|
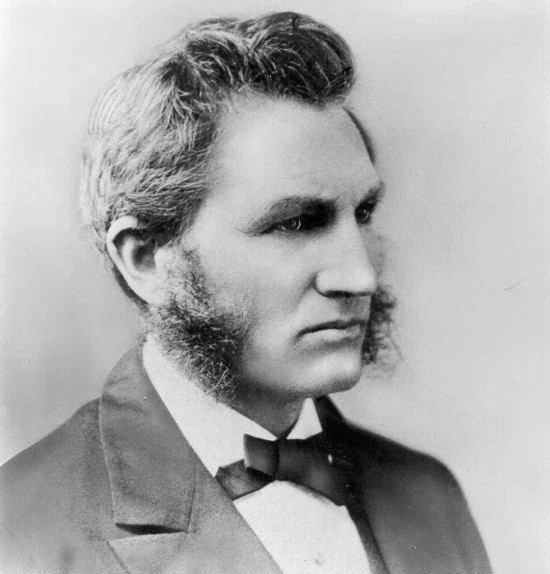
Gerhard Lenski
Gerhard Emmanuel "Gerry" Lenski, Jr. (August 13, 1924 – December 7, 2015) was an American sociologist known for contributions to the sociology of religion, social inequality, and introducing the ecological-evolutionary theory. He spent much of his career as a professor at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, where he served as chair of the Department of Sociology, 1969–72, and as chair of the Division of Social Sciences, 1976-78. Life and career Lenski was born and raised in Washington, DC, the son of a Lutheran pastor, the grandson of German-born theologian Richard Charles Henry Lenski, and the nephew of children's author Lois Lenski. He attended Yale University where he received a BA degree in 1947, after serving as a cryptographer with the 8th Air Force in England in World War II, and then earned his PhD from Yale in 1950. Lenski was awarded a Pre-doctoral Fellowship by the Social Science Research Council, 1949–50, and later a Senior Faculty Fellowship, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Sociological Association
The American Sociological Association (ASA) is a non-profit organization dedicated to advancing the discipline and profession of sociology. Founded in December 1905 as the American Sociological Society at Johns Hopkins University by a group of fifty people, the first president of the association would be Lester Frank Ward. Today, most of its members work in academia, while around 20 percent of them work in government, business, or non-profit organizations. ASA publishes ten academic journals and magazines, along with four section journals. Among these publications, the ''American Sociological Review'' is perhaps the best known, while the newest is an open-access journal titled Socius: Sociological Research for a Dynamic World'. '' Contexts'' is one of their magazines, designed to share the study of sociology with other disciplines as well as the public. The ASA is currently the largest professional association of sociologists in the world, even larger than the International So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detroit
Detroit ( , ; , ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is also the largest U.S. city on the United States–Canada border, and the seat of government of Wayne County. The City of Detroit had a population of 639,111 at the 2020 census, making it the 27th-most populous city in the United States. The metropolitan area, known as Metro Detroit, is home to 4.3 million people, making it the second-largest in the Midwest after the Chicago metropolitan area, and the 14th-largest in the United States. Regarded as a major cultural center, Detroit is known for its contributions to music, art, architecture and design, in addition to its historical automotive background. ''Time'' named Detroit as one of the fifty World's Greatest Places of 2022 to explore. Detroit is a major port on the Detroit River, one of the four major straits that connect the Great Lakes system to the Saint Lawrence Seaway. The City of Detroit anchors the second-largest regional economy in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Wuthnow
Robert John Wuthnow (born 1946) is an American sociologist who is widely known for his work in the sociology of religion. He is the Gerhard R. Andlinger Professor of Sociology Emeritus at Princeton University, where he is also the former Chair of the Department of Sociology and Director of the Princeton University Center for the Study of Religion. Life and career Wuthnow was born in Kansas on June 23, 1946. He earned his Bachelor of Arts degree at the University of Kansas in 1968 and his Doctor of Philosophy degree in sociology at the University of California at Berkeley in 1975. His dissertation was ''Consciousness and the Transformation of Society''. While at Berkeley, Wuthnow worked closely with Charles Glock, Neil Smelser, Robert Bellah, Guy Swanson, and Gertrude Selznick. Wuthnow's first years at Berkeley were during the widespread protests on campus around the US, which ultimately inspired his dissertation. Glock and Bellah received a grant to study the symbolic—especia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commentary (magazine)
''Commentary'' is a monthly American magazine on religion, Judaism, and politics, as well as social and cultural issues. Founded by the American Jewish Committee in 1945 under Elliot E. Cohen, editor from 1945 to 1959, ''Commentary'' magazine developed into the leading postwar journal of Jewish affairs. The periodical strove to construct a new American Jewish identity while processing the events of the Holocaust, the formation of the State of Israel, and the Cold War. Norman Podhoretz edited the magazine in its heyday from 1960 to 1995. Besides its coverage of cultural issues, ''Commentary'' provided a voice for the anti-Stalinist left. As Podhoretz shifted from his original ideological beliefs as a liberal Democrat to neoconservatism in the 1970s and 1980s, he moved the magazine with him to the right and toward the Republican Party. History Founding and early years ''Commentary'' was the successor to the ''Contemporary Jewish Record'', which was published by the American Jewis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sociology Of Religion
Sociology of religion is the study of the beliefs, practices and organizational forms of religion using the tools and methods of the discipline of sociology. This objective investigation may include the use both of quantitative methods (surveys, polls, demographic and census analysis) and of qualitative approaches (such as participant observation, interviewing, and analysis of archival, historical and documentary materials). Modern sociology as an academic discipline began with the analysis of religion in Émile Durkheim's 1897 study of suicide rates among Catholic and Protestant populations, a foundational work of social research which served to distinguish sociology from other disciplines, such as psychology. The works of Karl Marx (1818-1883) and Max Weber (1864-1920) emphasized the relationship between religion and the economic or social structure of society. Contemporary debates have centered on issues such as secularization, civil religion, and the cohesiveness of religio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubert M
Hubert is a Germanic masculine given name, from ''hug'' "mind" and ''beraht'' "bright". It also occurs as a surname. Saint Hubertus or Hubert (c. 656 – 30 May 727) is the patron saint of hunters, mathematicians, opticians, and metalworkers. People with the given name Hubert This is a small selection of articles on people named Hubert; for a comprehensive list see instead . *Hubert Aaronson (1924–2005), F. Mehl University Professor at Carnegie Mellon University *Hubert Adair (1917–1940), World War II Royal Air Force pilot *Hubert Boulard, a French comics creator who is unusually credited as "Hubert" * Hubert Brasier (1917–1981), a Church of England clergyman, more famously the father of UK Prime Minister Theresa May *Hubert Buchanan (born 1941), a United States Air Force captain and fighter pilot *Hubert Chevis (1902–1931), a lieutenant in the Royal Artillery of the British Army who died of strychnine poisoning in June 1931 * Hubert Davies, British playwright and d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Lenski
Richard Eimer Lenski (born August 13, 1956) is an American evolutionary biologist, a Hannah Distinguished Professor of Microbial Ecology at Michigan State University. He is a member of the National Academy of Sciences and a MacArthur fellow. Lenski is best known for his still ongoing -year-old long-term ''E. coli'' evolution experiment, which has been instrumental in understanding the core processes of evolution, including mutation rates, clonal interference, antibiotic resistance, the evolution of novel traits, and speciation. He is also well known for his pioneering work in studying evolution digitally using self-replicating organisms called Avida. Early life Richard E. Lenski is the son of sociologist Gerhard Lenski and poet Jean Lenski ( Cappelmann). He is also the great-nephew of children's author Lois Lenski and the great-grandson of Lutheran commentator Richard C. H. Lenski. He earned his BA from Oberlin College in 1976, and his PhD from the University of North Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolutionary Biology
Evolutionary biology is the subfield of biology that studies the evolutionary processes (natural selection, common descent, speciation) that produced the diversity of life on Earth. It is also defined as the study of the history of life forms on Earth. Evolution is based on the theory that all species are related and they gradually change over time. In a population, the genetic variations affect the physical characteristics i.e. phenotypes of an organism. These changes in the phenotypes will be an advantage to some organisms, which will then be passed onto their offspring. Some examples of evolution in species over many generations are the Peppered Moth and Flightless birds. In the 1930s, the discipline of evolutionary biology emerged through what Julian Huxley called the modern synthesis of understanding, from previously unrelated fields of biological research, such as genetics and ecology, systematics, and paleontology. The importance of studying Evolutionary biology is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vietnam and South Vietnam. The north was supported by the Soviet Union, China, and other communist states, while the south was United States in the Vietnam War, supported by the United States and other anti-communism, anti-communist Free World Military Forces, allies. The war is widely considered to be a Cold War-era proxy war. It lasted almost 20 years, with direct U.S. involvement ending in 1973. The conflict also spilled over into neighboring states, exacerbating the Laotian Civil War and the Cambodian Civil War, which ended with all three countries becoming communist states by 1975. After the French 1954 Geneva Conference, military withdrawal from Indochina in 1954 – following their defeat in the First Indochina War – the Viet Minh to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Rights Movement
The civil rights movement was a nonviolent social and political movement and campaign from 1954 to 1968 in the United States to abolish legalized institutional Racial segregation in the United States, racial segregation, Racial discrimination in the United States, discrimination, and disenfranchisement in the United States, disenfranchisement throughout the United States. The movement had its origins in the Reconstruction era during the late 19th century, although it made its largest legislative gains in the 1960s after years of direct actions and grassroots protests. The social movement's major nonviolent resistance and civil disobedience campaigns eventually secured new protections in federal law for the civil rights of all Americans. After the American Civil War and the subsequent Abolitionism in the United States, abolition of slavery in the 1860s, the Reconstruction Amendments to the United States Constitution granted emancipation and constitutional rights of citizenship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taiwanese Mandarin
Taiwanese Mandarin, ''Guoyu'' ( zh, s=, t=國語, p=Guóyǔ, l=National Language, first=t) or ''Huayu'' ( zh, s=, t=華語, p=Huáyǔ, first=t, l=Mandarin Language, labels=no) refers to Mandarin Chinese spoken in Taiwan. A large majority of the Taiwanese population is fluent in Mandarin, though many also speak Taiwanese Hokkien, commonly called ''Minnanyu'' ( ''Mǐnnányǔ'') or Southern Min, a variety of Min Chinese. This language has had significant influence on Mandarin as spoken on the island. ''Guoyu'' is not the indigenous language of Taiwan. Chinese settlers came to Taiwan in the 16th century, but spoke other Chinese languages, primarily Southern Min. Japan annexed Taiwan in 1895 and governed the island as a colony for the next 50 years, during which time Japanese was introduced and taught in schools, while non-Mandarin languages were spoken at home. With the defeat of Imperial Japan in World War II, Taiwan was returned to the Republic of China under the Kuomintang (KMT), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |