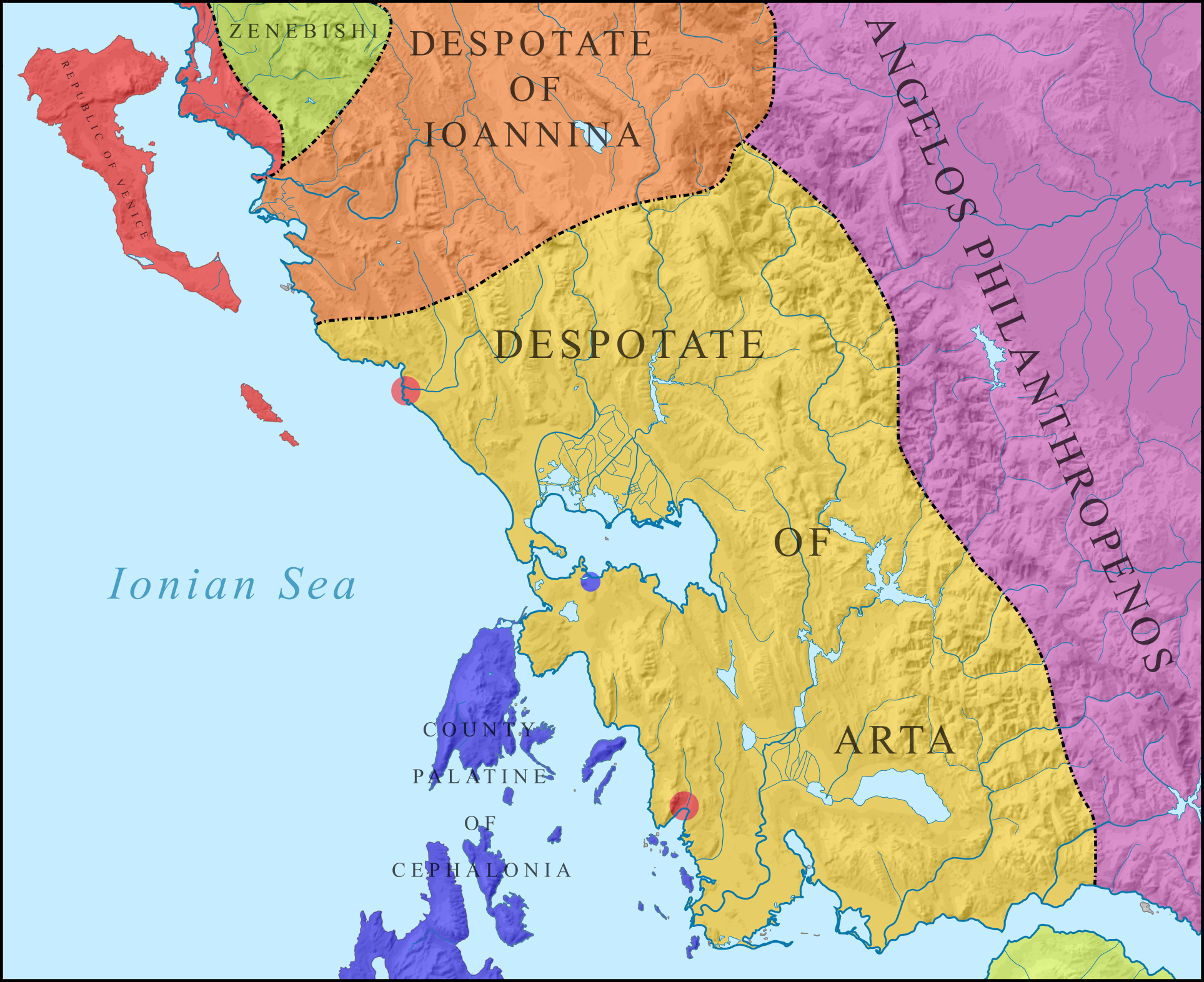
Gjin Bua Shpata
Gjin Bua Shpata (sometimes anglicized as ''John Spata'') ( 1358 – 29 October 1399) was an Albanian ruler in Western Greece with the title of Despot. Together with Peter Losha, he led raids into Epirus, Acarnania and Aetolia in 1358. He was recognized as Despot by the titular Eastern Roman Emperor in the early 1360s and ruled Aetolia (1360s–?), Angelokastron (?–1399), Naupactus (1378–1399), and Arta (1370s–1399). Name The word ''spata'', in Albanian ''shpatë'', pl. ''shpata'', 'sword'. According to Orel (1998), the word was borrowed from Latin ''spāta''. Hammond thus believes that he was called "John the Sword". Spatha being a type of Roman sword. Life Karl Hopf's genealogy of the Shpata family is "altogether inaccurate"; according to it, his father was Pietro, the lord of Angelokastron and Delvina (1354) during the reign of Serbian emperor Stefan Dušan (r. 1331–55). It is known that Shpata had a brother, Sgouros Spata. In 1358, some Albanian commanders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gjin Aleksi's Mosque
Gjin Aleksi Mosque ( sq, Xhamia e Gjin Aleksit, tr, Kinaleksi Mescidi) is a 15th-century mosque in the village of Rusan, near Delvinë, Albania. It is a Cultural Monument of Albania. The mosque is distinguished for the high quality of acoustics that is obtained through casks that are strategically placed in holes in the walls. See also * Islam in Albania Islam in Albania mainly arrived during the Ottoman period when the majority of Albanians over time converted to Islam. Following the Albanian National Awakening (Rilindja) tenets and the deemphasizing of religion during the 20th century, t ... References Cultural Monuments of Albania Buildings and structures in Delvinë Mosques in Vlorë County {{Albania-mosque-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gjinovec
Gjinovec ( bg, Гиновец, mk, Ѓиновец) is a village in the former Trebisht in Dibër County in northeastern Albania. At the 2015 local government reform it became part of the municipality Bulqizë. It is situated within the Gollobordë region, near the border with North Macedonia. Name The name of the village is derived from a personal name ''Gjin'' or ''Gin'' with the suffix ''ovec''. "Името е образувано со суфиксот -овец од личното име Ѓин или Гин и има госесивно значење." Demographics A demographic Bulgarian survey of the population of the village, done in 1873, recorded the village as having 90 households with 134 male Bulgarian Christian residents and 118 male Muslim (Pomak) residents. The inhabitants of Gjinovec are speakers of a south Slavic language "Heute umfaßt das Gebiet von Golloborda in Albanien 22 Dörfer, die verwaltungstechnisch auf drei verschiedene Gemeinden aufgeteilt sind: 1. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gjinar
Gjinar is a village and a former municipality in the Elbasan County, central Albania. At the 2015 local government reform it became a subdivision of the municipality Elbasan. The population at the 2011 census was 3,478. The municipal unit consists of the villages Lleshan, Gjinar, Valesh, Pashtresh, Derstile, Llukan, Sterstan, Xibresh, Maskarth, Kaferr and Pobrat. It is part of the Shpati mountainous area, and a touristic destination. It is near a massive pine forest. It is known for weekly bazaar days. Every Thursday Thursday is the Names of the days of the week, day of the week between Wednesday and Friday. According to the ISO 8601 international standard, it is the fourth day of the week. In countries which adopt the "Sunday-first" convention, it is the fi ... in center of Gjinar takes place bazaar day. There you can buy fresh products from villages nearby that comes to sell products. As a touristic center there can be enjoyed weekends in the fresh air, beautiful nature and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
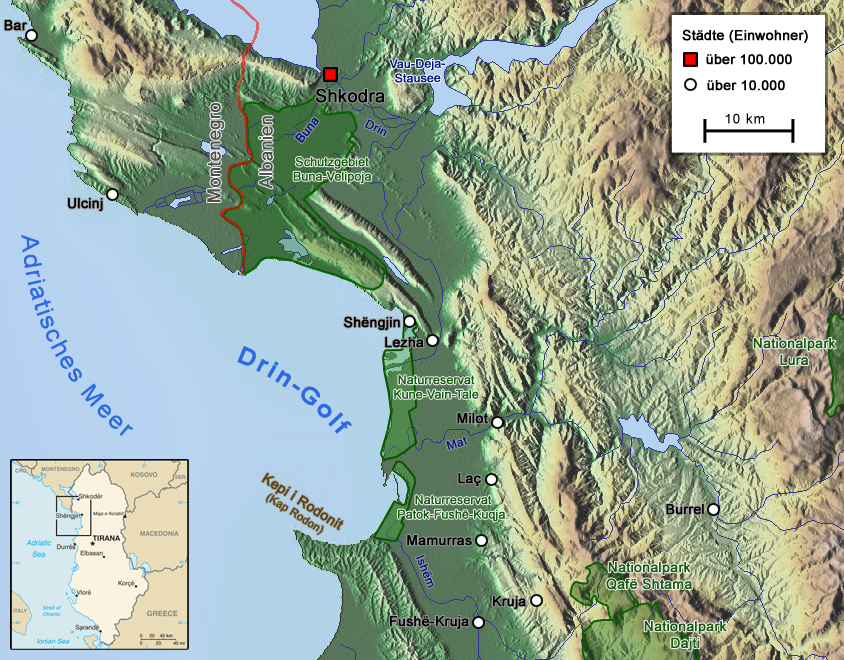
Shëngjin
Shëngjin is a coastal town and a former municipality in Lezhë County, northwestern Albania. At the 2015 local government reform it became a subdivision of the municipality of Lezhë. The population at the 2011 census was 8,091.2011 census results Shëngjin is a growing tourist destination, well known for its beaches and resort accommodations. Shëngjin is one of many cities within the District of Lezhë and is home to one of Albania's entry ports, Port of Shëngjin. History The area of Shëngjin has been identified with the site of the ancient harbour of on the coast of |
Mirdita
Mirdita is a region of northern Albania whose territory is synonymous with the historic Albanian tribe of the same name. Etymology The name Mirdita derives from a legendary ancestor named Mir Diti from whom the tribe claims descent. Other alternative folk etymologies have been presented. Another folk etymology links the word to the Albanian greeting "mirëdita" meaning hello, "good day". Geography Historically Mirdita was the largest tribal region of Albania in terms of geographic spread and population. The region is situated in northern Albania, and it borders the traditional tribal areas of Puka (Berisha, Kabashi, Qerreti) in the north; the Lezha highlands (Vela, Bulgëri, Manatia, Kryeziu) in the west and southwest; the northern Albanian coastal plain of Lezha and Zadrima between the Drin and Mat rivers in the west; the river Mat and region of Mat in the south and the area of the Black Drin river in the east. The traditional areas and settlements of Mirdita are: Bisak, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |