|
Gesila Island
Gesila Island is a small island separating West Channel, East Channel and China Strait, just south of Milne Bay, in Milne Bay Province, Papua New Guinea. Administration The island belongs to Kuiaro, of Bwanabwana Rural Local Level Government Area LLG, Samarai-Murua District, which are in Milne Bay Province. History The island is owned by the Seventh-day Adventist church. From 1961 until the 1980s it was the site of the Adventist mission headquarters for the Milne Bay area (which is now administered from Popondetta). Geography The island is part of Samarai Islands of the Louisiade Archipelago The Louisiade Archipelago is a string of ten larger volcanic islands frequently fringed by coral reefs, and 90 smaller coral islands in Papua New Guinea. It is located 200 km southeast of New Guinea, stretching over more than and spread .... Demographics The population of 19 is located on a single village on the northwest point. Economy The islanders, are farmer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a region, geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern Hemisphere, Eastern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of and a population of around 44.5 million as of 2021. When compared with (and sometimes described as being one of) the continents, the region of Oceania is the smallest in land area and the list of continents and continental subregions by population, second least populated after Antarctica. Its major population centres are Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth, Auckland, Adelaide, Honolulu, and Christchurch. Oceania has a diverse mix of economies from the developed country, highly developed and globally competitive market economy, financial markets of Australia, French Polynesia, Hawaii, Hawaii, New Caledonia, and New Zealand, which rank high in quality of life and Human Development Index, to the much least developed countries, less developed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
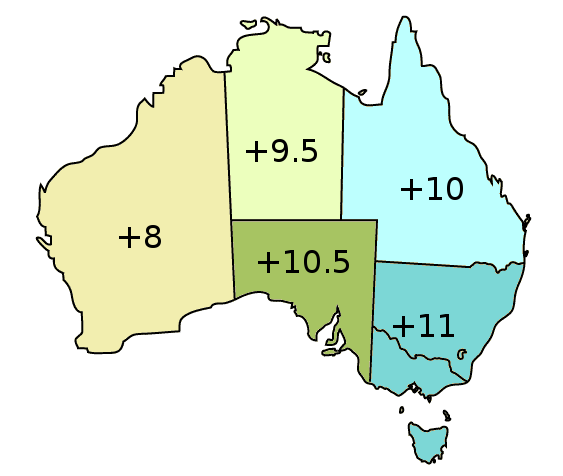
Time In Australia
Australia uses three main time zones: Australian Western Standard Time (AWST; UTC+08:00), Australian Central Standard Time (ACST; UTC+09:30), and Australian Eastern Standard Time (AEST; UTC+10:00). Time is regulated by the individual state governments, some of which observe daylight saving time (DST). Australia's external territories observe different time zones. Standard time was introduced in the 1890s when all of the Australian colonies adopted it. Before the switch to standard time zones, each local city or town was free to determine its local time, called local mean time. Now, Western Australia uses Western Standard Time; South Australia and the Northern Territory use Central Standard Time; while New South Wales, Queensland, Tasmania, Victoria, Jervis Bay Territory, and the Australian Capital Territory use Eastern Standard Time. Daylight saving time (+1 hour) is used in jurisdictions in the south and south-east: South Australia, New South Wales, Victoria, Tasmania, Je ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Popondetta
Popondetta (sometimes spelled Popondota) is the capital of Oro (Northern) Province in Papua New Guinea. Popondetta is a city. In 1951 the city became the focus of relief efforts after nearby Mount Lamington erupted and killed 4,000 people. Popondetta is near to Buna on the Northern Papua coast and is not far from the beginning of the Kokoda Trail, made famous during World War II. This area of New Guinea is home to the endangered Queen Alexandra's birdwing, the world's largest butterfly. Climate Popondetta has a tropical rainforest climate (Köppen ''Af'') with heavy rainfall year-round. Education Newton Theological College Newton Theological College is a Papua New Guinean educational institution in Popondetta, Papua New Guinea. It trains candidates for ordination in the Anglican Church of Papua New Guinea. History Anglican mission activity commenced in the Territ ... is located in Popondetta. References Populated places in Oro Province Provincial capitals in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seventh-day Adventist Church
The Seventh-day Adventist Church is an Adventist Protestant Christian denomination which is distinguished by its observance of Saturday, the seventh day of the week in the Christian (Gregorian) and the Hebrew calendar, as the Sabbath, and its emphasis on the imminent Second Coming (advent) of Jesus Christ. The denomination grew out of the Millerite movement in the United States during the mid-19th century and it was formally established in 1863. Among its co-founders was Ellen G. White, whose extensive writings are still held in high regard by the church. Much of the theology of the Seventh-day Adventist Church corresponds to common evangelical Christian teachings, such as the Trinity and the infallibility of Scripture. Distinctive post-tribulation teachings include the unconscious state of the dead and the doctrine of an investigative judgment. The church places an emphasis on diet and health, including adhering to Kosher food laws, advocating vegetarianism, and its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samarai-Murua District
Samarai-Murua District is a district of the Milne Bay Province of Papua New Guinea. Its capital is Murua. The population of the district was 58,590 at the 2011 census. at statoids.com The district derives its name from the of and Woodlark Island
Woodlark Island, known to its inhabitants simply as Woodlark or Muyua, is the main island of the Woodlark Islands archipelago, located in Milne Bay Province and the Solomon Sea, Papua New Guinea. ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Districts And LLGs Of Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea has 326 local-level governments (LLGs) comprising 6,112 wards as of 2018. ''Note'': LLG names with slashes (/) are listed with dashes (-) due to technical limitations on previous versions of the Wikipedia software. Administrative divisions At the highest level, Papua New Guinea is divided into four List of regions of Papua New Guinea, regions, namely the Highlands Region, Highlands, Islands Region, Islands, Momase Region, Momase, and Southern Region, Papua New Guinea, Southern regions. Below, Papua New Guinea has 22 Provinces of Papua New Guinea, province-level divisions: 20 integrated provinces, the autonomous province of Bougainville Province, North Solomons (Bougainville) and the National Capital District (Papua New Guinea), National Capital District. Each province has one or more Districts of Papua New Guinea, districts, and each district has one or more local-level government (LLG) areas. For census purposes, the LLG areas are subdivided into wards and tho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milne Bay Province
Milne Bay is a province of Papua New Guinea. Its capital is Alotau. The province covers 14,345 km² of land and 252,990 km² of sea, within the province there are more than 600 islands, about 160 of which are inhabited. The province has about 276,000 inhabitants, speaking about 48 languages, most of which belong to the Eastern Malayo-Polynesian branch of the Austronesian language family. Economically the province is dependent upon tourism, oil palm, and gold mining on Misima Island; in addition to these larger industries there are many small-scale village projects in cocoa and copra cultivation. The World War II Battle of Milne Bay took place in the province. Culturally the Milne Bay region is sometimes referred to as "the Massim," a term originating from the name of Misima Island. Massim societies are usually characterized by matrilineal descent, elaborate mortuary sequences and complex systems of ritual exchange including the Kula ring. From island group to island g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milne Bay
Milne Bay is a large bay in Milne Bay Province, south-eastern Papua New Guinea. More than long and over wide, Milne Bay is a sheltered deep-water harbor accessible via Ward Hunt Strait. It is surrounded by the heavily wooded Stirling Range to the north and south, and on the northern shore, a narrow coastal strip, soggy with sago and mangrove swamps. The bay is named after Sir Alexander Milne. History * Surveyed by Luis Vaez de Torres in July 1606. * Surveyed by Captain Owen Stanley, R.N. F.R.S. in 1850. World War II During World War II, the area was the site of the Battle of Milne Bay in 1942 and by late 1943 it became the major support base, Naval Base Milne Bay, for the New Guinea campaign through the development of Finschhafen as an advanced base after that area was secured in the Huon Peninsula campaign. By January 1944 about 140 vessels were in harbor due to congestion at the facilities. Congestion was relieved by opening of a port at Finschhafen and extensive improveme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China Strait
The China Strait is a navigable strait in the Milne Bay Province of Papua New Guinea between mainland New Guinea and Samarai Island. The strait, in length and wide, connects the Solomon Sea with the Coral Sea The Coral Sea () is a marginal sea of the South Pacific off the northeast coast of Australia, and classified as an interim Australian bioregion. The Coral Sea extends down the Australian northeast coast. Most of it is protected by the Fre .... References External links ITouch Map of the China Strait* Straits of Papua New Guinea {{PapuaNewGuinea-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanesians
Melanesians are the predominant and indigenous inhabitants of Melanesia, in a wide area from Indonesia's New Guinea to as far East as the islands of Vanuatu and Fiji. Most speak either one of the many languages of the Austronesian language family, especially ones in the Oceanic branch, or from one of the many unrelated families of Papuan languages. Other languages are the several creoles of the region, such as Tok Pisin, Hiri Motu, Solomon Islands Pijin, Bislama, and Papuan Malay. Origin and genetics The original inhabitants of the group of islands now named Melanesia were likely the ancestors of the present-day Papuan people. They appear to have occupied these islands as far east as the main islands in the Solomon Islands, including Makira and possibly the smaller islands farther to the east. Particularly along the north coast of New Guinea and in the islands north and east of New Guinea, the Austronesian people, who had migrated into the area more than 3,000 years ago, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louisiade Archipelago
The Louisiade Archipelago is a string of ten larger volcanic islands frequently fringed by coral reefs, and 90 smaller coral islands in Papua New Guinea. It is located 200 km southeast of New Guinea, stretching over more than and spread over an ocean area of between the Solomon Sea to the north and the Coral Sea to the south. The aggregate land area of the islands is about , with Vanatinai (Tagula) being the largest. Rogeia, Samarai and Sariba lie closest to New Guinea, while Misima, Vanatinai, and Rossel islands lie further east. History The islands were discovered by a Spanish expedition led by Luis Váez de Torres in 1606, that was part of the Fernandez de Quiros fleet which had sailed from South America in search of Australia. The Torres expedition visited various islands including Basilaki Island, which he named ''San Buenaventura'' in July 1606. It is possible that Malay and Chinese sailors also visited the islands earlier. More than a century later, in 17 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |