|
Gharraf Canal
The Gharraf Canal, Shaṭṭ al-Ḥayy (Arabic: شط الحي), also known as Shaṭṭ al-Gharrāf (Arabic: شط الغرّاف) or the Hai river, is an ancient canal in Iraq that connects the Tigris at Kut al Amara with the Euphrates east of Nasiriyah. As an Ottoman (Turkish) position lay along the canal, it was one of the objectives of intense military action during the First World War, especially the siege of Kut (December 1915 to April 1916). Between 1934 and 1939, the Kut Barrage was constructed in the Tigris to control the water level of the river and to provide a constant inflow of water to the Shatt al-Hayy. First World War The Turks surrounded and besieged General Charles Townshend's British Empire forces which occupied Kut. The Gharraf River was picked by the Ottoman Army as an advantage point as part of that siege. During the siege the Ottomans repelled relief attempts by Anglo-Indian forces in the Battle of Hanna in January 1916 and the Battle of Dujaila in March ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qalat Sukkar Iraq 1
Qalat, Qelat, Kalat, Kalaat, Kalut, or Kelat, may refer to: * Qalat (fortress), a fortified place or fortified village Afghanistan * Qalat, Zabul, a city and provincial capital * Kalat, Badakhshan, a small village Algeria * Qalat Ibn Salama, a fortress near Tihert (present-day Tiaret) Bahrain * Qal'at al-Bahrain, an archaeological site Burma *Kalat, Banmauk, Burma Iran * Kalat, Kangan, Bushehr Province * Kalat, Tangestan, Bushehr Province * Kalat, Chaharmahal and Bakhtiari * Kalat, East Azerbaijan * Qalat, Bavanat, Fars Province * Qalat, Jahrom, Fars Province * Qalat, Larestan, Fars Province * Qalat, Qir and Karzin, Fars Province * Qalat, Shiraz, Fars Province * Kalat, Hormozgan * Kalut, Iran, Hormozgan Province * Qalat-e Bala, Hormozgan Province * Kalat-e Mahmak, Hormozgan Province * Qalat-e Pain, Hormozgan Province * Qalat-e Rostam, Hormozgan Province * Kelat, Ilam * Qalat, Bahmai, Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad Province * Qalat, Charam, Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad Provi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin/Boston, 2011. Having emerged in the 1st century, it is named after the Arabs, Arab people; the term "Arab" was initially used to describe those living in the Arabian Peninsula, as perceived by geographers from ancient Greece. Since the 7th century, Arabic has been characterized by diglossia, with an opposition between a standard Prestige (sociolinguistics), prestige language—i.e., Literary Arabic: Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Classical Arabic—and diverse vernacular varieties, which serve as First language, mother tongues. Colloquial dialects vary significantly from MSA, impeding mutual intelligibility. MSA is only acquired through formal education and is not spoken natively. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canal
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface flow under atmospheric pressure, and can be thought of as artificial rivers. In most cases, a canal has a series of dams and locks that create reservoirs of low speed current flow. These reservoirs are referred to as ''slack water levels'', often just called ''levels''. A canal can be called a ''navigation canal'' when it parallels a natural river and shares part of the latter's discharges and drainage basin, and leverages its resources by building dams and locks to increase and lengthen its stretches of slack water levels while staying in its valley. A canal can cut across a drainage divide atop a ridge, generally requiring an external water source above the highest elevation. The best-known example of such a canal is the Panama Canal. Many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and Kuwait to the southeast, Saudi Arabia to the south, Jordan to Iraq–Jordan border, the southwest and Syria to Iraq–Syria