|
Ghaba North
Ghaba is a Neolithic cemetery mound and African archaeological site located in Central Sudan in the Shendi region of the Nile Valley. The site, discovered in 1977 by the Section Française de la Direction des Antiquités du Soudan (SFDAS) while they were investigating nearby Kadada, dates to 4750–4350 and 4000–3650 cal BC. Archaeology of the site originally heavily emphasized pottery, as there were many intact or mostly intact vessels. Recent analysis has focused on study of plant material found, which indicates that Ghaba may have been domesticating cereals earlier than previously believed. Though the site is a cemetery, little analysis has taken place on the skeletons due to circumstances of the excavation and poor preservation due to the environment. The artifacts at Ghaba suggest the people who used the cemetery were part of a regionalization separating central Sudan's Neolithic from Nubia. While many traditions match with Nubia, the people represented at Ghaba had some of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of settlement. It began about 12,000 years ago when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East, and later in other parts of the world. The Neolithic lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BC), marked by the development of metallurgy, leading up to the Bronze Age and Iron Age. In other places the Neolithic followed the Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age) and then lasted until later. In Ancient Egypt, the Neolithic lasted until the Protodynastic period, 3150 BC.Karin Sowada and Peter Grave. Egypt in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerita
''Nerita'' is a genus of medium-sized to small sea snails with a gill and an operculum, marine gastropod molluscs in the subfamily Neritinae of the family Neritidae, the nerites.MolluscaBase eds. (2021). MolluscaBase. Nerita Linnaeus, 1758. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=138254 on 2021-09-20 This is the type genus of the family Neritidae. Distribution and habitat Species of ''Nerita'' can be found worldwide in tropical waters in the middle and upper intertidal zones. They are gregarious herbivores. Description The thick shell is broadly ovate or globular and low-spired. It has a smooth surface. The shells are spirally ribbed or show some axial sculpturing. The ventral side has a large columellar callus or parietal wall. The callus shows small pustules. The aperture and the edge of the columella are usually dentate with fine or robust teeth. The calcareus operculum is thick and can be smooth or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calculus (dental)
In dentistry, calculus or tartar is a form of hardened dental plaque. It is caused by precipitation of minerals from saliva and gingival crevicular fluid (GCF) in plaque on the teeth. This process of precipitation kills the bacterial cells within dental plaque, but the rough and hardened surface that is formed provides an ideal surface for further plaque formation. This leads to calculus buildup, which compromises the health of the gingiva (gums). Calculus can form both along the gumline, where it is referred to as supragingival ("above the gum"), and within the narrow sulcus that exists between the teeth and the gingiva, where it is referred to as subgingival ("below the gum"). Calculus formation is associated with a number of clinical manifestations, including bad breath, receding gums and chronically inflamed gingiva. Brushing and flossing can remove plaque from which calculus forms; however, once formed, calculus is too hard (firmly attached) to be removed with a toothb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bivalvia
Bivalvia (), in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class of marine and freshwater molluscs Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estim ... that have laterally compressed bodies enclosed by a shell consisting of two hinged parts. As a group, bivalves have no head and they lack some usual molluscan organs, like the radula and the odontophore. They include the clams, oysters, Cockle (bivalve), cockles, mussels, scallops, and numerous other family (biology), families that live in saltwater, as well as a number of families that live in freshwater. The majority are filter feeders. The gills have evolved into Ctenidium (mollusc), ctenidia, specialised organs for feeding and breathing. Most bivalves bury themselves in sediment, where they a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerma
Kerma was the capital city of the Kerma culture, which was located in present-day Sudan at least 5,500 years ago. Kerma is one of the largest archaeological sites in ancient Nubia. It has produced decades of extensive excavations and research, including thousands of graves and tombs and the residential quarters of the main city surrounding the Western/Lower Deffufa. The locale that is now Kerma was first settled around 8350 BC, during the Mesolithic. Between 5550 BC and 5150 BC, the site was mostly abandoned, possibly due to decreased Nile flow during this time interval. A second hiatus in occupation occurred between 4050 BC and 3450 BC, likely as a result of minimal flow from the White Nile. Around 3000 BC, a cultural tradition began around Kerma. It was a large urban center that was built around a large adobe temple known as the Western Deffufa. A state society formed between 2550 BC and 1550 BC, with a significant decrease in cattle breeding being evidenced by the archaeologica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bucranium
Bucranium (plural ''bucrania''; Latin, from Greek ''βουκράνιον'', referring to the skull of an ox) was a form of carved decoration commonly used in Classical architecture. The name is generally considered to originate with the practice of displaying garlanded, sacrificial oxen, whose heads were displayed on the walls of temples, a practice dating back to the sophisticated Neolithic site of Çatalhöyük in eastern Anatolia, where cattle skulls were overlaid with white plaster. Etymology and sphere of application The word "bucranium" (latin ''bucranium'') comes from Ancient Greek: βουκράνιον - being composed of βοῦς (''ox'') and κρανίον (''skull'') - and literally means "ox skull". Analogic, the Greek word αἰγικράνιον (''latin'' aegicranium) means a "goat skull", also used as a decorative element in architecture. The technical term "bucranium" was originally used in the description of classical architecture. Its application to the fie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ochre
Ochre ( ; , ), or ocher in American English, is a natural clay earth pigment, a mixture of ferric oxide and varying amounts of clay and sand. It ranges in colour from yellow to deep orange or brown. It is also the name of the colours produced by this pigment, especially a light brownish-yellow. A variant of ochre containing a large amount of hematite, or dehydrated iron oxide, has a reddish tint known as "red ochre" (or, in some dialects, ruddle). The word ochre also describes clays coloured with iron oxide derived during the extraction of tin and copper. Earth pigments Ochre is a family of earth pigments, which includes yellow ochre, red ochre, purple ochre, sienna, and umber. The major ingredient of all the ochres is iron(III) oxide-hydroxide, known as limonite, which gives them a yellow colour. * Yellow ochre, , is a hydrated iron hydroxide (limonite) also called gold ochre. * Red ochre, , takes its reddish colour from the mineral hematite, which is an anhydrous iron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gebel Ramlah
...
Gebel may refer to: Places * Gebel Edmonstone, a flat-topped mesa * Gebel Elba, a peak in Egypt * Gebel el-Haridi, an archaeological site in Egypt * Gebel el-Silsila, an archaeological quarry site in Egypt * Gebel Ramlah, an archaeological site in Egypt * Ġebel San Pietru, a hill in Malta * Gebel Tingar, small mountain in Egypt * Gebel-al-Tarik (Mountain of Tarik), the Arabic name for Gibraltar * Tuna el-Gebel, the necropolis of Khmun Other * Gebel (surname), Turkish and German surname * Gebel el-Arak Knife, an ivory and flint knife * Gebel Kamil (meteorite) * Gebel, a fictional character in '' Bloodstained: Ritual of the Night'' and its companion game ''Bloodstained: Curse of the Moon'' See also * Jabal (other) Jabal, Jabel, Jebel or Jibal may refer to: People * Jabal (name), a male Arabic given name * Jabal (Bible), mentioned in the Hebrew Bible Places In Arabic, ''jabal'' or ''jebel'' (spelling variants of the same word) means 'mountain'. * Dzhebel, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang (tools)
A tang or shank is the back portion of the blade component of a tool where it extends into stock material or connects to a handle – as on a knife, sword, spear, arrowhead, chisel, file, coulter, pike, scythe, screwdriver, etc. One can classify various tang designs by their appearance, by the manner in which they attach to a handle, and by their length in relation to the handle. ''Nakago'' is the term in Japanese, used especially when referring to the tang of the katana or the wakizashi. Full vs partial tang A full tang extends the full length of the grip-portion of a handle, versus a ''partial'' tang which does not. A full tang may or may not be as wide as the handle itself, but will still run the full length of the handle. There are a wide variety of full and partial tang designs. In perhaps the most common design in full tang knives, the handle is cut in the shape of the tang and handle scales are then fastened to the tang by means of pins, screws, bolts, metal tubing, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
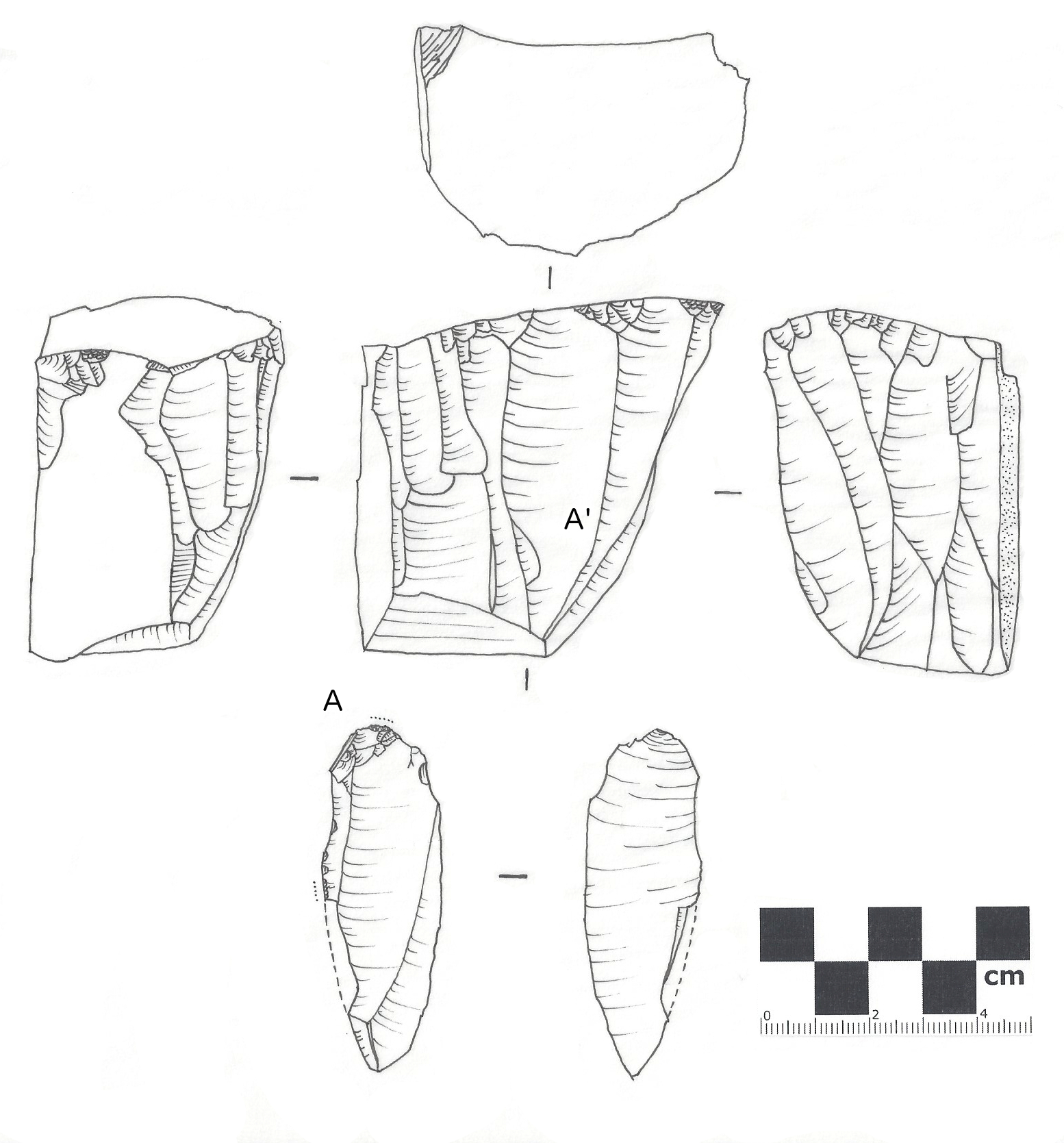
Flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Flint was widely used historically to make stone tools and start fires. It occurs chiefly as nodules and masses in sedimentary rocks, such as chalks and limestones.''The Flints from Portsdown Hill'' Inside the nodule, flint is usually dark grey, black, green, white or brown in colour, and often has a glassy or waxy appearance. A thin layer on the outside of the nodules is usually different in colour, typically white and rough in texture. The nodules can often be found along s and |
Lithic Flake
In archaeology, a lithic flake is a "portion of rock removed from an objective piece by percussion or pressure,"Andrefsky, W. (2005) ''Lithics: Macroscopic Approaches to Analysis''. 2d Ed. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press and may also be referred to as simply a ''flake'', or collectively as debitage. The objective piece, or the rock being reduced by the removal of flakes, is known as a core.Andrefsky, W. (2005) ''Lithics: Macroscopic Approaches to Analysis''. 2d Ed. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press Once the proper tool stone has been selected, a percussor or pressure flaker (e.g., an antler tine) is used to direct a sharp blow, or apply sufficient force, respectively, to the surface of the stone, often on the edge of the piece. The energy of this blow propagates through the material, often ( but not always) producing a Hertzian cone of force which causes the rock to fracture in a controllable fashion. Since cores are often struck on an edge with a suitable angle (<90°) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(4574792797).jpg)