|
Giampietro Campana
Giampietro Campana (1808 – 10 October 1880), created marchese di Cavelli (1849), was an Italian art collector who assembled one of the nineteenth century's greatest collection of Greek and Roman sculpture and antiquities. The part of his collection of Hellenistic and Roman gold jewellery conserved in the Musée du Louvre warranted an exhibition devoted to it in 2005–06. He was an early collector of early Italian paintings, the so-called "primitives" of the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries, which were overlooked by his contemporaries. And like many collectors of his generation, he coveted Italian maiolica of the 15th and 16th centuries. Career Campana was born in Rome into a sophisticated milieu: the family was also entrusted with the operation of the Monte di Pietà, a papal charitable trust that operated as pawnbroker to Rome; Giampietro entered as an assistant in 1831 and was so efficient he was appointed director general in 1833. In 1835 he was made a ''cavaliere'' of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giampietro Campana Carte De Visite Vers 1865
Giampietro is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: *Michael Giampietro (Born 1990), Australian Electronics and Communication Technician *Domenico Pellegrini Giampietro (1899–1970), Italian academic, economist, lawyer, politician and journalist *Frank Giampietro, American poet * Gordon P. Giampietro (born 1965), American lawyer *Sydney Giampietro Sydney ( ) is the capital city of the state of New South Wales, and the most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Sydney Harbour and extends about towards the Blue Mountains ... (born 1999), Italian sho putter See also * Giampietro (given name) {{surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Pius IX
Pope Pius IX ( it, Pio IX, ''Pio Nono''; born Giovanni Maria Mastai Ferretti; 13 May 1792 – 7 February 1878) was head of the Catholic Church from 1846 to 1878, the longest verified papal reign. He was notable for convoking the First Vatican Council in 1868 and for permanently losing control of the Papal States in 1870 to the Kingdom of Italy. Thereafter he refused to leave Vatican City, declaring himself a " prisoner of the Vatican". At the time of his election, he was seen as a champion of liberalism and reform, but the Revolutions of 1848 decisively reversed his policies. Upon the assassination of his Prime Minister Rossi, Pius escaped Rome and excommunicated all participants in the short-lived Roman Republic. After its suppression by the French army and his return in 1850, his policies and doctrinal pronouncements became increasingly conservative, seeking to stem the revolutionary tide. In his 1849 encyclical '' Ubi primum'', he emphasized Mary's role in salvation. In 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basilica Of St
In Ancient Roman architecture Ancient Roman architecture adopted the external language of classical Greek architecture for the purposes of the ancient Romans, but was different from Greek buildings, becoming a new architectural style. The two styles are often considered one ..., a basilica is a large public building with multiple functions, typically built alongside the town's Forum (Roman), forum. The basilica was in the Latin West equivalent to a stoa in the Greek East. The building gave its name to the