|
Gerd Pfeiffer
Gerd Pfeiffer (22 December 1919 – 1 February 2007) was a German jurist who served as the fourth President of the Federal Court of Justice of West Germany from 1977 to 1987. Biography In March 1937, Pfeiffer finished his Abitur and was recruited into the Reich Labour Service (German: ''Reichsarbeitsdienst'', abbr. RAD) in Breslau. From 1937 onwards he completed his mandatory service in the Wehrmacht. After the start of World War II in 1939, he served in the '' Heer'' until 1945. He was wounded five times. After the war ended, he studied law at the University of Erlangen-Nuremberg from 1945 to 1948. In 1948, he was promoted to Dr. iur. by the university faculty. After passing the second Staatsexamen in 1951, he entered into judicial service in Bavaria. Following that, he served as a scientific employee at the Federal Constitutional Court (German: ''Bundesverfassungsgericht'', abbr. BVG) from 1952 to 1958, being promoted to judge at the Landgericht München I and later at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Fischer (judge)
Robert Fischer (22 August 1911 – 4 March 1983) was a German jurist who served as the third President of the Federal Court of Justice of West Germany from 1968 to 1977, succeeding Bruno Heusinger. Biography Fischer was born in Gießen in 1911, the son of Hans Albrecht Fischer, a professor specialising in Roman law, Civil law and legal philosophy. From 1932 to 1934, he studied law at the University of Tübingen, where he became a part of the Academic Union “Igel” (German for hedgehog), as well as at the universities of Breslau and Jena. In 1935 he graduated while studying under the auspices of Alfred Hueck, to whom he remained connected throughout his life. After passing the second Staatsexamen in 1938, he became a legal professional for the Deutsche Bank. During World War II, he served as a reserve officer. Once the war concluded in 1945, he decided to pursue a career as a judge. Following the war's conclusion, he was appointed Director and Deputy President of the Stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Erlangen-Nuremberg
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, the designation is reserved for colleges that have a graduate school. The word ''university'' is derived from the Latin ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". The first universities were created in Europe by Catholic Church monks. The University of Bologna (''Università di Bologna''), founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *Being a high degree-awarding institute. *Having independence from the ecclesiastic schools, although conducted by both clergy and non-clergy. *Using the word ''universitas'' (which was coined at its foundation). *Issuing secular and non-secular degrees: grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law, notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Cross Of Merit
The Order of Merit of the Federal Republic of Germany (german: Verdienstorden der Bundesrepublik Deutschland, or , BVO) is the only federal decoration of Germany. It is awarded for special achievements in political, economic, cultural, intellectual or honorary fields. It was created by the first President of the Federal Republic of Germany, Theodor Heuss, on 7 September 1951. Colloquially, the decorations of the different classes of the Order are also known as the Federal Cross of Merit (). It has been awarded to over 200,000 individuals in total, both Germans and foreigners. Since the 1990s, the number of annual awards has declined from over 4,000, first to around 2,300–2,500 per year, and now under 2,000, with a low of 1752 in 2011. Since 2013, women have made up a steady 30–35% of recipients. Most of the German federal states (''Länder'') have each their own order of merit as well, with the exception of the Free and Hanseatic Cities of Bremen and Hamburg, which rejec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Democratic Party Of Germany
The Social Democratic Party of Germany (german: Sozialdemokratische Partei Deutschlands, ; SPD, ) is a centre-left social democratic political party in Germany. It is one of the major parties of contemporary Germany. Saskia Esken has been the party's leader since the 2019 leadership election together with Lars Klingbeil, who joined her in December 2021. After Olaf Scholz was elected chancellor in 2021 the SPD became the leading party of the federal government, which the SPD formed with the Greens and the Free Democratic Party, after the 2021 federal election. The SPD is a member of 11 of the 16 German state governments and is a leading partner in seven of them. The SPD was established in 1863. It was one of the earliest Marxist-influenced parties in the world. From the 1890s through the early 20th century, the SPD was Europe's largest Marxist party, and the most popular political party in Germany. During the First World War, the party split between a pro-war mainstream ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Zimmermann
Friedrich Zimmermann (18 July 1925 – 16 September 2012) was a German politician and a member of the Christian Social Union (CSU). From 1982 to 1989, he was the federal minister of interior. From 1989 to 1991 he held the position of federal minister for transport. Biography Zimmermann was born on 18 July 1925. He served in the Second World War between 1943 and 1945 and held a lieutenant rank. In 1946, he studied law and economics in Munich, where he received a PhD. From 1951 until 1954, he was a civil servant in Bavaria and became a lawyer in 1963. In 1943, Zimmermann became a member of the NSDAP. From 1948, he was a member of the CSU. In 1955, he was managing director of the CSU and then from 1956 to 1963 held the position of General Secretary. As part of the CSU's hard-fought struggle against the Bayernpartei for political supremacy in Bavaria, Zimmermann was convicted in 1960 of perjury in connection with the Bavarian casino affair, but was finally acquitted in 1961 aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freiburg
Freiburg im Breisgau (; abbreviated as Freiburg i. Br. or Freiburg i. B.; Low Alemannic: ''Friburg im Brisgau''), commonly referred to as Freiburg, is an independent city in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. With a population of about 230,000 (as of 31 December 2018), Freiburg is the fourth-largest city in Baden-Württemberg after Stuttgart, Mannheim, and Karlsruhe. The population of the Freiburg metropolitan area was 656,753 in 2018. In the south-west of the country, it straddles the Dreisam river, at the foot of the Schlossberg. Historically, the city has acted as the hub of the Breisgau region on the western edge of the Black Forest in the Upper Rhine Plain. A famous old German university town, and archiepiscopal seat, Freiburg was incorporated in the early twelfth century and developed into a major commercial, intellectual, and ecclesiastical center of the upper Rhine region. The city is known for its medieval minster and Renaissance university, as well as for its high stand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
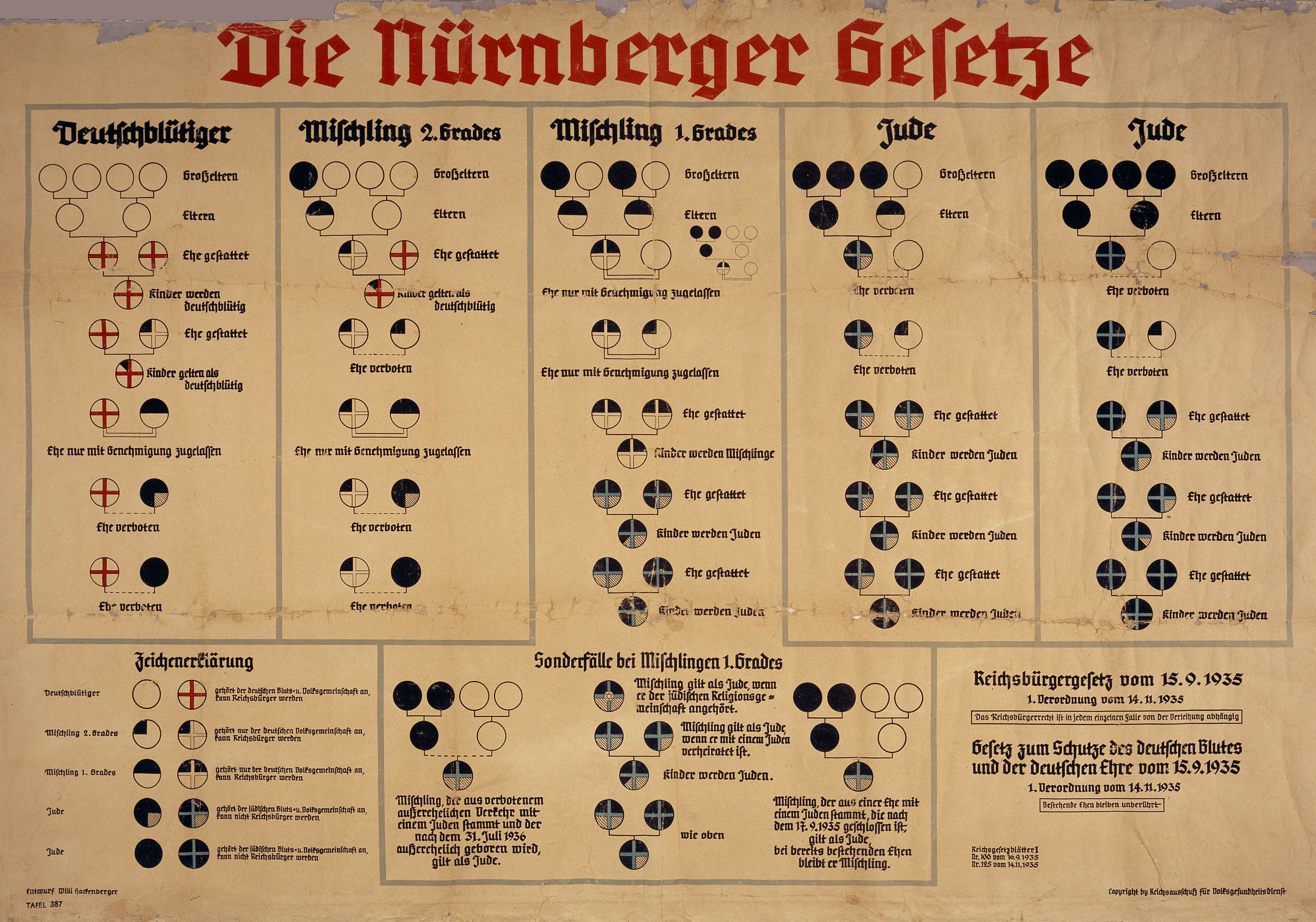
Law In Nazi Germany
From 1933 to 1945, the Nazi regime ruled Germany and controlled almost all of Europe. During this time, Nazi Germany shifted from the post-World War I society which characterized the Weimar Republic and introduced an ideology of "biological racism" into the country's legal and justicial systems. The shift from the traditional legal system (the "normative state") to the Nazis' ideological mission (the "prerogative state") enabled all of the subsequent acts of the Hitler regime (including its atrocities) to be performed "legally". For this to succeed, the normative judicial system needed to be reworked; judges, lawyers and other civil servants acclimatized themselves to the new Nazi laws and personnel. History After World War 1, Germany considered the law a "most respected entity" as the country regained stability and public confidence. Many German lawyers and judges were Jewish. Adolf Hitler was inspired by Benito Mussolini's October 1922 March on Rome, which brought Mussolini's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machtergreifung
Adolf Hitler's rise to power began in the newly established Weimar Republic in September 1919 when Hitler joined the '' Deutsche Arbeiterpartei'' (DAP; German Workers' Party). He rose to a place of prominence in the early years of the party. Being one of its best speakers, he was made the party leader after he threatened to otherwise leave. In 1920, the DAP renamed itself to the ''Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei'' – NSDAP (National Socialist German Workers' Party, commonly known as the Nazi Party). Hitler chose this name to win over German workers. Despite the NSDAP being a right-wing party, it had many anti-capitalist and anti-bourgeois elements. Hitler later initiated a purge of these elements and reaffirmed the Nazi Party's pro-business stance. By 1922 Hitler's control over the party was unchallenged. In 1923, Hitler and his supporters attempted a coup to remove the government via force. This seminal event was later called the Beer Hall Putsch. Upon its fai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reichsgericht
The Reichsgericht (, ''Reich Court'') was the supreme criminal and civil court in the German Reich from 1879 to 1945. It was based in Leipzig, Germany. The Supreme Court was established when the Reichsjustizgesetze (Imperial Justice Laws) came into effect and it built a widely regarded body of jurisprudence during the period of the German Empire and Weimar Republic. During the rise of the Third Reich, the Reichsgericht became deeply embroiled in the National Socialist agenda. It even involved itself in matters of Nazi Matrimonial and Contract Law before enactment of the Nuremberg Laws. During and after the Nazi period it received criticism for the ease, and even willingness, with which it provided the highest level of formal legal justification for Nazi programs. Immediately after the end of World War II, the Reichsgericht was dissolved, and reformed into the German High Court for the ''Unified Economic Region'' (Trizone), the Allied occupation zones of France, the United Kingdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartel Senate
A cartel is a group of independent market participants who collude with each other in order to improve their profits and dominate the market. Cartels are usually associations in the same sphere of business, and thus an alliance of rivals. Most jurisdictions consider it anti-competitive behavior and have outlawed such practices. Cartel behavior includes price fixing, bid rigging, and reductions in output. The doctrine in economics that analyzes cartels is cartel theory. Cartels are distinguished from other forms of collusion or anti-competitive organization such as corporate mergers. Etymology The word ''cartel'' comes from the Italian word '' cartello'', which means a "leaf of paper" or "placard", and is itself derived from the Latin ''charta'' meaning "card". The Italian word became ''cartel'' in Middle French, which was borrowed into English. In English, the word was originally used for a written agreement between warring nations to regulate the treatment and exchange of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munich
Munich ( ; german: München ; bar, Minga ) is the capital and most populous city of the States of Germany, German state of Bavaria. With a population of 1,558,395 inhabitants as of 31 July 2020, it is the List of cities in Germany by population, third-largest city in Germany, after Berlin and Hamburg, and thus the largest which does not constitute its own state, as well as the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, 11th-largest city in the European Union. The Munich Metropolitan Region, city's metropolitan region is home to 6 million people. Straddling the banks of the River Isar (a tributary of the Danube) north of the Northern Limestone Alps, Bavarian Alps, Munich is the seat of the Bavarian Regierungsbezirk, administrative region of Upper Bavaria, while being the population density, most densely populated municipality in Germany (4,500 people per km2). Munich is the second-largest city in the Bavarian dialects, Bavarian dialect area, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landgericht München I , a regional magistracy in the Holy Roman Empire
{{dab ...
''Landgericht'' may refer to: * Landgericht (Germany), a mid-level court in the present-day judicial system of Germany *: For example, ** Landgericht Berlin ** Landgericht Bremen * Landgericht (medieval) The ''Landgericht'' (plural: ''Landgerichte''), also called the ''Landtag'' in Switzerland, was a regional magistracy or court in the Holy Roman Empire that was responsible for high justice within a territory, such as a county (''Grafschaft''), on b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_4029.jpg)