border, the west. The Capital city, capital and largest city is Baghdad. Iraq is home to diverse ethnic groups including Iraqi Arabs, Kurds, Iraqi Turkmen, Turkmens, Assyrian people, Assyrians, Armenians in Iraq, Armenians, Yazidis, Mandaeans, Iranians in Iraq, Persians and Shabaks, Shabakis with similarly diverse Geography of Iraq, geography and Wildlife of Iraq, wildlife. The vast majority of the country's 44 million residents are Muslims – the notable other faiths are Christianity in Iraq, Christianity, Yazidism, Mandaeism, Yarsanism and Zoroastrianism. The official langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tigris
The Tigris () is the easternmost of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian and Arabian Deserts, and empties into the Persian Gulf. Geography The Tigris is 1,750 km (1,090 mi) long, rising in the Taurus Mountains of eastern Turkey about 25 km (16 mi) southeast of the city of Elazığ and about 30 km (20 mi) from the headwaters of the Euphrates. The river then flows for 400 km (250 mi) through Southeastern Turkey before becoming part of the Syria-Turkey border. This stretch of 44 km (27 mi) is the only part of the river that is located in Syria. Some of its affluences are Garzan, Anbarçayi, Batman, and the Great and the Little Zab. Close to its confluence with the Euphrates, the Tigris splits into several channels. First, the artificial Shatt al-Hayy branches off, to join the Euphrates near Nasiriyah. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers''). Originating in Turkey, the Euphrates flows through Syria and Iraq to join the Tigris in the Shatt al-Arab, which empties into the Persian Gulf. Etymology The Ancient Greek form ''Euphrátēs'' ( grc, Εὐφράτης, as if from Greek εὖ "good" and φράζω "I announce or declare") was adapted from Old Persian 𐎢𐎳𐎼𐎠𐎬𐎢 ''Ufrātu'', itself from Elamite language, Elamite 𒌑𒅁𒊏𒌅𒅖 ''ú-ip-ra-tu-iš''. The Elamite name is ultimately derived from a name spelt in cuneiform as 𒌓𒄒𒉣 , which read as Sumerian language, Sumerian is "Buranuna" and read as Akkadian language, Akkadian is "Purattu"; many cuneiform signs have a Sumerian pronunciation and an Akkadian pronunciation, taken from a Sumerian word a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasiriyah
Nasiriyah ( ar, ٱلنَّاصِرِيَّة; United States Board on Geographic Names, BGN: ''An Nāşirīyah''; also spelled ''Nassiriya'' or ''Nasiriya'') is a city in Iraq. It is on the lower Euphrates River, Euphrates, about south-southeast of Baghdad, near the ruins of the ancient city of Ur. It is the capital of the Dhi Qar Governorate. Its population in 2003 was about 560,000, making it the fourth-largest city in Iraq. It had a diverse population of Muslims, Mandaeans and Jews in the early 20th century;Field Museum of Natural History, 1940, p. 258. today its inhabitants are predominantly Shia muslims. Nasiriyah was founded by the Muntafiq tribe in the late 19th century during the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman era. It has since become a major hub for transportation. Nasiriyah is the center of a Date palm#Dates, date-growing area. The city's cottage industries include boat-building, carpentry and silver working. The city museum has a large collection of Sumerian, Assyrian, Babyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Of The Ottoman Empire
The military of the Ottoman Empire ( tr, Osmanlı İmparatorluğu'nun silahlı kuvvetleri) was the armed forces of the Ottoman Empire. Army The military of the Ottoman Empire can be divided in five main periods. The foundation era covers the years between 1300 (Byzantine expedition) and 1453 (Conquest of Constantinople), the classical period covers the years between 1451 (second enthronement of Sultan Mehmed II) and 1606 (Peace of Zsitvatorok), the reformation period covers the years between 1606 and 1826 ( Vaka-i Hayriye), the modernisation period covers the years between 1826 and 1858 and decline period covers the years between 1861 (enthronement of Sultan Abdülaziz) and 1918 (Armistice of Mudros). The Ottoman army is the forerunner of the Turkish Armed Forces. Foundation period (1300–1453) The earliest form of the Ottoman military was a steppe-nomadic cavalry force.Mesut Uyar, Edward J. Erickson, ''A Military History of the Ottomans: From Osman to Atatürk'', Pleager ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising France, Russia, and Britain) and the Triple Alliance (containing Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy). Tensions in the Balkans came to a head on 28 June 1914, following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
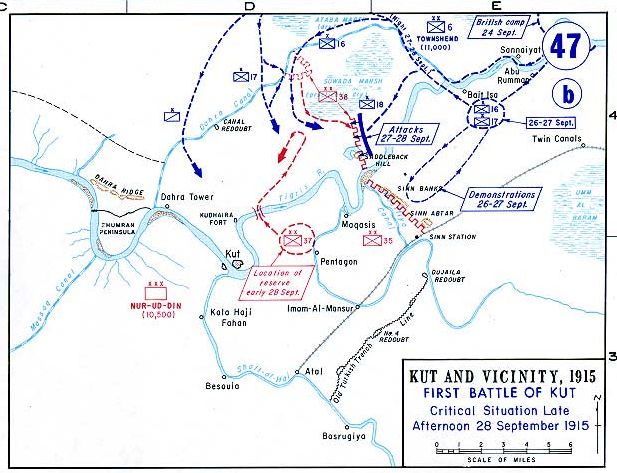
Siege Of Kut
The siege of Kut Al Amara (7 December 1915 – 29 April 1916), also known as the first battle of Kut, was the besieging of an 8,000 strong British Army garrison in the town of Kut, south of Baghdad, by the Ottoman Army. In 1915, its population was around 6,500. Following the surrender of the garrison on 29 April 1916, the survivors of the siege were marched to imprisonment at Aleppo, during which many died. Historian Christopher Catherwood has called the siege "the worst defeat of the Allies in World War I". Ten months later, the British Indian Army, consisting almost entirely of newly recruited troops from Western India, conquered Kut, Baghdad and other regions in between in the Fall of Baghdad. Prelude The 6th (Poona) Division of the Indian Army, under Major-General Charles Townshend, had fallen back to the town of Kut after retreating from Ctesiphon. The British Empire forces arrived at Kut around 3 December 1915. They had suffered significant losses, numbering only 11,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kut Barrage
The Kut Barrage is a barrage on the Tigris river, located in the modern town of Kut in Wasit Governorate, Iraq. Technical details It is long, high, and consists of 56 gates, each wide. The maximum discharge of the barrage is , but actual discharge has not exceeded in the last 10 years. The barrage supports a road and includes a lock for boats passing up and down the Tigris. Its purpose is to maintain a sufficiently high water level in the Tigris to provide water for the Gharraf irrigation canal, which branches off the Tigris just upstream from the Kut Barrage. Before the construction of the Kut Barrage, the Gharraf canal only received water during periods of flood in the Tigris. The water level in the canal is maintained by the Gharraf Head Regulator, which was constructed at the same time as the Kut Barrage. History The Kut Barrage was constructed between 1934 and 1939 by the British firm Balfour Beatty Balfour Beatty plc () is an international infrastructure gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Kut
The siege of Kut Al Amara (7 December 1915 – 29 April 1916), also known as the first battle of Kut, was the besieging of an 8,000 strong British Army garrison in the town of Kut, south of Baghdad, by the Ottoman Army. In 1915, its population was around 6,500. Following the surrender of the garrison on 29 April 1916, the survivors of the siege were marched to imprisonment at Aleppo, during which many died. Historian Christopher Catherwood has called the siege "the worst defeat of the Allies in World War I". Ten months later, the British Indian Army, consisting almost entirely of newly recruited troops from Western India, conquered Kut, Baghdad and other regions in between in the Fall of Baghdad. Prelude The 6th (Poona) Division of the Indian Army, under Major-General Charles Townshend, had fallen back to the town of Kut after retreating from Ctesiphon. The British Empire forces arrived at Kut around 3 December 1915. They had suffered significant losses, numbering only 11,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |