|
Ghaza Thesis
The Ghaza or Ghazi thesis (from ota, غزا, ''ġazā'', "holy war," or simply "raid") is a historical paradigm first formulated by Paul Wittek which has been used to interpret the nature of the Ottoman Empire during the earliest period of its history, the fourteenth century, and its subsequent history. The thesis addresses the question of how the Ottomans were able to expand from a small principality on the frontier of the Byzantine Empire into a centralized, intercontinental empire. According to the Ghaza thesis, the Ottomans accomplished this by attracting recruits to fight for them in the name of Islamic holy war against the non-believers. Such a warrior was known in Ottoman Turkish as a '' ghazi'', and thus this thesis sees the early Ottoman state as a "Ghazi State," defined by an ideology of holy war. The Ghaza Thesis dominated early Ottoman historiography throughout much of the twentieth century before coming under increasing criticism beginning in the 1980s. Historians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
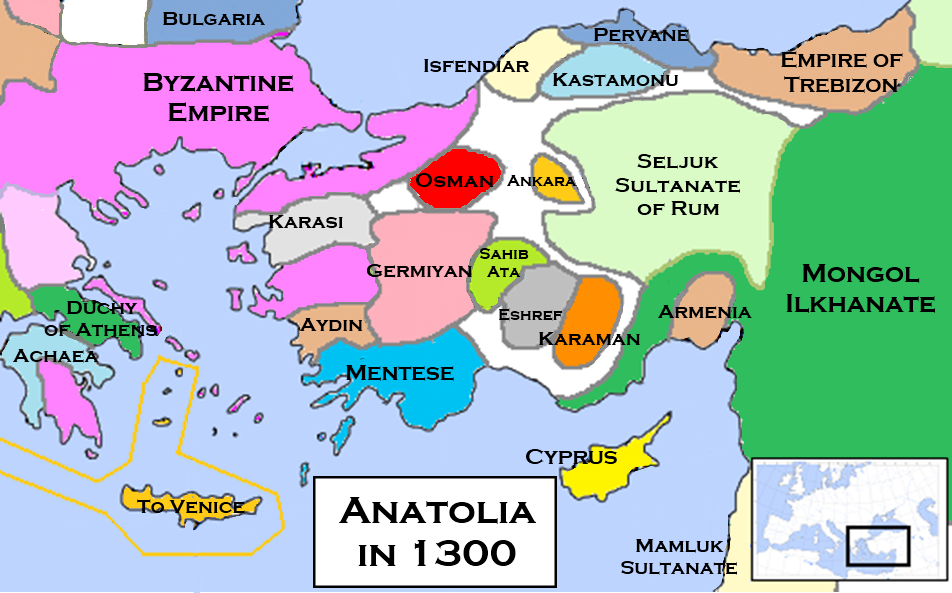
Anatolian Beyliks In 1300
Anatolian or anatolica may refer to: * Anything of, from, or related to the region Anatolia * Anatolians, ancient Indo-European peoples who spoke the Anatolian languages * Anatolian High School, a type of Turkish educational institution * Anatolian Plate, the tectonic plate on which Turkey sits * Anatolian hieroglyphs, a script of central Anatolia * Anatolian languages, a group of extinct Indo-European languages * Anatolian rock, a genre of rock music from Turkey * Anatolian Shepherd, a breed of dog See also * * * * Anadolu (other) * Anatolia (other) Anatolia, also known as Asia Minor, is the peninsular region between the Black Sea in the north and Mediterranean Sea in the south. Anatolia may also refer to: * Air Anatolia, a defunct Turkish airline * ''Anatolia'' (album), a 1997 album by Meza ... {{Disambig Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osman I
Osman I or Osman Ghazi ( ota, عثمان غازى, translit= ʿOsmān Ġāzī; tr, I. Osman or ''Osman Gazi''; died 1323/4), sometimes transliterated archaically as Othman, was the founder of the Ottoman Empire (first known as the Ottoman Beylik or Emirate). While initially a small Turkoman principality during Osman's lifetime, his descendants transformed into a world empire in the centuries after his death. It existed until shortly after the end of World War I. Owing to the scarcity of historical sources dating from his lifetime, very little factual information about Osman has survived. Not a single written source survives from Osman's reign, and the Ottomans did not record the history of Osman's life until the fifteenth century, more than a hundred years after his death. Because of this, historians find it very challenging to differentiate between fact and myth in the many stories told about him. One historian has even gone so far as to declare it impossible, describing th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
14th Century In The Ottoman Empire
14 (fourteen) is a natural number following 13 and preceding 15. In relation to the word "four" ( 4), 14 is spelled "fourteen". In mathematics * 14 is a composite number. * 14 is a square pyramidal number. * 14 is a stella octangula number. * In hexadecimal, fourteen is represented as E * Fourteen is the lowest even ''n'' for which the equation φ(''x'') = ''n'' has no solution, making it the first even nontotient (see Euler's totient function). * Take a set of real numbers and apply the closure and complement operations to it in any possible sequence. At most 14 distinct sets can be generated in this way. ** This holds even if the reals are replaced by a more general topological space. See Kuratowski's closure-complement problem * 14 is a Catalan number. * Fourteen is a Companion Pell number. * According to the Shapiro inequality 14 is the least number ''n'' such that there exist ''x'', ''x'', ..., ''x'' such that :\sum_^ \frac < \frac where ''x'' = ''x'', ''x'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historiography Of The Ottoman Empire
The historiography of the Ottoman Empire refers to the studies, sources, critical methods and interpretations used by scholars to develop a history of the Ottoman Dynasty's empire. Scholars have long studied the Empire, looking at the causes for its formation (such as the Ghaza thesis), its relations to the Great Powers (such as Sick man of Europe) and other empires (such as Transformation of the Ottoman Empire), and the kinds of people who became imperialists or anti-imperialists (such as the Young Turks), together with their mindsets. The history of the breakdown of the Empire (such as Ottoman decline thesis) has attracted scholars of the histories of the Middle East (such as Partition of the Ottoman Empire), and Greece (Rise of nationalism in the Ottoman Empire). New Themes Western understanding of the Ottoman History. Ottoman history has been rewritten for political and cultural advantage and speculative theories rife with inconsistent research, ahistorical assumptions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Decline Thesis
The Ottoman decline thesis or Ottoman decline paradigm ( tr, Osmanlı Gerileme Tezi) is an obsolete * * * * * Leslie Peirce, "Changing Perceptions of the Ottoman Empire: the Early Centuries," ''Mediterranean Historical Review'' 19/1 (2004): 22. * Cemal Kafadar, "The Question of Ottoman Decline," ''Harvard Middle Eastern and Islamic Review'' 4/1–2 (1997–98), pp. 30–75. * M. Fatih Çalışır, "Decline of a 'Myth': Perspectives on the Ottoman 'Decline'," ''The History School'' 9 (2011): 37–60. * Donald Quataert, "Ottoman History Writing and Changing Attitudes towards the Notion of 'Decline,'" ''History Compass'' 1 (2003) historical narrative which once played a dominant role in the study of the history of the Ottoman Empire. According to the decline thesis, following a Golden age (metaphor), golden age associated with the reign of Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent (r. 1520–1566), the empire gradually entered into a period of all-encompassing stagnation and decline f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rise Of The Ottoman Empire
The rise of the Ottoman Empire is a period of history that started with the emergence of the Ottoman principality (Osmanlı Beyliği) in , and ended circa 1453. This period witnessed the foundation of a political entity ruled by the Ottoman Dynasty in the northwestern Anatolian region of Bithynia, and its transformation from a small principality on the Byzantine frontier into an empire spanning the Balkans, Anatolia, Middle East and North Africa. For this reason, this period in the empire's history has been described as the ''"Proto-Imperial Era"''. Throughout most of this period, the Ottomans were merely one of many competing states in the region, and relied upon the support of local warlords Ghazis and vassals (Beys) to maintain control over their realm. By the middle of the fifteenth century the Ottoman sultans were able to accumulate enough personal power and authority to establish a centralized imperial state, a process which was brought to fruition by Sultan Mehmed II (r. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akinji
Akinji or akindji ( ota, آقنجى, aḳıncı, lit=raider, ; plural: ''akıncılar'') were irregular light cavalry, scout divisions (deli) and advance troops of the Ottoman Empire's military. When the pre-existing Turkish ghazis were incorporated into the Ottoman Empire's military they became known as "akıncı." Unpaid, they lived and operated as raiders on the frontiers of the Ottoman Empire, subsisting on plunder. There is a distinction made between "akıncı" and "deli" cavalry. History In war their main role was to act as advance troops on the front lines and demoralise the marching opposing army by using guerrilla tactics, and to put them in a state of confusion and shock. They could be likened to a scythe in a wheat field. They would basically hit the enemy with arrows. When attacked in melee, they would retreat while still shooting backwards. They could easily outrun heavy cavalry because they were lightly armed and their horses were bred for speed as opposed to str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heath W
A heath () is a shrubland habitat found mainly on free-draining infertile, acidic soils and characterised by open, low-growing woody vegetation. Moorland is generally related to high-ground heaths with—especially in Great Britain—a cooler and damper climate. Heaths are widespread worldwide but are fast disappearing and considered a rare habitat in Europe. They form extensive and highly diverse communities across Australia in humid and sub-humid areas where fire regimes with recurring burning are required for the maintenance of the heathlands.Specht, R.L. 'Heathlands' in 'Australian Vegetation' R.H. Groves ed. Cambridge University Press 1988 Even more diverse though less widespread heath communities occur in Southern Africa. Extensive heath communities can also be found in the Texas chaparral, New Caledonia, central Chile, and along the shores of the Mediterranean Sea. In addition to these extensive heath areas, the vegetation type is also found in scattered locations across ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cemal Kafadar
Cemal Kafadar (born 1954) is Professor of History and the Vehbi Koç Professor of Turkish Studies in the Harvard University Department of History. He is an honorary member of the Turkish Historical Society. Kafadar graduated from Robert College, then Hamilton College, and received his PhD from the McGill University Institute of Islamic Studies in 1987 and taught for two years in Princeton's Near East, Near Eastern Studies department before going to Harvard. Kafadar teaches seminars related to popular culture, hagiography and Ottoman historiography as well as the early modern history of the Middle East and Balkans. He is a member of the editorial board of thHistorians of the Ottoman Empireand was a member of the jury of the Antalya Golden Orange Film Festival in 2009. He is the author of the book ''Between Two Worlds: The Construction of the Ottoman State'' (1995). Selected publications * * * * * * *Gülru Necipoğlu, Cemal Kafadar, and Cornell Fleischer, eds. (2019). ''Treasures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthropology
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including past human species. Social anthropology studies patterns of behavior, while cultural anthropology studies cultural meaning, including norms and values. A portmanteau term sociocultural anthropology is commonly used today. Linguistic anthropology studies how language influences social life. Biological or physical anthropology studies the biological development of humans. Archaeological anthropology, often termed as 'anthropology of the past', studies human activity through investigation of physical evidence. It is considered a branch of anthropology in North America and Asia, while in Europe archaeology is viewed as a discipline in its own right or grouped under other related disciplines, such as history and palaeontology. Etymology The abstract noun ''anthropology'' is first attested in reference t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colin Imber
Colin Imber is a lecturer in Turkish studies at Manchester University, UK. He completed his Oriental studies at Cambridge University, where he defended his doctorate on „The Ottoman Fleet in the Age of Sultan Suleiman I (1520-1566)”. His research interest is focused on the history of the Ottoman Empire until the 17th century and on Islamic law, in particular on the system of Ottoman law, until the 17th century. He is considered as "perhaps the leading, and...certainly the most productive, of the painfully few Ottoman historians currently working in British universities."https://reviews.history.ac.uk/review/431 He is noted for his opposition to Paul Wittek's "Ghaza thesis The Ghaza or Ghazi thesis (from ota, غزا, ''ġazā'', "holy war," or simply "raid") is a historical paradigm first formulated by Paul Wittek which has been used to interpret the nature of the Ottoman Empire during the earliest period of its ...". Publications * ''The Ottoman Empire 1300–1481'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syncretic
Syncretism () is the practice of combining different beliefs and various schools of thought. Syncretism involves the merging or assimilation of several originally discrete traditions, especially in the theology and mythology of religion, thus asserting an underlying unity and allowing for an inclusive approach to other faiths. Syncretism also occurs commonly in expressions of art and culture, known as eclecticism, as well as in politics, known as syncretic politics. Nomenclature The English word is first attested in the early 17th century, from Modern Latin , drawing on Greek grc, συγκρητισμός, synkretismos, labels=none, supposedly meaning "Cretan federation", but this is a spurious etymology from the naive idea in Plutarch's 1st-century AD essay on "Fraternal Love (Peri Philadelphias)" in his collection ''Moralia''. He cites the example of the Cretans, who compromised and reconciled their differences and came together in alliance when faced with external dang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpeg/1200px-Amrum_(187753235).jpeg)