architectural form of the basilica. Originally, a basilica was an ancient Roman architecture, ancient Roman public building, where courts were held, as well as serving other official and public functions. Basilicas are typically rectangular buildings with a central nave flanked by two or more longitudinal aisles, with the roof at two levels, being higher in the centre over the nave to admit a clerestory and lower over the side-aisles. An apse at one end, or less frequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand II Of Naples
Ferdinando Trastámara d'Aragona, of the branch of Naples, known to contemporaries especially with the name of Ferrandino (Naples, 26 June 1467 - Naples, 7 October 1496). Acclaimed "the first among all the Kings and Lords of the World" and universally praised for his excellent virtues was King of Naples for just under two years, from 23 January 1495 to 7 October 1496. Prince of Capua from birth until 25 January 1494 and Duke of Calabria from 25 January 1494 to 23 January 1495 as heir to the throne. A valiant prince, magnanimous, forgiving, and truly endowed with every good disposition of the soul as well as of the body, he demonstrated, in the few years he lived, great audacity and high military valor, as well as rare political acumen. Since adolescence he lent his sword for the defense of the kingdom, which among a thousand dangers due to the nefarious politics of his father, had been lost. For it, as an extreme sacrifice, he finally gave his life: exhausted by the many battles, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleon III
Napoleon III (Charles Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was the first President of France (as Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte) from 1848 to 1852 and the last monarch of France as Emperor of the French from 1852 to 1870. A nephew of Napoleon I, he was the last monarch to rule over France. Elected to the presidency of the Second Republic in 1848, he seized power by force in 1851, when he could not constitutionally be reelected; he later proclaimed himself Emperor of the French. He founded the Second Empire, reigning until the defeat of the French Army and his capture by Prussia and its allies at the Battle of Sedan in 1870. Napoleon III was a popular monarch who oversaw the modernization of the French economy and filled Paris with new boulevards and parks. He expanded the French overseas empire, made the French merchant navy the second largest in the world, and engaged in the Second Italian War of Independence as well as the disastrous Franco-Prussian War, dur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
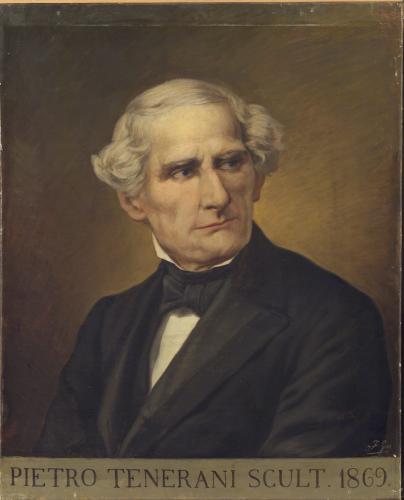
Pietro Tenerani
Pietro Tenerani (11 November 1789 – 16 December 1869) was an Italian sculptor of the Neoclassic style. Biography He was born in Torano, near Carrara. He initially trained with his maternal uncle, the sculptor Pietro Marchetti, and in 1813, obtained a stipend to study in Rome. There he studied mainly in the studio of Bertel Thorvaldsen. In 1816, he sculpted an ''Abandoned Psyche'' sold to Marchesa Lenzoni of Florence. He was prolific and worked in a chaste neoclassical style into the mid-nineteenth century, specialising in pious subjects. His most prominent commission was for the tomb of Pope Pius VIII in Rome. He completed a colossal statue of '' St Alfonso de Liguori'' for the Vatican. He sculpted a ''St John the Evangelist'' for the church of San Francesco di Paola in Naples, and of ''San Benedetto'' in the Basilica Ostiense. He made numerous busts of officials in the state and church, including Popes Pius VIII, Gregory XVI, and Pius IX. He depicted the Count Este ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triclinium
A ''triclinium'' (plural: ''triclinia'') is a formal dining room in a Roman building. The word is adopted from the Greek ()—from (), "three", and (), a sort of couch or rather chaise longue. Each couch was sized to accommodate a diner who reclined on their left side on cushions while some household slaves served multiple courses brought from the ''culina'', or kitchen, and others entertained guests with music, song, or dance. The ''triclinium'' was characterized by three '' lecti'' (singular ''lectus'': bed or couch), called ''triclinares'' ("of the ''triclinium''"), on three sides of a low square table, whose surfaces sloped away from the table at about 10 degrees. Diners would recline on these surfaces in a semi-recumbent position. The fourth side of the table was left free, presumably to allow service to the table. Usually the open side faced the entrance of the room. In Roman-era dwellings, particularly wealthy ones, ''triclinia'' were common and the hosts and guest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aqua Claudia
Aqua Claudia ("the Claudian water") was an ancient Roman aqueduct that, like the Aqua Anio Novus, was begun by Emperor Caligula (37–41 AD) in 38 AD and finished by Emperor Claudius (41–54 AD) in 52 AD. Together with Aqua Anio Novus, Aqua Anio Vetus and Aqua Marcia, it is regarded as one of the "four great aqueducts of Rome". Route Its mainsprings, the Caeruleus and Curtius, were situated 300 paces to the left of the 38th milestone of the Via Sublacensis. The total length was approximately , most of which was underground. The flow was about in 24 hours (about ). Directly after its filtering tank, near the seventh mile of the Via Latina, it finally emerged onto arches, which increase in height as the ground falls toward the city, reaching over . It is one of the two ancient aqueducts that flowed through the Porta Maggiore, the other being the Aqua Anio Novus. It is described in some detail by Frontinus in his work published in the later 1st century, ''De aquaeductu'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
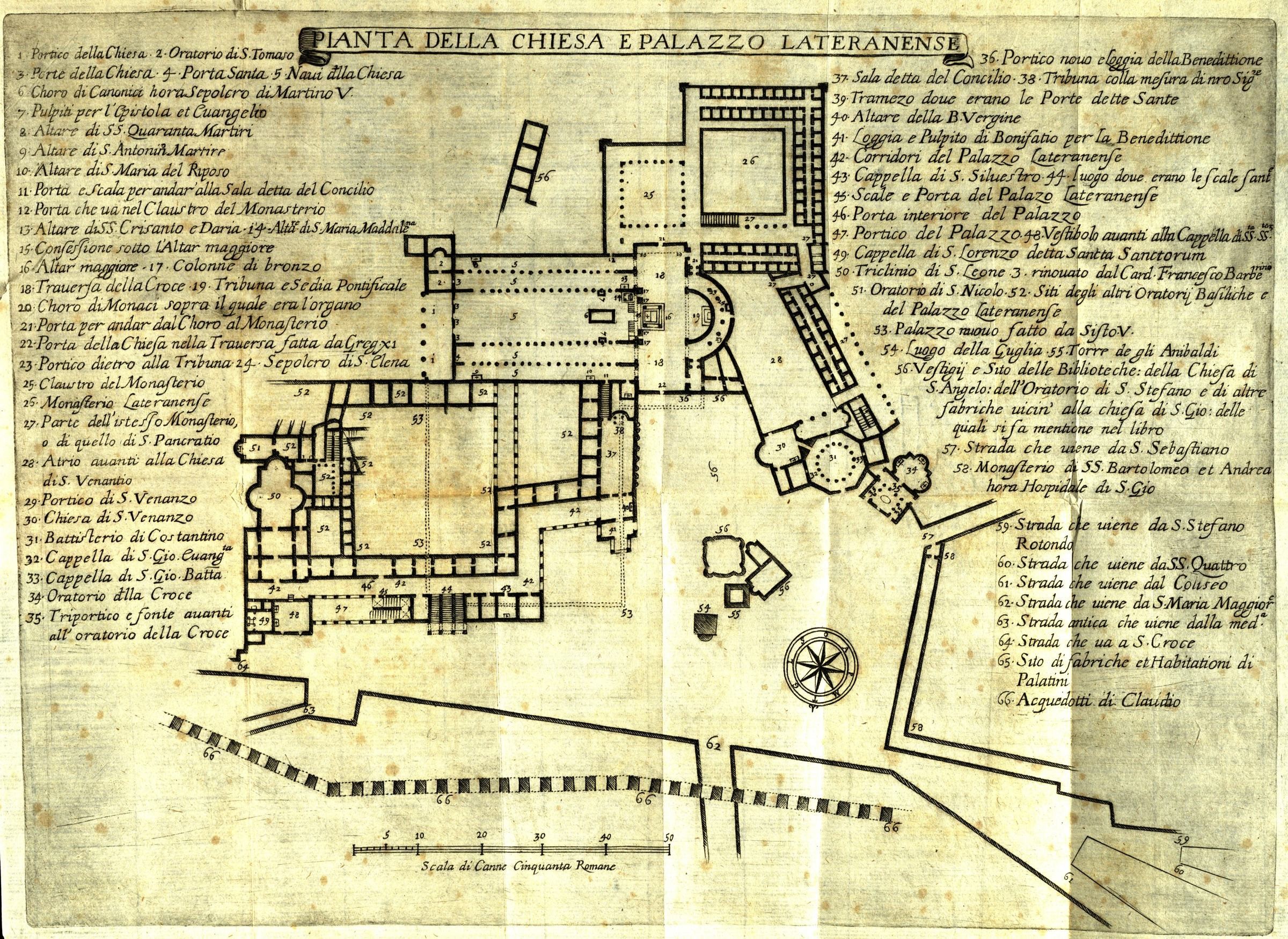
Lateran Palace
The Lateran Palace ( la, Palatium Lateranense), formally the Apostolic Palace of the Lateran ( la, Palatium Apostolicum Lateranense), is an ancient palace of the Roman Empire and later the main papal residence in southeast Rome. Located on St. John's Square in Lateran on the Caelian Hill, the palace is adjacent to the Archbasilica of Saint John Lateran, the cathedral church of Rome. From the fourth century, the palace was the principal residence of the popes, and continued so for about a thousand years until the Apostolic Residence ultimately moved to the Vatican. The palace is now used by the Vatican Historical Museum, which illustrates the history of the Papal States. The palace also houses the offices of the Vicariate of Rome, as well as the residential apartments of the Cardinal Vicar, the pope's delegate for the daily administration of the diocese. Until 1970, the palace was also home to the important collections of the Lateran Museum, now dispersed among other parts of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nero
Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; born Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus; 15 December AD 37 – 9 June AD 68), was the fifth Roman emperor and final emperor of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, reigning from AD 54 until his death in AD 68. He was adopted by the Roman emperor Claudius at the age of 13 and succeeded him on the throne. Nero was popular with the members of his Praetorian Guard and lower-class commoners in Rome and its provinces, but he was deeply resented by the Roman aristocracy. Most contemporary sources describe him as tyrannical, self-indulgent, and debauched. After being declared a public enemy by the Roman Senate, he committed suicide at age 30. Nero was born at Antium in AD 37, the son of Gnaeus Domitius Ahenobarbus and Agrippina the Younger, a great-granddaughter of the emperor Augustus. When Nero was two years old, his father died. His mother married the emperor Claudius, who eventually adopted Nero as his heir; when Cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domus
In Ancient Rome, the ''domus'' (plural ''domūs'', genitive ''domūs'' or ''domī'') was the type of town house occupied by the upper classes and some wealthy freedmen during the Republican and Imperial eras. It was found in almost all the major cities throughout the Roman territories. The modern English word ''domestic'' comes from Latin ''domesticus'', which is derived from the word ''domus''. The word in modern Slavic languages means "home" and is a cognate of the Latin word, going back to Proto-Indo-European. Along with a ''domus'' in the city, many of the richest families of ancient Rome also owned a separate country house known as a villa. Many chose to live primarily, or even exclusively, in their villas; these homes were generally much grander in scale and on larger acres of land due to more space outside the walled and fortified city. The elite classes of Roman society constructed their residences with elaborate marble decorations, inlaid marble paneling, door jamb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eucalyptus
''Eucalyptus'' () is a genus of over seven hundred species of flowering trees, shrubs or mallees in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae. Along with several other genera in the tribe Eucalypteae, including '' Corymbia'', they are commonly known as eucalypts. Plants in the genus ''Eucalyptus'' have bark that is either smooth, fibrous, hard or stringy, leaves with oil glands, and sepals and petals that are fused to form a "cap" or operculum over the stamens. The fruit is a woody capsule commonly referred to as a "gumnut". Most species of ''Eucalyptus'' are native to Australia, and every state and territory has representative species. About three-quarters of Australian forests are eucalypt forests. Wildfire is a feature of the Australian landscape and many eucalypt species are adapted to fire, and resprout after fire or have seeds which survive fire. A few species are native to islands north of Australia and a smaller number are only found outside the continent. Eucalypts have been grow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |